35 diagram of ground water
Write each term in the correct place on the groundwater diagram below. groundwater: water that infiltrates into the earth and is stored in usable amounts in the soil and rock below the earth's surface; surface water: water found above the surface of the land, including lake, rivers, streams and ponds. Concepts related to ground water and the move-ment of ground water are introduced in Box A. As illustrated in Figure 3, ground water moves along flow paths of varying lengths from areas of recharge to areas of discharge. The generalized flow paths in Figure 3 start at the water table, continue through the ground-water system, and
Groundwater Model Setup. Split students into groups of three "well owners," and provide each group with a groundwater model setup and three beakers with at least a 100ml capacity. Fill each groundwater model with water until the water sits 1 - 2 cm above the surface of the sand.

Diagram of ground water
This diagram shows a groundwater contaminant plume in red. The source of the contamination has been removed but if the plume is not dealt with, it will eventually enter the stream and threaten the health of wildlife. Pumping the contaminant from well B for treatment will not be sufficient to prevent some of the contamination from making it to ... Keywords: New diagram; Banaga diagram; Groundwater quality Introduction To understanding the quality of groundwater is as important as it is quantity because it is the main factor determining the suitability for domestic, drinking, agricultural and industrial purposes depending mainly on Banaga's diagram. Groundwater is the most important The majority of fresh groundwater occurs in the middle part of the boomerang (water-rock interaction) on Gibbs Diagram, but groundwaters—unlike most surface waters—can span the entire range of Na/ (Na + Ca) values (i.e., from <0.1 to >0.9) at mid-range TDS levels. We evidence the wide range of groundwater chemistry in Gibbs Diagram space by ...
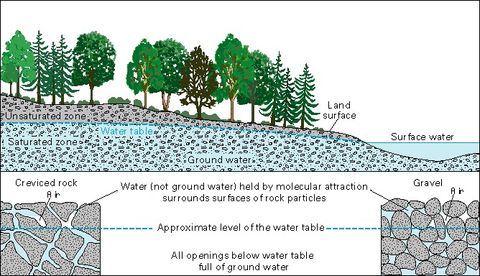
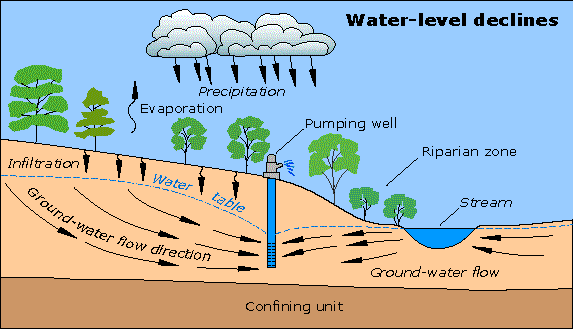
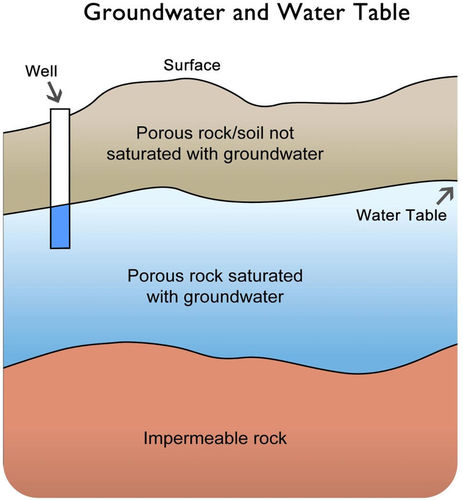
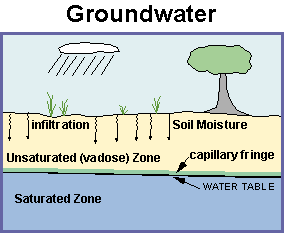
Diagram of ground water. V = K * i. (where V is the velocity of the groundwater flow, K is the hydraulic conductivity, and i is the hydraulic gradient). We can apply this equation to the scenario in Figure 14.5. If we assume that the permeability is 0.00001 m/s we get: V = 0.00001 * 0.08 = 0.0000008 m/s. That is equivalent to 0.000048 m/min, 0.0029 m/hour or 0.069 m/day. EPA GROUND WATER RULE • Utilities Covered: -The GWR applies to all public water systems (PWS) that use ground water including consecutive systems, except that it does not apply to all PWSs that combine all of their ground water with surface water or with groundwater under the direct influence of surface water (GUDI) prior to treatment. Visualizing groundwater. In the diagram below, you can see how the ground below the water table (the blue area) is saturated with water. The "unsaturated zone" above the water table (the gray area) still contains water (after all, plants' roots live in this area), but it is not totally saturated with water. ... The importance of considering ... As the diagram shows, the direction and speed of groundwater movement is determined by the various characteristics of aquifers and confining layers of subsurface rocks (which water has a difficult time penetrating) in the ground. Water moving below ground depends on the permeability (how easy or difficult it is for water to move) and on the ...
