36 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.
Question. : Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood Reset Help 23 percent of CO2 transported bound to hemoglobin CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT dissolved CO2 diffuses out of the plasma Most CO2 in the blood has been converted to bicarbonate ion, HCO VENOUS BLOOD Ht ions ... Google's free service instantly translates words, phrases, and web pages between English and over 100 other languages.
Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Dalton's Law Each gas in a mixture of gases exerts its own pressure as if no other gases were present Pressure of a specific gas is partial pressure P x Total pressure is the sum of all the partial pressures Atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg) = P N2 + P O2 + P H2O + P CO2 + P other gases
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.
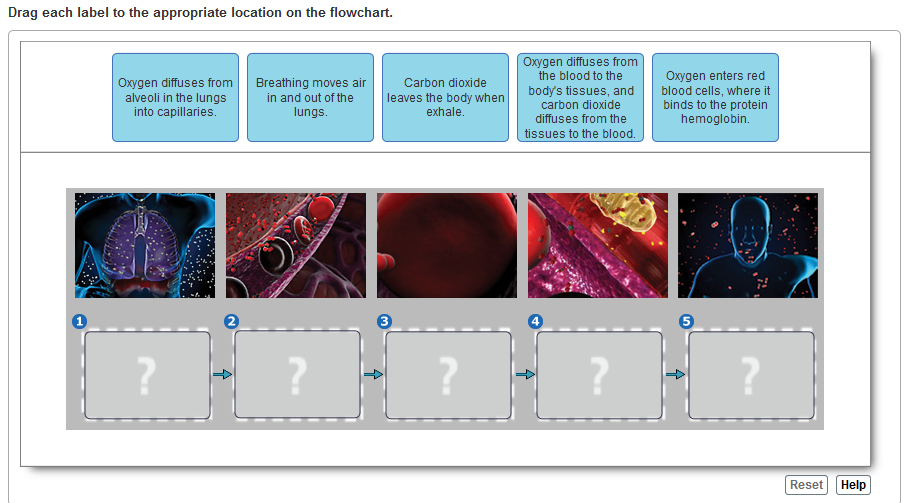
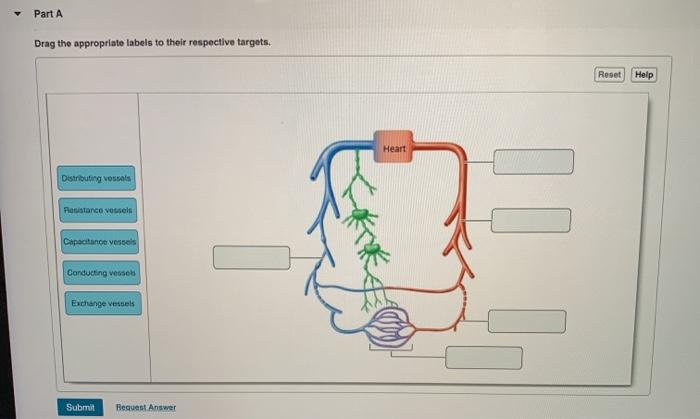
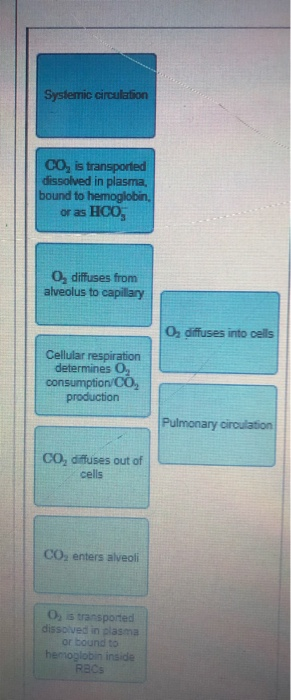
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways ...1 answer · 0 votes: The sequence of carbon dioxide transport in body - 1. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria ... BioFlix Activity: Gas Exchange -- Oxygen Transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Left to right: 1: Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into surrounding capillaries 2:Oxygen enters a red blood cell ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures of the upper respiratory system. Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: Solution A catalyst does not affect the energy of reactant or product, so those aspects of the diagrams can be ignored; they are, as we would expect, identical in that respect.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.. 2.3 Cell structure and function (ESG4S) Section 3: Cell Structure and Function. In this section the learners now expand their knowledge and learn the various cell structures and related functions. The roles of the organelles within the cells need to be introduced and relate structure and location of organelles to their function. appropriate model or diagram. Size, Location, and Orientation The modest size and weight of the heart give few hints of its incredible strength. Approximately the size of a person's fist, the hollow, cone-shaped heart weighs less than a pound. Snugly enclosed within the inferior mediastinum (me″de-as-ti′num), the 1. Air enters through the nose or mouth. 2. Air travels down the trachea and then enters the bronchi. 3. Air travels down smaller and smaller bronchioles. 4. Air reaches small sacs called alveoli. Drag each label to the appropriate location on this diagram of the human respiratory system. Describe the structure and function of blood in the body. Blood is important for regulation of the body's pH, temperature, osmotic pressure, the circulation of nutrients and removal of waste, the distribution of hormones from endocrine glands, and the elimination of excess heat; it also contains components for blood clotting.
