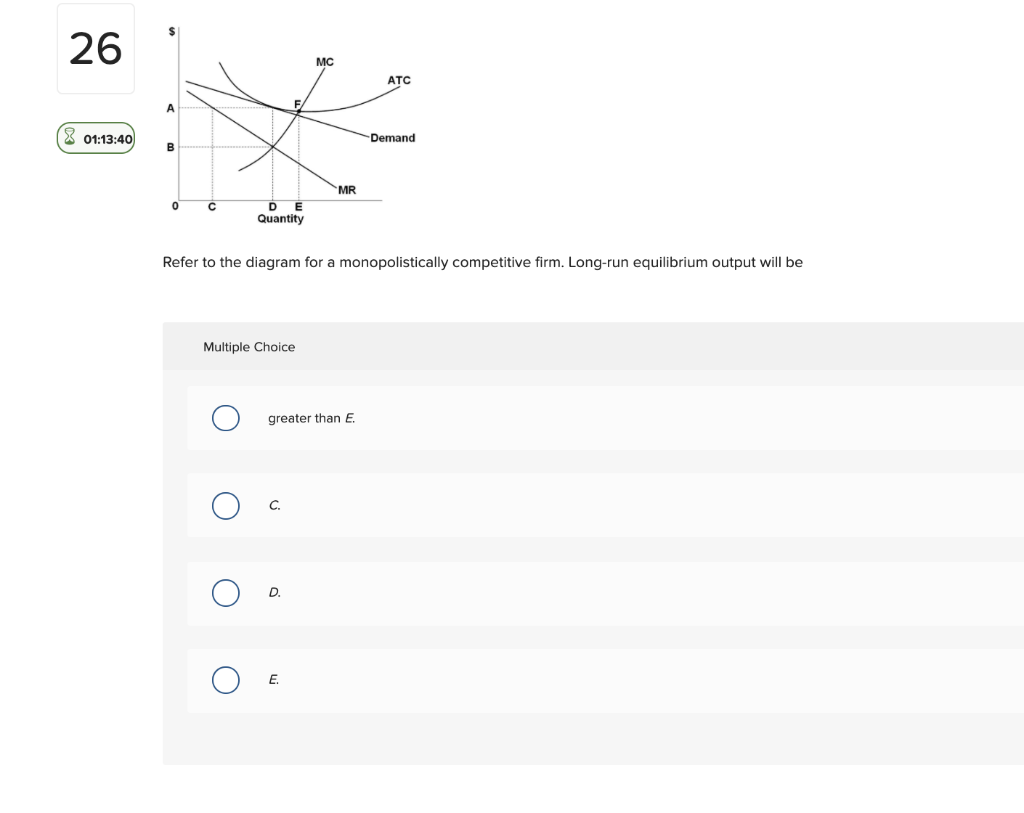
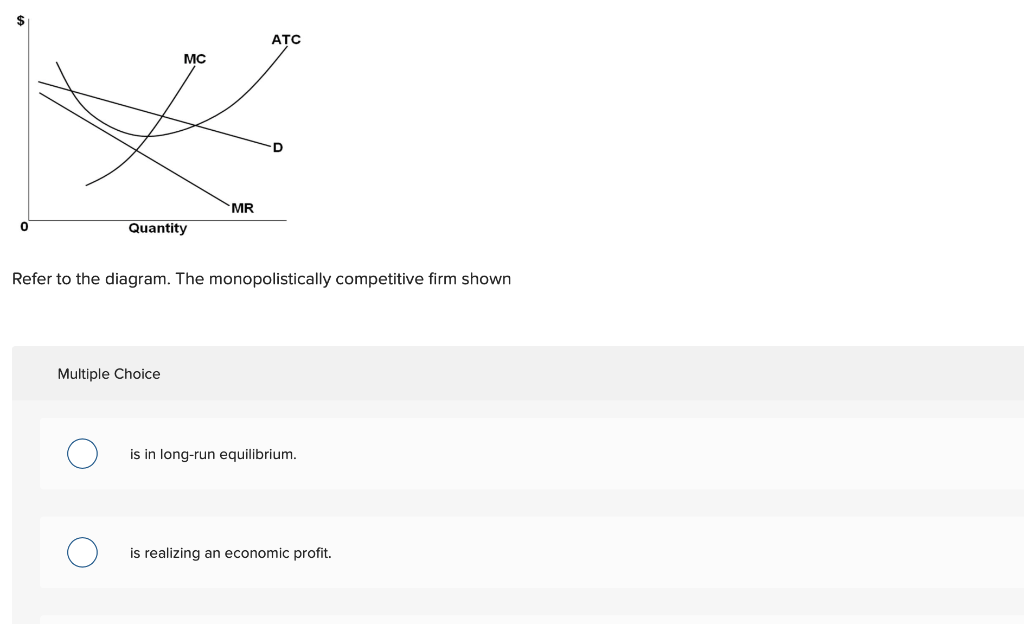
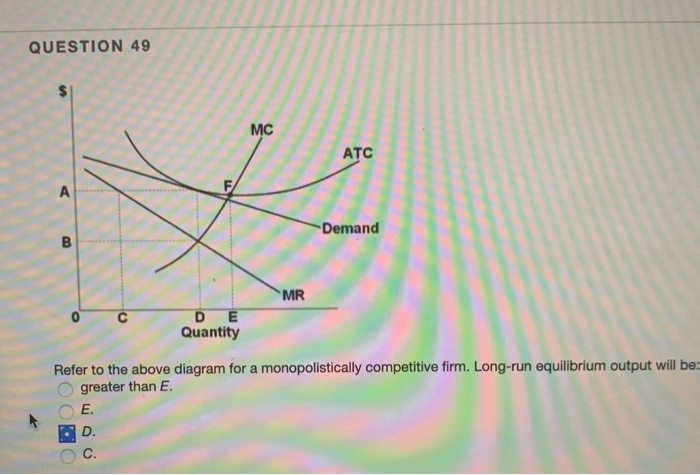
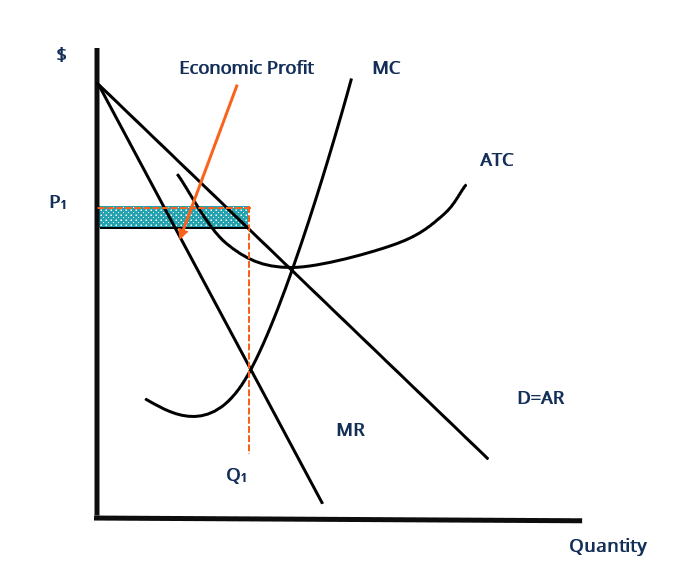
36 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium output will be
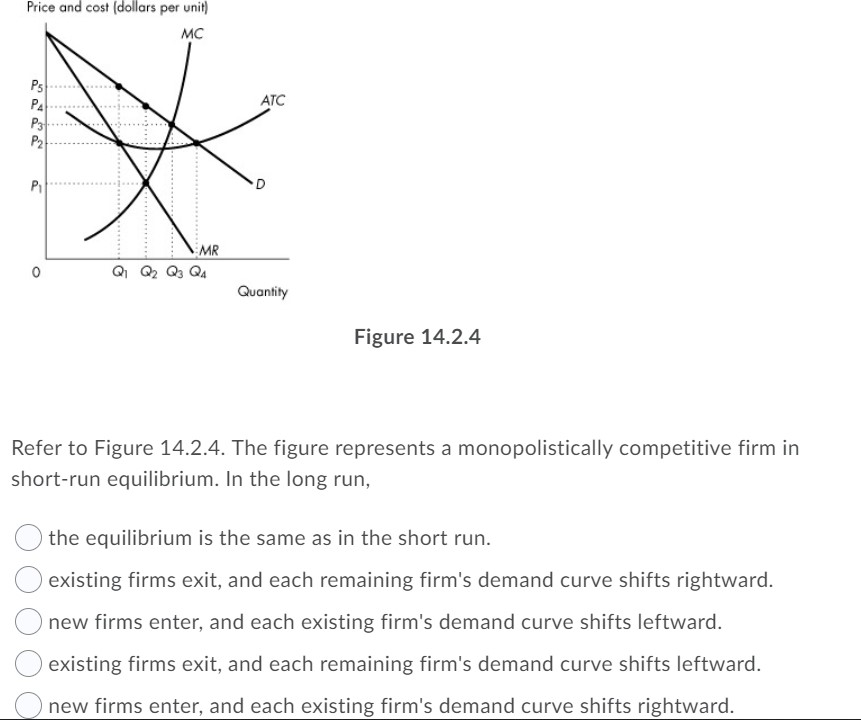
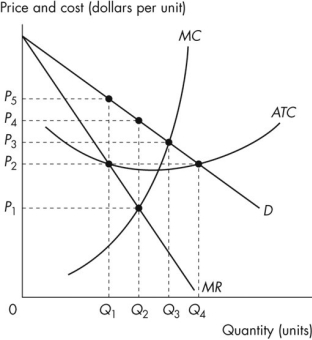