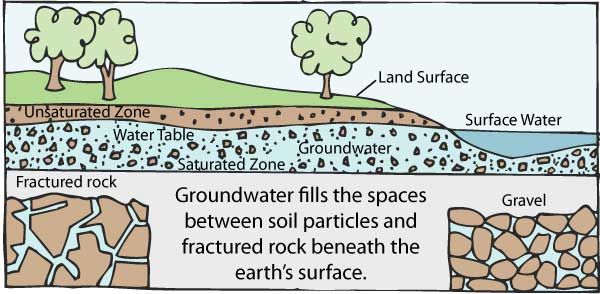
Groundwater diagram. This landform cross-section shows the role of groundwater in the water cycle. Groundwater is a key part of the system. Aquifers provide water for drinking water wells, irrigation, and industrial uses. Groundwater also recharges lakes, rivers, and streams at certain times of year. LSASDPROC-105-R4 Groundwater Level and Well Depth Measurement Effective Date: May 15, 2020 . Page 1 of 8 . Purpose . This document describes general and specific procedures, methods and considerations to be used and The schematic diagram in Figure 5.1 depicts the conceptual hydrogeologic model of groundwater flow in the Carrizo-Wilcox aquifer. Figure 5.1 represents the aquifer under predevelopment conditions. With the addition of pumping as the resource is developed, an additional discharge from each aquifer layer would occur. The pumping discharge would be In this video I have tried to show easiest way of drawing diagram Kindly comment below which diagram do you want in coming videos #howtodraw #sciencediagram...
day-1, which is about 95 per cent of the total supply to a population of nearly 20 million people (Foster et al., 1987). In Europe also, groundwater has always played a major part in water supplies. The proportion of groundwater in drinking water supplies in some Ground water in confined aquifer is under pressure which is greater than the atmospheric pressure. The water level in a well penetrating a confined aquifer indicates the piezometric pressure at that point and will be above the bottom of the upper confining formation. Basic Groundwater diagram showing an ocean, river, wetland, recharge and discharge arrows. Image provided by USGS. 3-dimensional cut-away view showing water movement in an underground aquifer. Image provided by USGS. Colorful diagram showing potential sources of groundwater contamination. Image provided by USGS. Ground-Water Development, Sustainability, and Water Budgets. A ground-water system consists of a mass of water flowing through the pores or cracks below the Earth's surface. This mass of water is in motion. Water is constantly added to the system by recharge from precipitation, and water is constantly leaving the system as discharge to surface ...

Graphic Courtesy Of Usgs Surface Water And Groundwater Diagram Hd Png Download Transparent Png Image Pngitem
The shallow ground-water in the back swamp deposit (clay and Kankar beds) is generally unconfined and static water level is only a few meters below the water level (at about 20-60-m ... diagram is used to categorize the water facies on the basis of dominant ions. Analysis of Piper diagram reveals that
ground water from the subsurface. Water may flow to the surface naturally after exca-vation of the hole or shaft. Such a well is known as aflowing artesian well. More com-monly, water must be pumped out of the well. Most wells are vertical shafts, but they may also be horizontal or at an inclined
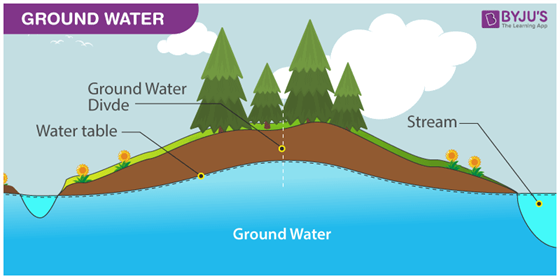
Figure 1. Ground water is the second smallest of the four main pools of water on Earth, and river flow to the oceans is one of the smallest fluxes, yet ground water and surface water are the components of the hydrologic system that humans use most.
