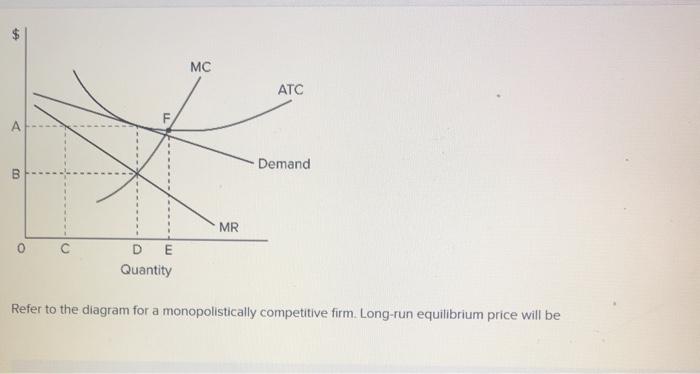
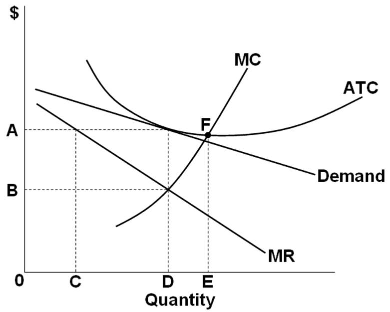
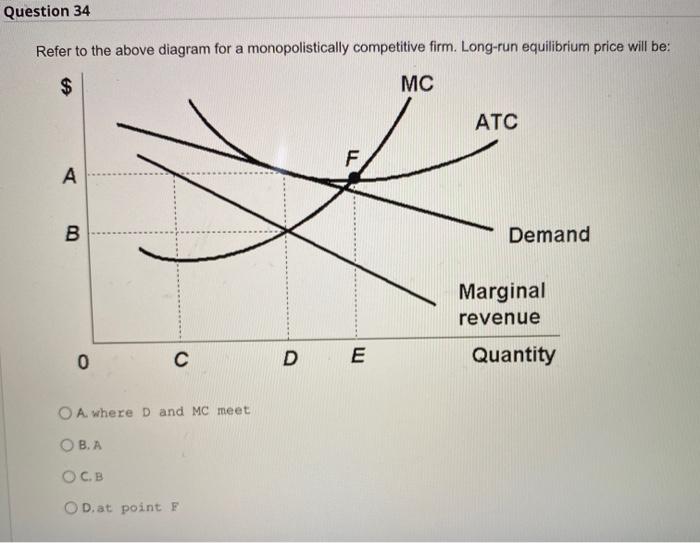
36 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: diagram a only. Long run equilibrium is shown by. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics 4both diagrams b and c. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium price will be. Refer to the above diagram wherein the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars.
A. The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... A. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium.

Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
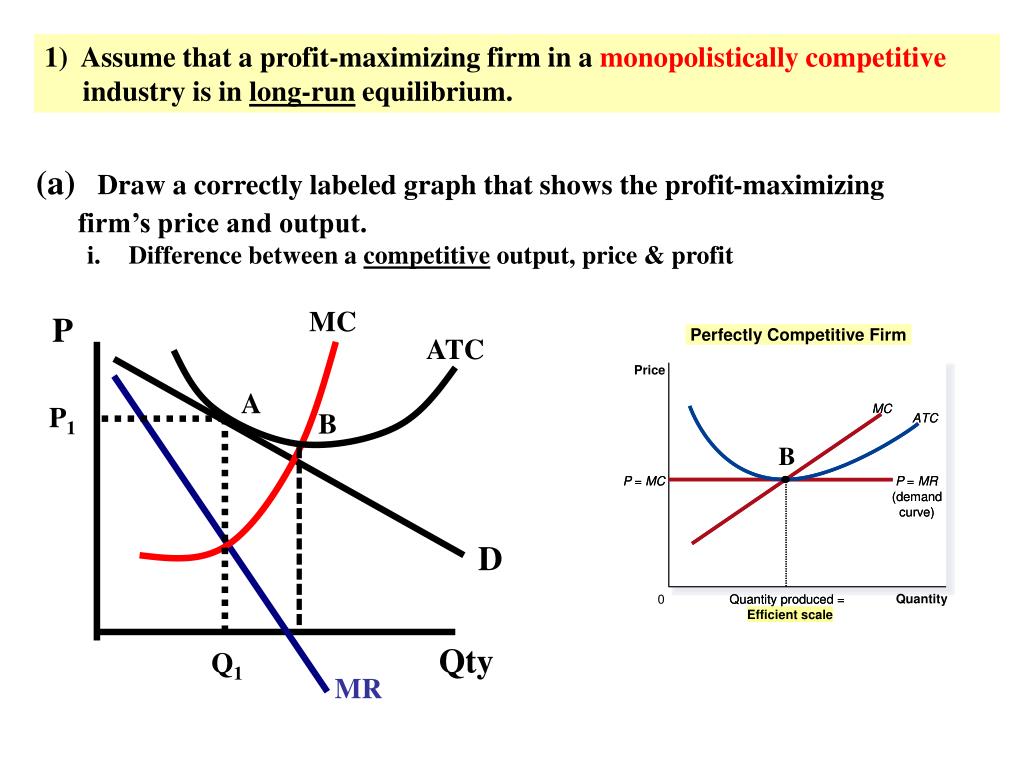
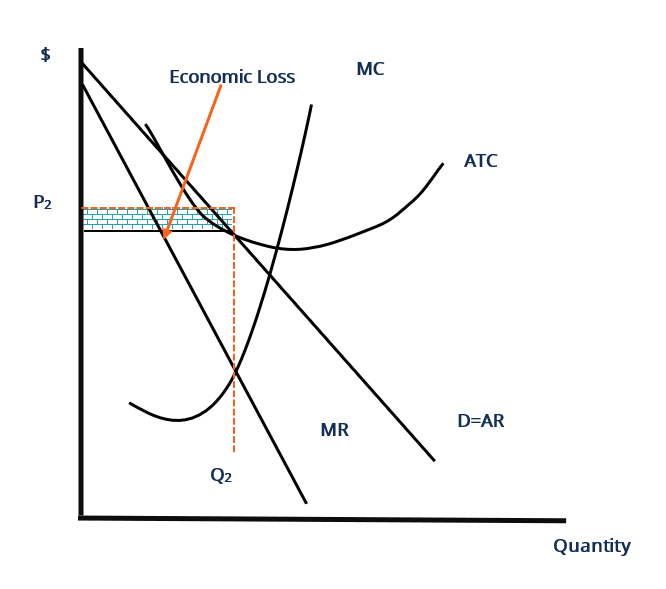
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing ... The monopolistic (monopoly) market model in long run equilibrium is ... Refer to the above diagram where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. 4both diagrams b and c. Long run equilibrium price will be. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. P mc atc. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will:
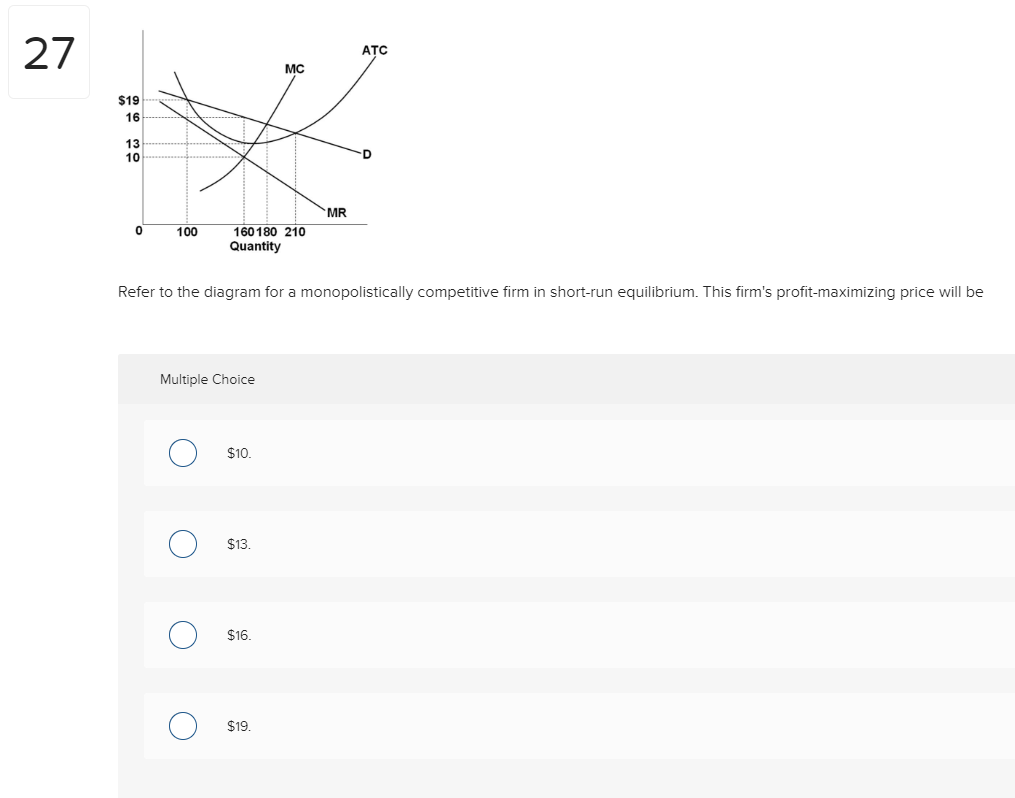
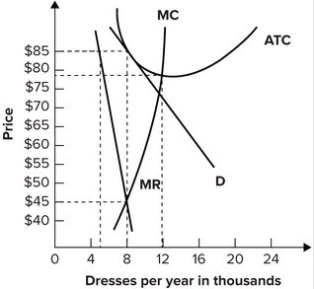