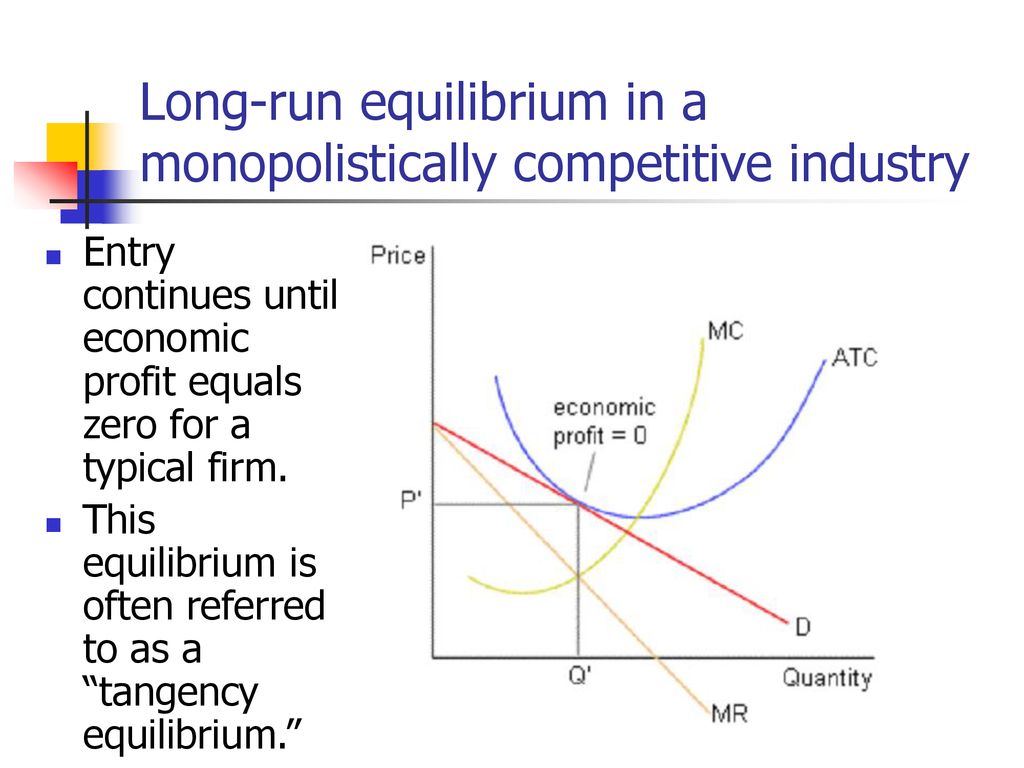
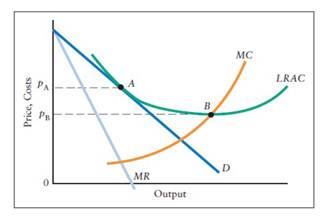
The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure .. The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left. As entry into the market increases, the firm's demand curve will continue shifting to the left until it is just tangent to the average total ... 82. Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: A.diagram a only. B. diagram b only. C. diagram c only. D. both diagrams b and c. Difficulty: Medium Learning Objective: 12-02 Explain why monopolistic competitors earn only a normal profit in the long run.
Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run. 1refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Let us learn about the short run and long run equilibrium of a firm under monopolistic competition. 4both diagrams b and c. 3refer to the diagram above.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium output will be
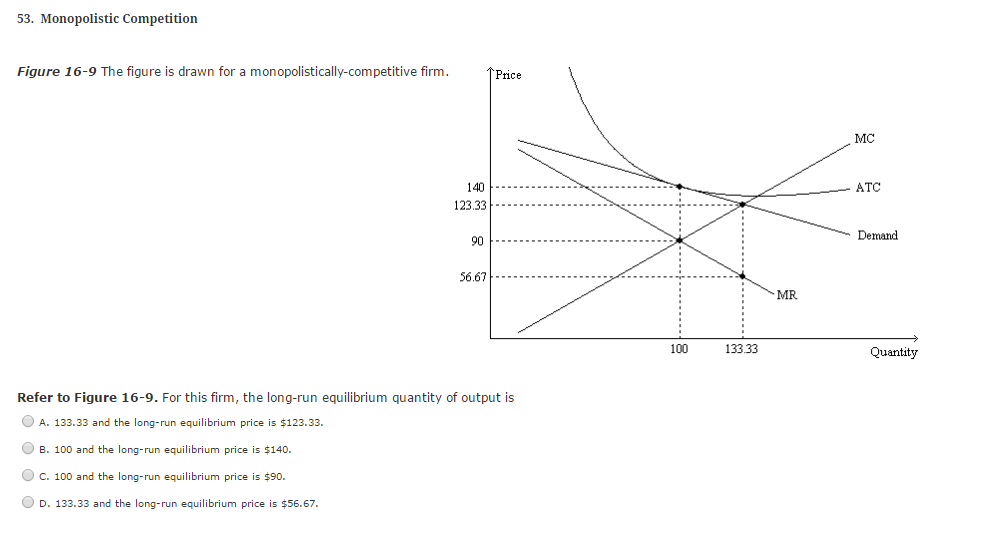
Refer to the above graphs. The long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm is represented by graph -B. 52. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. If more firms were to enter the industry and product differentiation were to weaken, then -the demand curve would become more elastic. 53. Refer to the diagrams. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: 1. greater than E. 2. E. 3. D. 4. C. 9. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from: 1. rising marginal costs. 2. a perfectly elastic product demand curve. 3. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from relatively easy entry. Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm.
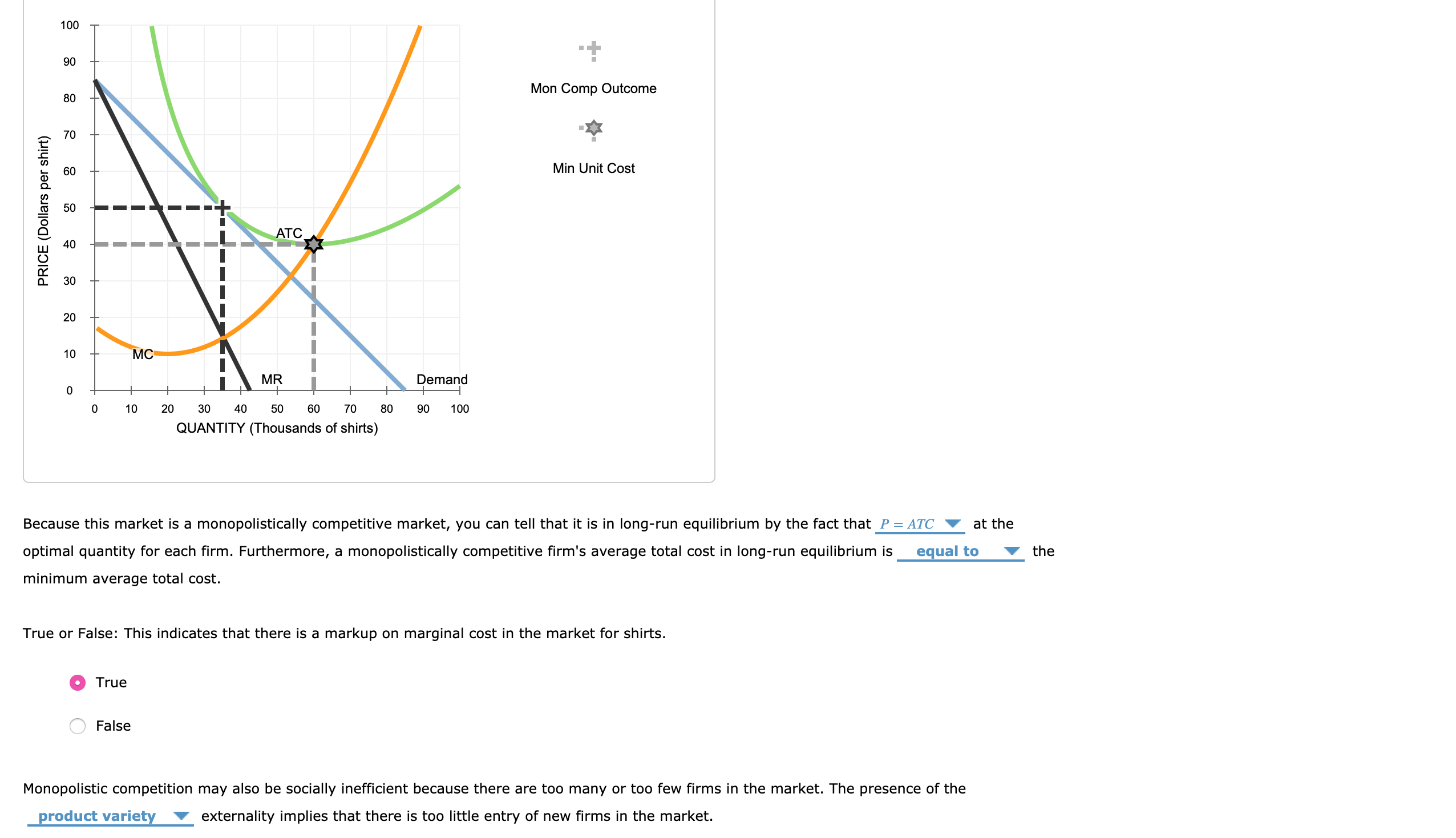
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium output will be. In the long run, economic theory predicts that a monopolistically competitive firm will have excess production capacity. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Therefore, at the long-run equilibrium output at the MR = LMC point, we have, for the monopolist, p > LMC. In other words, in the long-run equilibrium, price is equal to marginal cost for the competitive firm and price is greater than marginal cost for the monopolistic firm. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be. D. Product differentiation in monopolistic competition involves a trade-off between. consumer choice and productive efficiency. Your grades could look better! All our academic papers are written from scratch. All our clients are privileged to have all their academic papers written from scratch.