Q = AKi or Q = AK dh/dl Where Q is the discharge and A is the cross-sectional area of the aquifer in question. Groundwater will flow down the hydraulic gradient. When we look at flow over the area of an aquifer we are typically interested in two-dimensional flow. In most cases the X and Y dimensions (100s to 10,000s of m) are
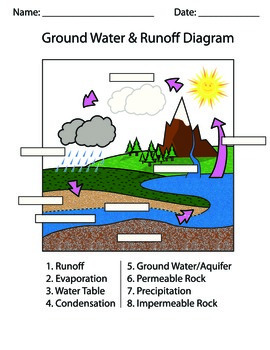
Looking for a clear diagram that shows the different parts of a groundwater system? Look no further. This download includes two versions of a fill-in-the-blank diagram, two versions of a coloring activity, and ready-to-print posters for your classroom!This product includes a fill-in-the-blank diagra
contamination entering moving groundwater, an area of contaminated groundwater, called a plume, can form (Diagram 3). A combination of moving groundwater and a continuous source of contamination can, therefore, pollute very large volumes and areas of groundwater. Some plumes at Superfund sites are several miles long.
Animated diagram of groundwater, water cycle, and water wells.
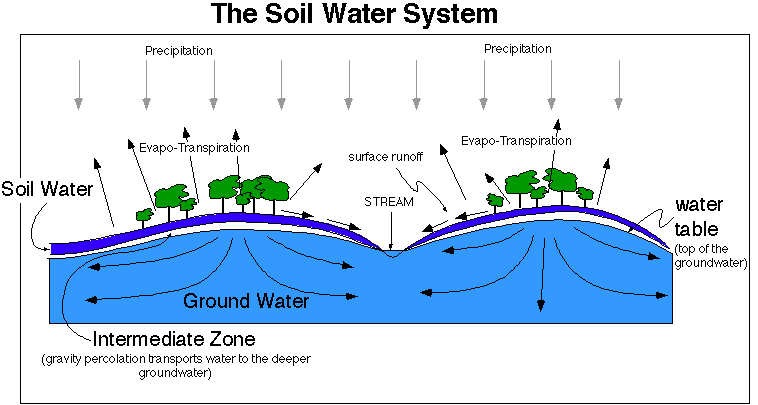
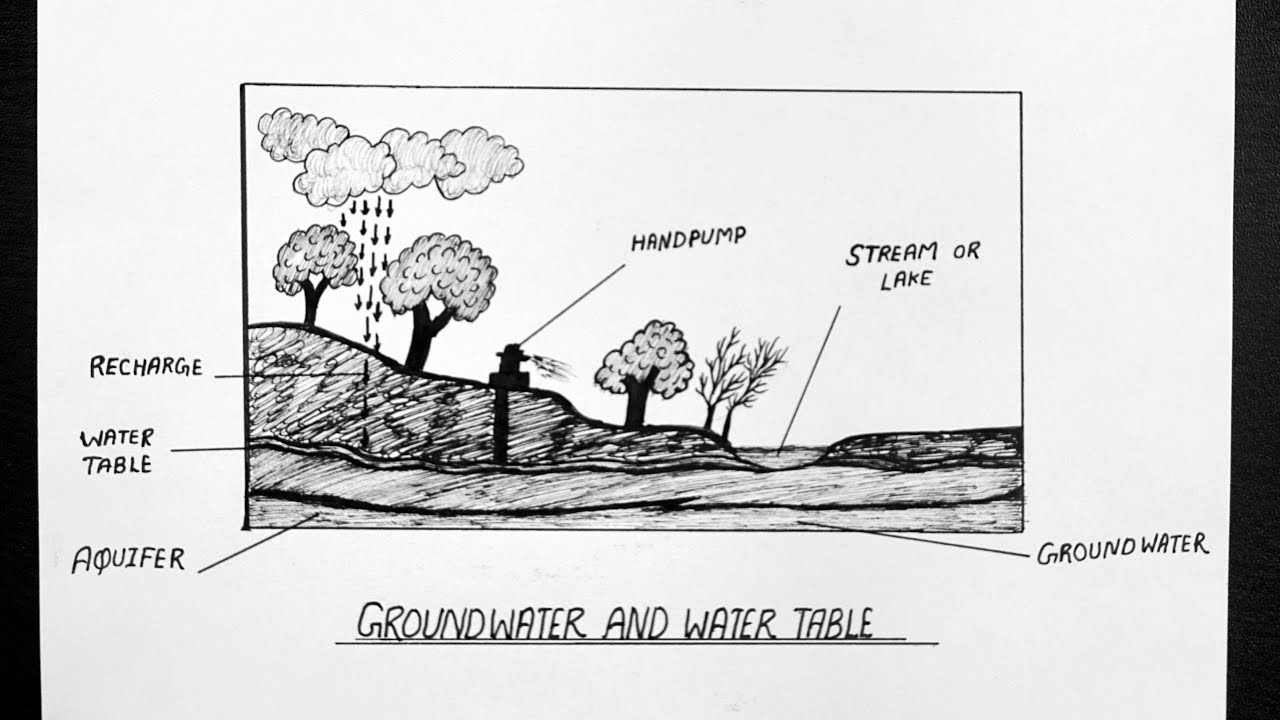
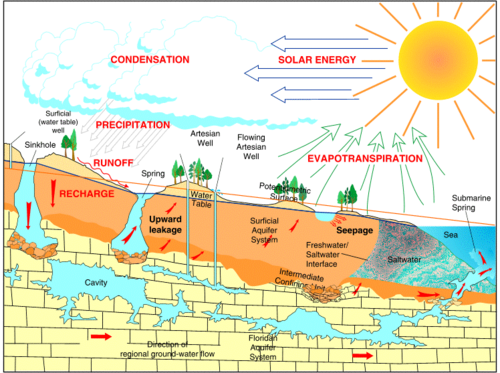