Label the mechanisms of carbon dioxide transport. (Refer to the posted image for labeled answers) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood. 8.1 The Concept of Homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to physiologically regulate its inner environment to ensure its stability in response to fluctuations in external or internal conditions.The liver, the pancreas, the kidneys, and the brain (hypothalamus, the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system) help maintain homeostasis. The Slow Carbon Cycle. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity, carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks, soil, ocean, and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. On average, 10 13 to 10 14 grams (10-100 million metric tons) of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year. Drag the labels onto this diagram of the carbon cycle. Mastering environmental science 5th ed. In fuels in water co2 in. Drag the labels onto the flowchart to identify the sequence in which carbon moves through these organisms 1. Then drag the pink labels onto the pink targets to identify the processes and reservoirs in the carbon cycle.
Biology. Biology questions and answers. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange ResetHel CO2 diffuses out of pulmonary capillaries CO2 O2 Airways CO2 diffuses into systemic capillaries Alveoli of lungs co, o O2-rich blood 02 CO2-rich blood 02 diffuses from alveolus to capillary Blood flow to and from ... Discuss the parts of a rib and rib classifications. The thoracic cage (rib cage) forms the thorax (chest) portion of the body. It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum ( Figure 7.5.1 ). The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12). The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the location and position of the heart within the body cavity. Describe the internal and external anatomy of the heart. Identify the tissue layers of the heart. Relate the structure of the heart to its function as a pump. Compare systemic circulation to pulmonary circulation. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the processes of reabsorption in the tubular epithelium. Most reabsorption of fluid from the filtrate back into the blood occurs from the _____. proximal tubule. In which process can glucose transport reach saturation? Reabsorption.
16 Apr 2016 — Part b transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide gas exchange involves the transport of two respiratory gases oxygen and carbon dioxide. Drag the ...
Two important aspects of gas exchange in the lung are ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs, and perfusion is the flow of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. For gas exchange to be efficient, the volumes involved in ventilation and perfusion should be compatible.
Identify the different epithelia of the body, and describe the chief function(s) and location(s) of each. An epithelium (ep″ ı˘-the ′le-um; "covering") is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (Figure 4.1). Epithelial tissue occurs in two different forms:

Ch 18 Hw Pdf Ch18hw Ch18hw Due 11 59pmonsunday April5 2015 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer Higherbraince Course Hero
Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures involved in respiratory epithelium function. Mastering A and PAssignment Unit 5 - Respiratory System Art-labeling Activity Figure 17.5 Anion channel Oland Secondary active transport of Facilitated diffusion of CI ECF pical Mucus layer Id One model of se Watery saline layer Paracellular diffusion of Na drawn by ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Human cadaver anatomical models histology cat and fetal pig. Drag the labels onto the flowchart to identify the sequence in which carbon moves through these organisms 1. Glycolysis citric acid cycle and electron transport.