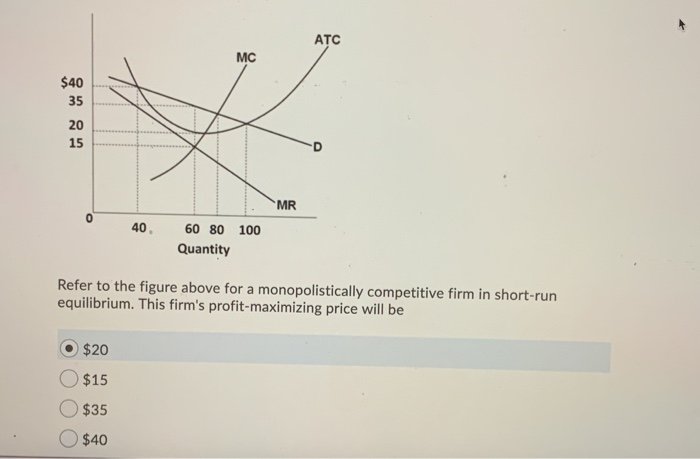
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $24, it will produce. 4 units at a loss of $138. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: Rating: 4 · 4 reviews Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be. A. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from. relatively easy entry. Option d is correct. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, the long run price will be a …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: $ MC ATC A Demand MR DE Quantity Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be Multiple Choice above A EF 8.