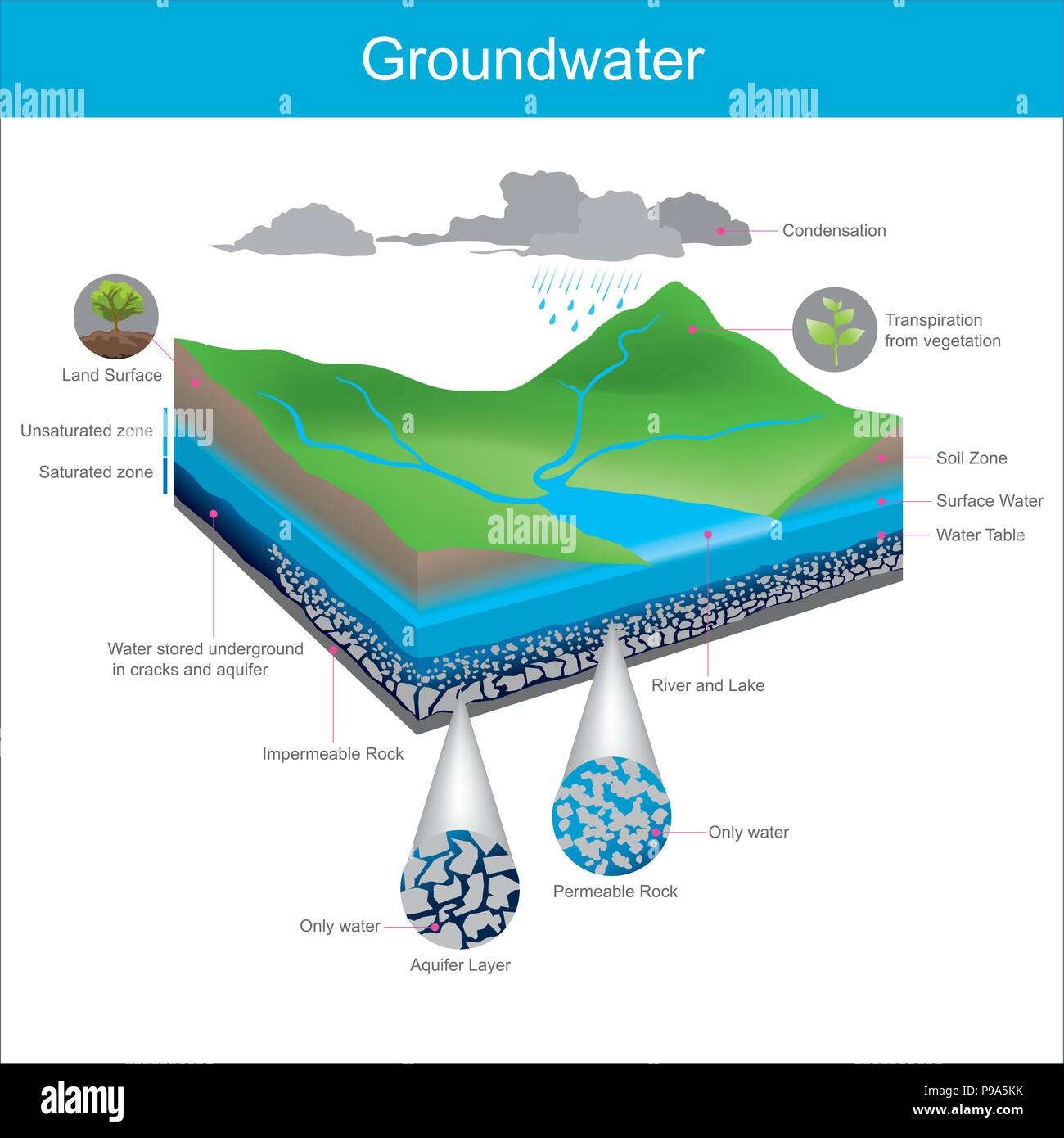
Groundwater is a part of the natural water cycle (check out our interactive water cycle diagram). Some part of the precipitation that lands on the ground surface infiltrates into the subsurface. The part that continues downward through the soil until it reaches rock material that is saturated is groundwater recharge.
Simple Groundwater Diagram. steam enthalpy entropy h s diagram for steam pressure enthalpy p h diagram for steam temperature entropy t s diagram for steam groundwater sampling and analysis - a field guide years and are very well documented groundwater sampling requirements and goals are often quite different to those of surface water sampling and there has
Groundwater: Origin, Sources and Other Details (with diagram) Article shared by : ADVERTISEMENTS: Water existing in the voids of the geological stratum below the surface of the earth is called groundwater. Groundwater is found in pores and fissures of rocks. It is regulated by the quantum and speed of rains, extent of vaporization at the time ...
Hello!Ground Water And Water Table Diagram || Diagram Of Ground Water And Water TableGroundwater And Water Table Diagram, groundwater, aquifer, water table, ...
GROUNDWATER DIAGRAMS . Dry Month - A period of dry weather, in which a lack of precipitation, combined with ongoing evaporation and transpiration, causes groundwater levels to decline. Wet Month - A rainy period, in which enough precipitation falls to significantly raise groundwater levels.
4. Classifications of Groundwater. 4.1. Piper Diagrams. The Piper diagram is a representative method for classifying groundwater by producing a diagram of the distribution of cations and anions in groundwater.
Here are some of the more important elements included in the water well diagram above. Borehole – The borehole should be about 50mm (2 inches) wider all around than the well casing.The borehole needs to be clear of obstructions all the way down, and should be deep enough to reach the lowest expected water level.
bottom. A plan view, to-scale diagram of it is shown below. There is an impermeable pillar in the center of the filter. Reservoirs on the left and right are separated from the sand by a screen that only crosses a portion of the reservoir wall. The head in the inlet reservoir on the left is 20 m and the outlet reservoir on the right is 12m.