15.3 Hearing Audition (Hearing) Hearing, or audition, is the transduction of sound waves into a neural signal that is made possible by the structures of the ear (Figure 15.3.1).The large, fleshy structure on the lateral aspect of the head is known as the auricle.Some sources will also refer to this structure as the pinna, though that term is more appropriate for a structure that can be moved ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to correctly identify the structures and pathways involved in transporting water through the root. ... The continuum of spaces between cell walls of neighboring cells in the _ route of water and solute transport from root hairs to xylem. extracellular. ... the balance between water uptake and gas exchange.
View Homework Help - Ch 18 HW.pdf from BIOL 65 at California State University, Fresno. 4/11/2015 Ch18HW Ch18HW Due:11:59pmonSunday,April5,2015 ...
Terms in this set (33) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. the diaphragm and rib muscles contract. Which statement is correct? In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells.
Virtually every cell, tissue, organ, and system in the body is impacted by the circulatory system. This includes the generalized and more specialized functions of transport of materials, capillary exchange, maintaining health by transporting white blood cells and various immunoglobulins (antibodies), hemostasis, regulation of body temperature, and helping to maintain acid-base balance.
Key events in gas exchange. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the major components of the respiratory system. Part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify features of cell signaling and receptors. The other major requirement for protein synthesis is the translator molecules that physically read the mrna codons.

Exploiting Self Healing In Lithium Batteries Strategies For Next Generation Energy Storage Devices Mezzomo 2020 Advanced Energy Materials Wiley Online Library
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and functions of the nephron. (Refer to the posted image at the right for labeled answers) What is the primary driving force for glucose transport into proximal tubule cells? Sodium concentration gradient allows secondary active transport of glucose.
Problem: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. FREE Expert Solution. Respiration: Answer: ...
Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways CO2 is transported dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin or as HCO3 Alveoli of lungs CO₂ O₂ O2 diffuses from alveolus to capillary co, so O2 diffuses into cells Cellular respiration determines 02 ...
When identifying a patient's blood type, the Rh group is designated by adding the word positive or negative to the ABO type. For example, A positive (A +) means ABO group A blood with the Rh antigen present, and AB negative (AB −) means ABO group AB blood without the Rh antigen. The following chart summarizes the distribution of the ABO and ...

Roadmap On Emerging Concepts In The Physical Biology Of Bacterial Biofilms From Surface Sensing To Community Formation Iopscience
That is: NFP = GBHP - [CHP + BCOP] = 10 mm Hg. Or: NFP = 55 - [15 + 30] = 10 mm Hg ( Figure 25.4.1 ). Figure 25.4.1 - Net Filtration Pressure: The NFP is the sum of osmotic and hydrostatic pressures. A proper concentration of solutes in the blood is important in maintaining osmotic pressure both in the glomerulus and systemically.

A P2 Lab 13 Hw A P2 Lab 12 Hw A P2 Lab 11 Hw A P2 Lab 10 Hw Lab 9 Hw Lab 8 Hw A P2 Lab 1 Hw A P2 Lab 2 Hw A P2 Lab
Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the figure. ... Gas exchange involves the transport of two respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide. Review how each gas is transported between the atmosphere and the cells of your body by completing this exercise. ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the path a secretory protein ...
Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Art-labeling Activity Figure 18.1 Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT 6032 Airways CO, is transported dissolved in plasma bound to hemoglobin or as HCO, Alveoli of lungs O, diffuses ...
Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: Solution A catalyst does not affect the energy of reactant or product, so those aspects of the diagrams can be ignored; they are, as we would expect, identical in that respect.
BioFlix Activity: Gas Exchange -- Oxygen Transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Left to right: 1: Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into surrounding capillaries 2:Oxygen enters a red blood cell ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures of the upper respiratory system.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways ...1 answer · 0 votes: The sequence of carbon dioxide transport in body - 1. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria ...