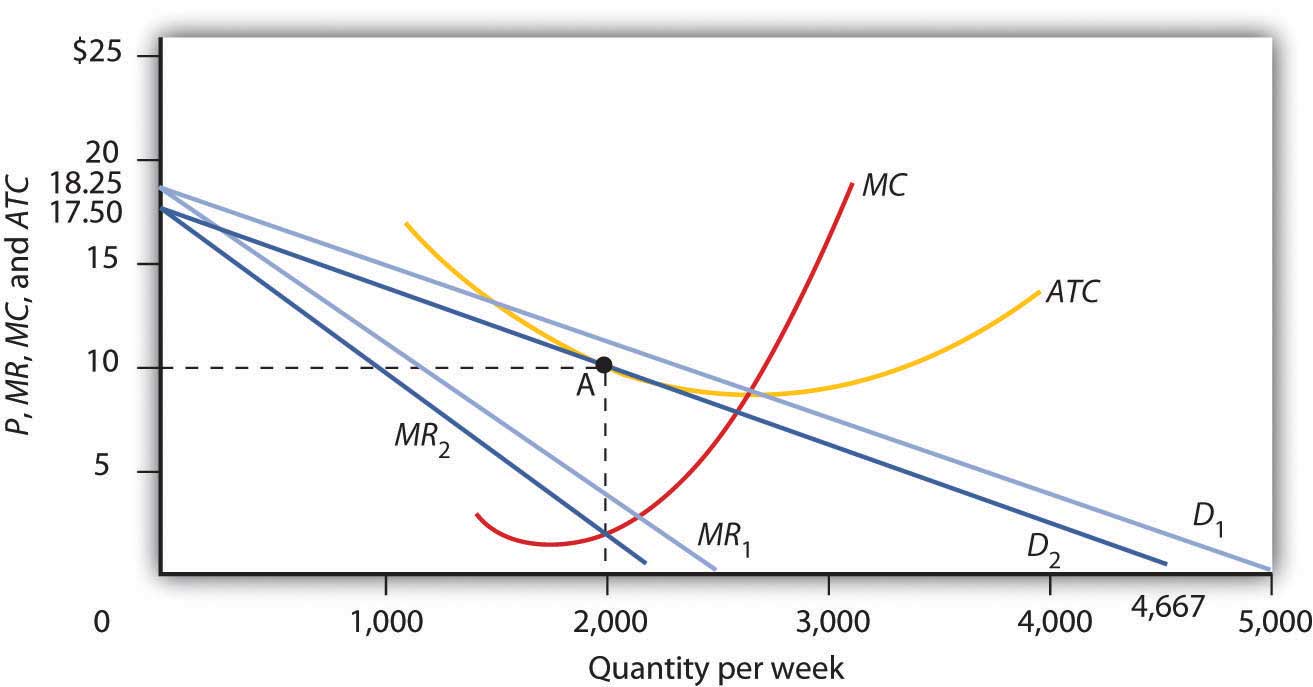
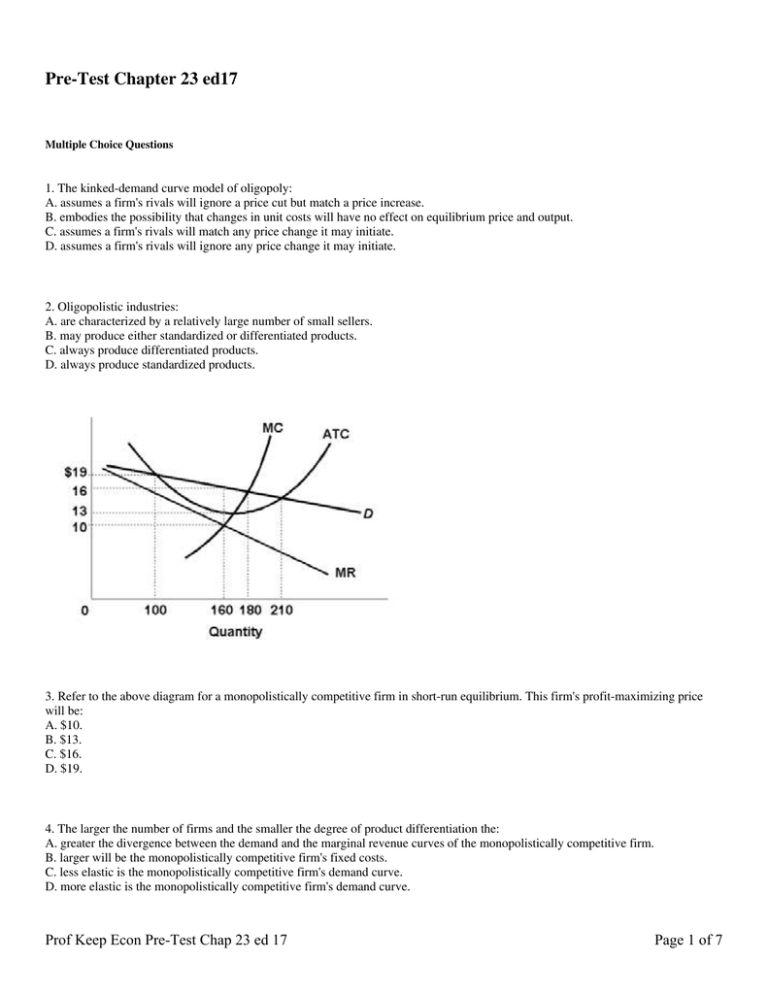
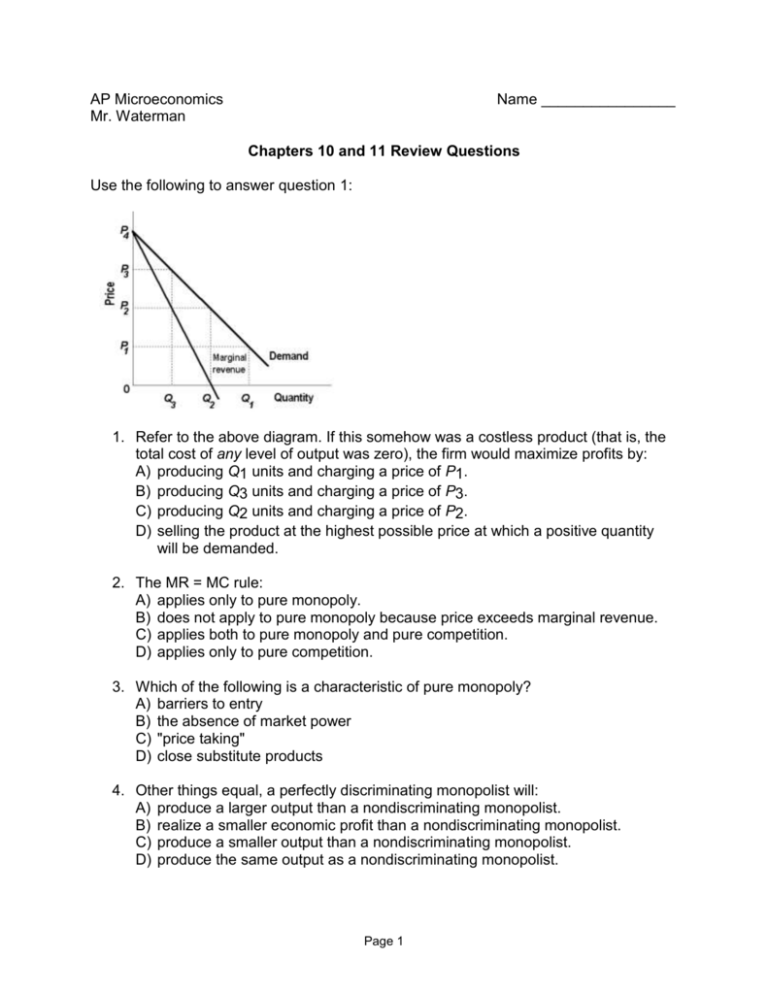
We always make sure that writers follow all your instructions precisely. You can choose your academic level: high school, college/university, master's or pHD, and we will assign you a writer who can satisfactorily meet your professor's expectations. The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 38) Refer to Figure 11-3. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will A) produce Q2 at Price P1. B) produce Q1 at Price P2. C) produce Q1 at Price P1. D) produce Q2 at Price P2. E) produce the output where AC is at its minimum. 39) Refer to ... 33) In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms produce where . A) excess capacity exists . B) the markup is equal to zero . C) the demand curve has shifted so that it intersects the minimum average total cost point . D) average total cost is minimized . Answer: A . 34) In monopolistic competition, in the long run firms produce Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A.