We wanted to model groundwater flow through the following 2-D aquifer: Figure 1. Diagram of aquifer. The PDE equation that describes 2-D groundwater flow in a confined aquifer is: (1) Here h is the hydraulic head and T is the constant conductivity of the aquifer medium.
Groundwater is one component of the complete hydrologic cycle of the earth. For all practical purposes groundwater originates from surface water source. Water infiltrates into ground by natural recharge process. Rainfall, water from stream flow, reservoirs and lakes are the sources for infiltration. Also surface irrigation contributes ...
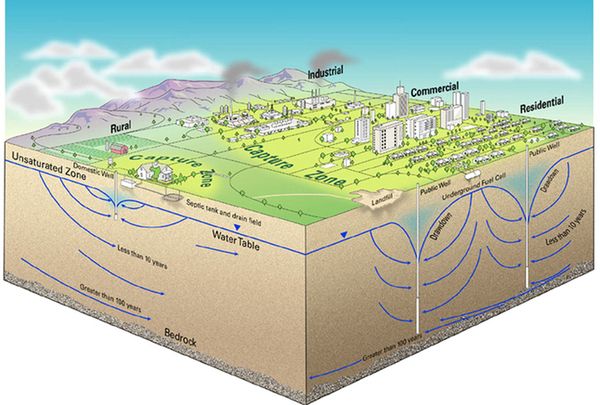
The Groundwater Foundation Students And Educators Get Involved Science Olympiad Events Diagrams And Visual Aids
Groundwater chemistry was assessed and natural processes are identified as the controlling factors of hydrochemistry.Piper and Chadha´s diagram was created for comparing the results of water types.
Water Balance of the Earth's Surface (with diagram) The word 'water balance' was first of all used in 1944 by the famous meteorological and climate scholar C. Warren Thornthwaite (1899-1963), who meant that it is a balance between precipitation, water obtained by melting of snow and evaporation, groundwater recharging and surface flow of ...
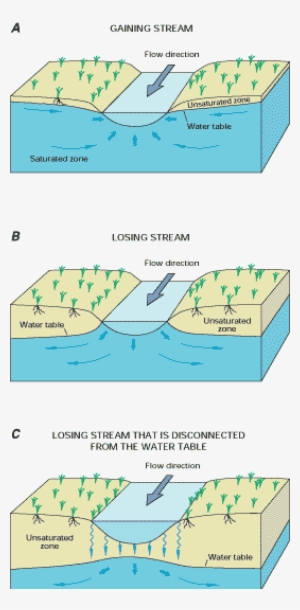
Diagram Of Interaction Of Streams And Ground Water Surface Water Groundwater Interaction Transparent Png 264x537 Free Download On Nicepng
The factors that control the occurrence and distribution of ground water in a region: • Topography • Morphology • Soil conditions • Lithology of the area • Structural Aspect Influencing Factors Topography. 6. Lithology Soil conditions Stratigraphy Morphology. 7. The pore spaces, opening and other cavities. 8.
The majority of fresh groundwater occurs in the middle part of the boomerang (water-rock interaction) on Gibbs Diagram, but groundwaters—unlike most surface waters—can span the entire range of Na/ (Na + Ca) values (i.e., from <0.1 to >0.9) at mid-range TDS levels. We evidence the wide range of groundwater chemistry in Gibbs Diagram space by ...
Keywords: New diagram; Banaga diagram; Groundwater quality Introduction To understanding the quality of groundwater is as important as it is quantity because it is the main factor determining the suitability for domestic, drinking, agricultural and industrial purposes depending mainly on Banaga's diagram. Groundwater is the most important
This diagram shows a groundwater contaminant plume in red. The source of the contamination has been removed but if the plume is not dealt with, it will eventually enter the stream and threaten the health of wildlife. Pumping the contaminant from well B for treatment will not be sufficient to prevent some of the contamination from making it to ...



















0 Response to "35 diagram of ground water"
Post a Comment