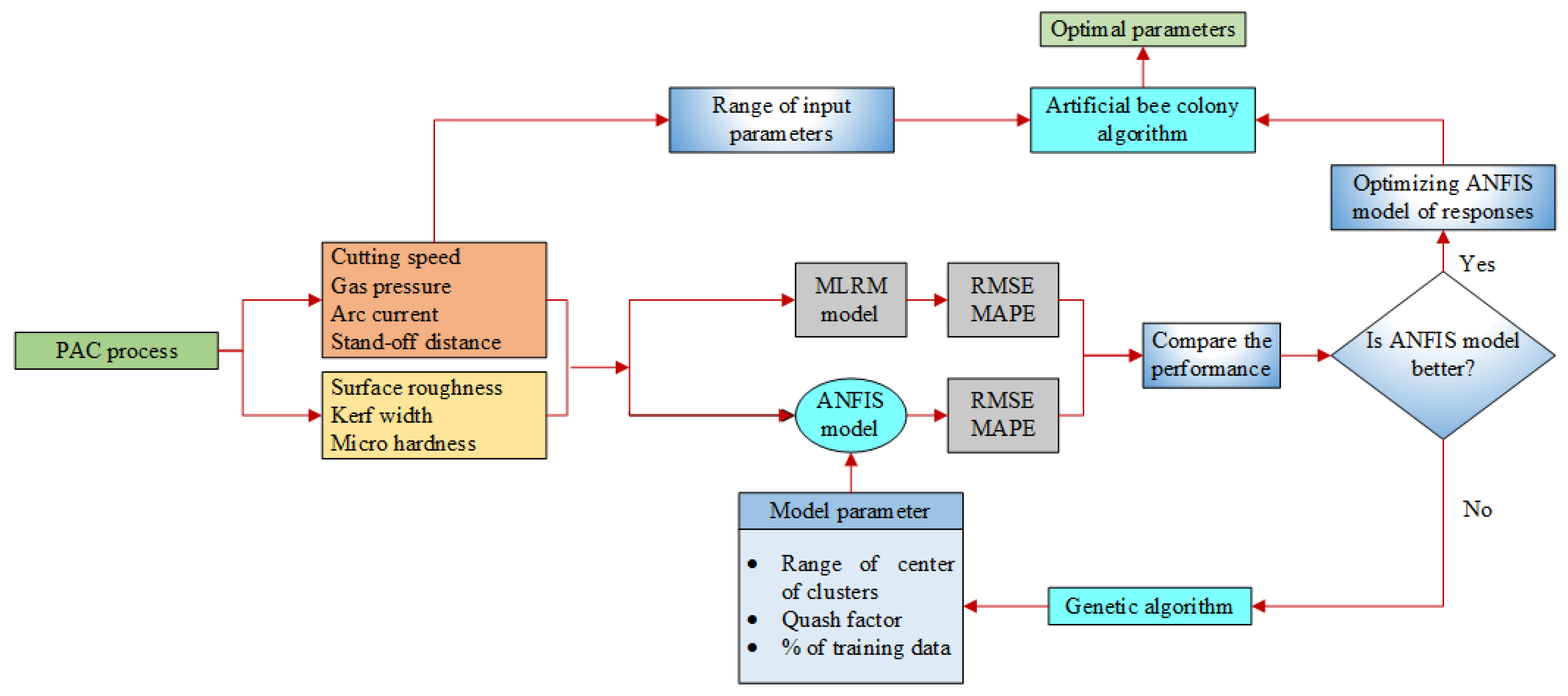
Materials Free Full Text A Hybrid Approach Of Anfis Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm For Intelligent Modeling And Optimization Of Plasma Arc Cutting On Monel 400 Alloy Html
Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide Release 3 0 Basic Setup Cisco Identity Services Engine Cisco













0 Response to "36 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange."
Post a Comment