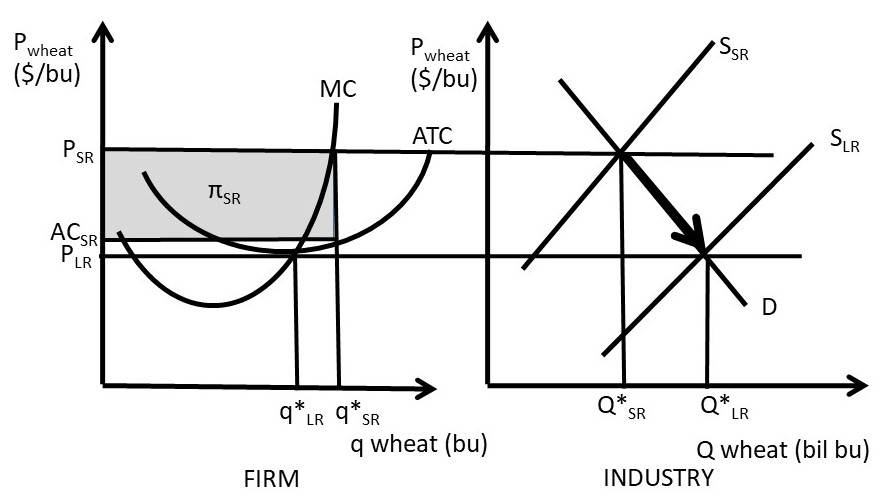
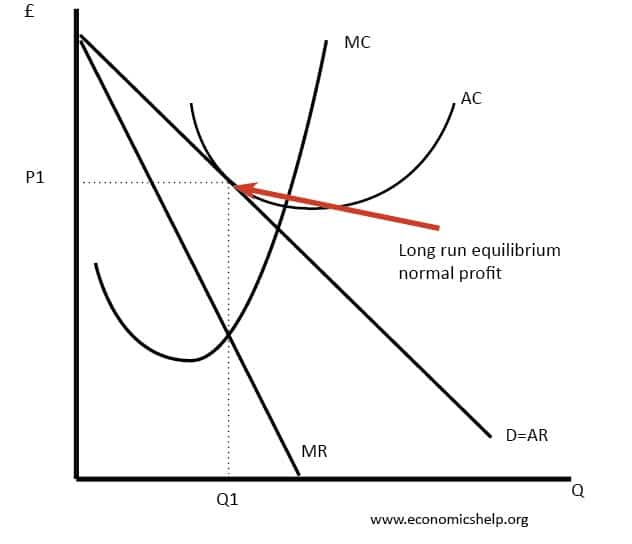
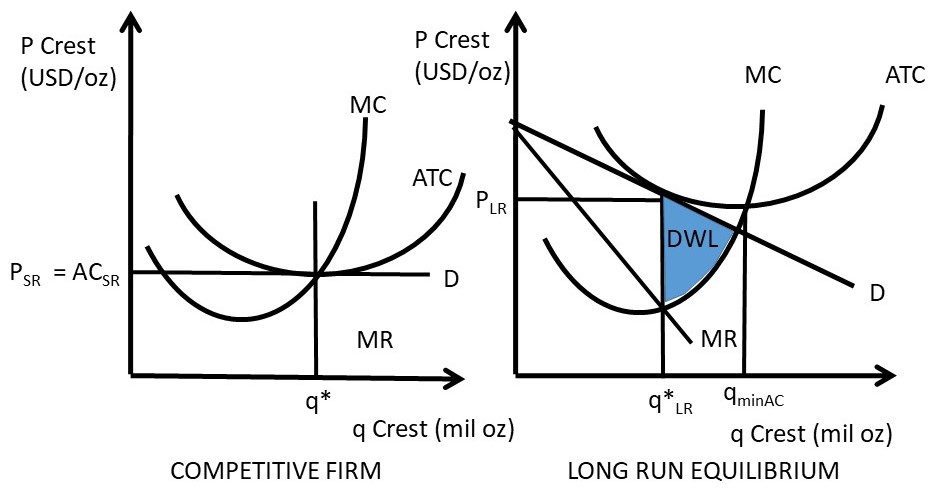
Hence the long run equilibrium for monopolistic competition will equate the market price to the average total cost where marginal revenue marginal cost as shown in the diagram below. The above diagrams show a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be A. The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... A. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. Rating: 5 · 2 reviews Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged?
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. ... underallocated because long-run equilibrium occurs where price exceeds marginal cost. In the long run, economic theory predicts that a monopolistically competitive firm will have excess production capacity. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from. ... refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. this firms profit-maximizing price will be. 16. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run equilibrium. The profit maximizing output for this firm will be.

The Figure Below Depicts A Monopolistically Competitive Firm Operating In The Short Run Label The Diagram Homeworklib
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will:
Refer to the above diagram where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. 4both diagrams b and c. Long run equilibrium price will be. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. P mc atc.
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing ... The monopolistic (monopoly) market model in long run equilibrium is ...

Refer To The Graph Above At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Short Run Output This Monopolistically Competitive Firm Will Be Making A Profit Of A 275 B 350 C 500 D 525 Study Com

Figure 16 3 This Figure Depicts A Situation In A Monopolistically Competitive Market Be 9 Refer To Figure 16 3 W Homeworklib


















0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be"
Post a Comment