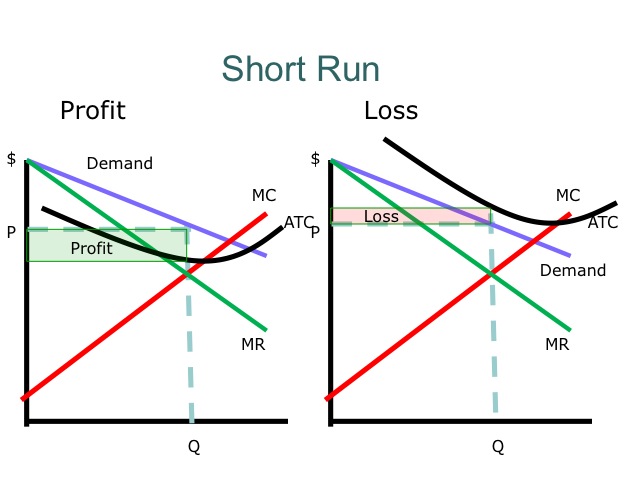
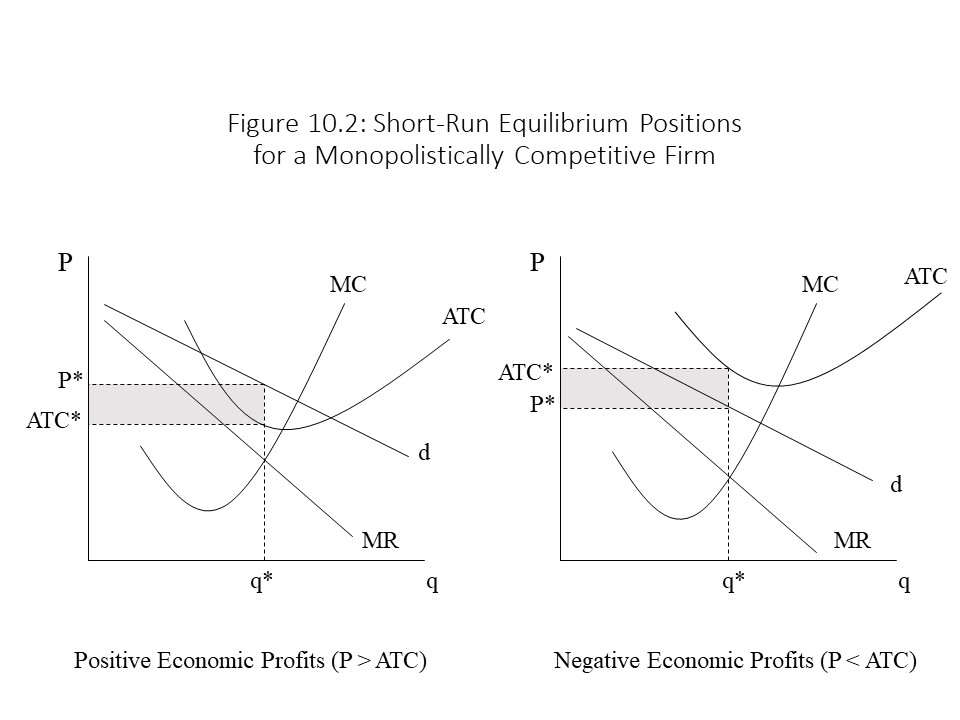
Economics Q&;A Library Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only. diagram a only. none of these diagrams. diagram c only. SR Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Given the short run equilibrium described, why does entry occur? As entry occurs, demand shifts leftward until profit equals zero. Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs ... The profitmaximizing output for this firm will be:160.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic:profit of $480. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. 3. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320. B. profit of $480. C. profit of $280. D. profit of $600.
The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D1 to D2) in the immediate market period, the short run, and the long run. In the long run, the increase in demand will A) have no effect on either equilibrium price or quantity.
Find equilibrium price and analyse what would be the excess demand or supply if price changes to Rs 400 and Rs 120. 2. ... 1 What does foreign trade refer to and why is it important for any country to participate in foreign trade. ... corporate houses feel insights can increase their sales in the long run.
B. monopolistically competitive firms cannot realize an economic profit in the long run. C. the number of firms in the industry is larger. D. monopolistically competitive producers use strategic pricing strategies to combat rivals.
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3 19) Refer to Figure 11-3. A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long-run equilibrium A) MC is greater than price. B) price is greater than LRAC at QL.
The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be If some firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curves of the remaining firms will shift to the right.
Econ 101 final exam
Economics questions and answers. 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: a. greater than E. b. E. c. D. d. C. 2.Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown.
Solved Refer To Figure 16 5 Given This Firm S Cost Curves If The Firm Were Perfectly Competitive Rather Than Monopolistically Competitive Then I Course Hero
The graph shows that: - ScieMce. Refer to the graph shown of a monopolistically competitive firm. The graph shows that: asked Sep 2, 2019 in Economics by livdinome. A. new firms will enter the industry. B. some existing firms will leave the industry. C. the price of the product is $90. D. the industry is in long-run equilibrium.
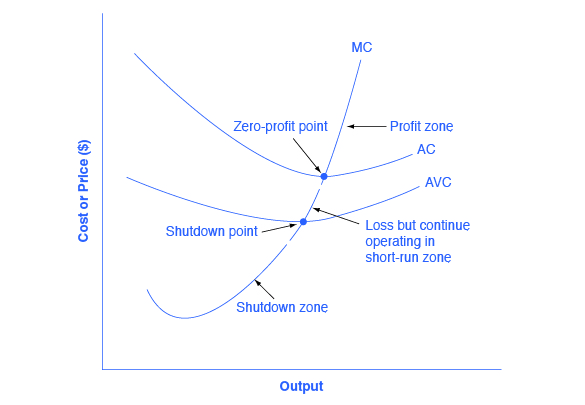
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
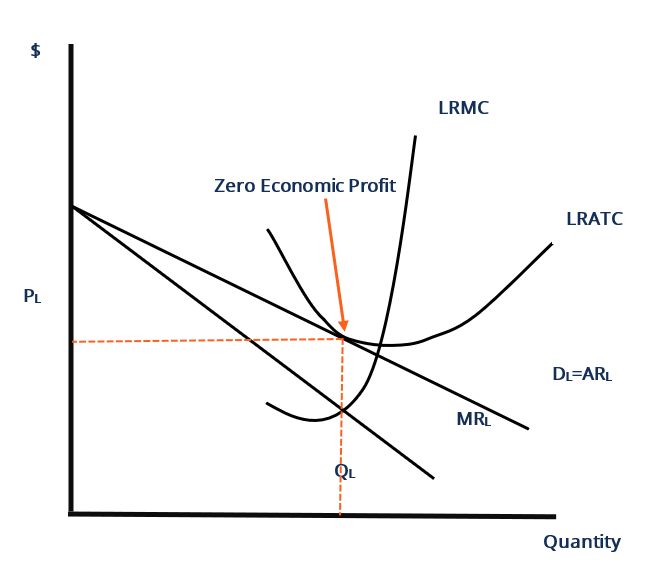
Eventually, the monopolistically competitive firm will reach long-run equilibrium (profit-maximization) position whereby it receives a price (P) that is equal to the Long-run Average Total Cost (LAC) so that it will be earning only a normal profit as illustrated in Figure 10.6. Fig. 10.6: Long-run profit-maximising position of a ...

Refer To The Graph Above At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Short Run Output This Monopolistically Competitive Firm Will Be Making A Profit Of A 275 B 350 C 500 D 525 Study Com
International Economics, Theory and Policy, Global Edition by Paul R. Krugman, Maurice Obstfeld, Marc J. Melitz
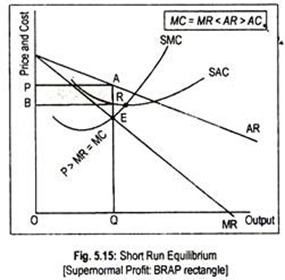
Long run equilibrium is achieved at point E where LMC equals MR (Fig. 5.16). The equilibrium output thus determined is OQ M. At this output, AR equals AC. The firm gets normal profit by selling OQ M output at the price OP M. Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve.
A) equilibrium output would rise and equilibrium price would fall. B) the demand curve would become more elastic. C) equilibrium output would decline and equilibrium price would rise. D) none of these above. B. Refer to the diagram below for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium.
Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from relatively easy entry. Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm.
8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: 1. greater than E. 2. E. 3. D. 4. C. 9. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from: 1. rising marginal costs. 2. a perfectly elastic product demand curve. 3.
Refer to the above graphs. The long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm is represented by graph -B. 52. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. If more firms were to enter the industry and product differentiation were to weaken, then -the demand curve would become more elastic. 53. Refer to the diagrams.






0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium output will be"
Post a Comment