37 trigeminal nerve branches diagram
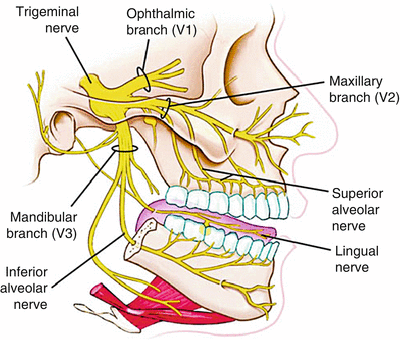
Jul 23, 2019 · Trigeminal Nerve Innervation Diagram. Trigeminal Nerve Innervation Diagram. In this image, you will find ophthalmic branch, trigeminal nerve, maxillary brach, superior alveolar nerve, mandibular branch, inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve in it. Health care advices from Overseas Doctor . We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Trigeminal Nerve Innervation Diagram. Chapter 56 Neurology: Spinal Cord & Nerves Figure 56.11 CN V: trigeminal nerve. The three branches include the ophthalmic nerve (V1), maxillary nerve (V2), and mandibular nerve (V3). Figure 56.12 CN VII: facial nerve, including the intracranial and extracranial branches.
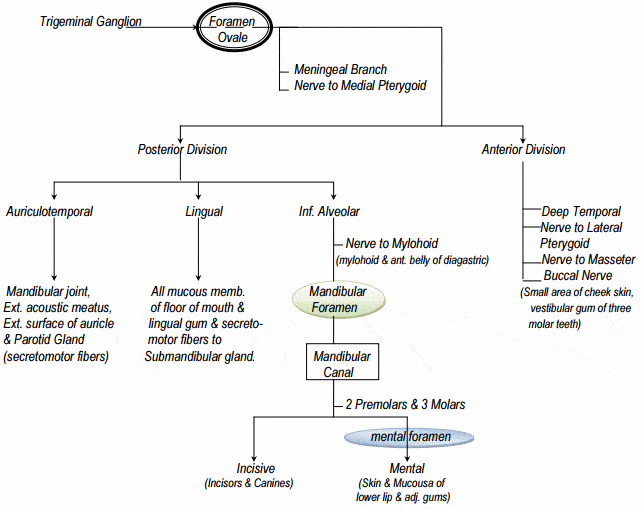
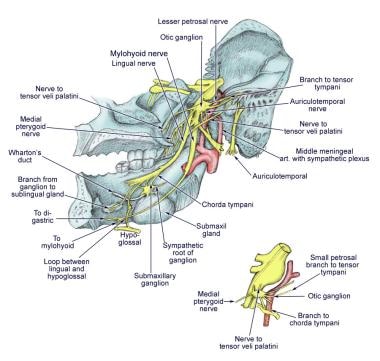
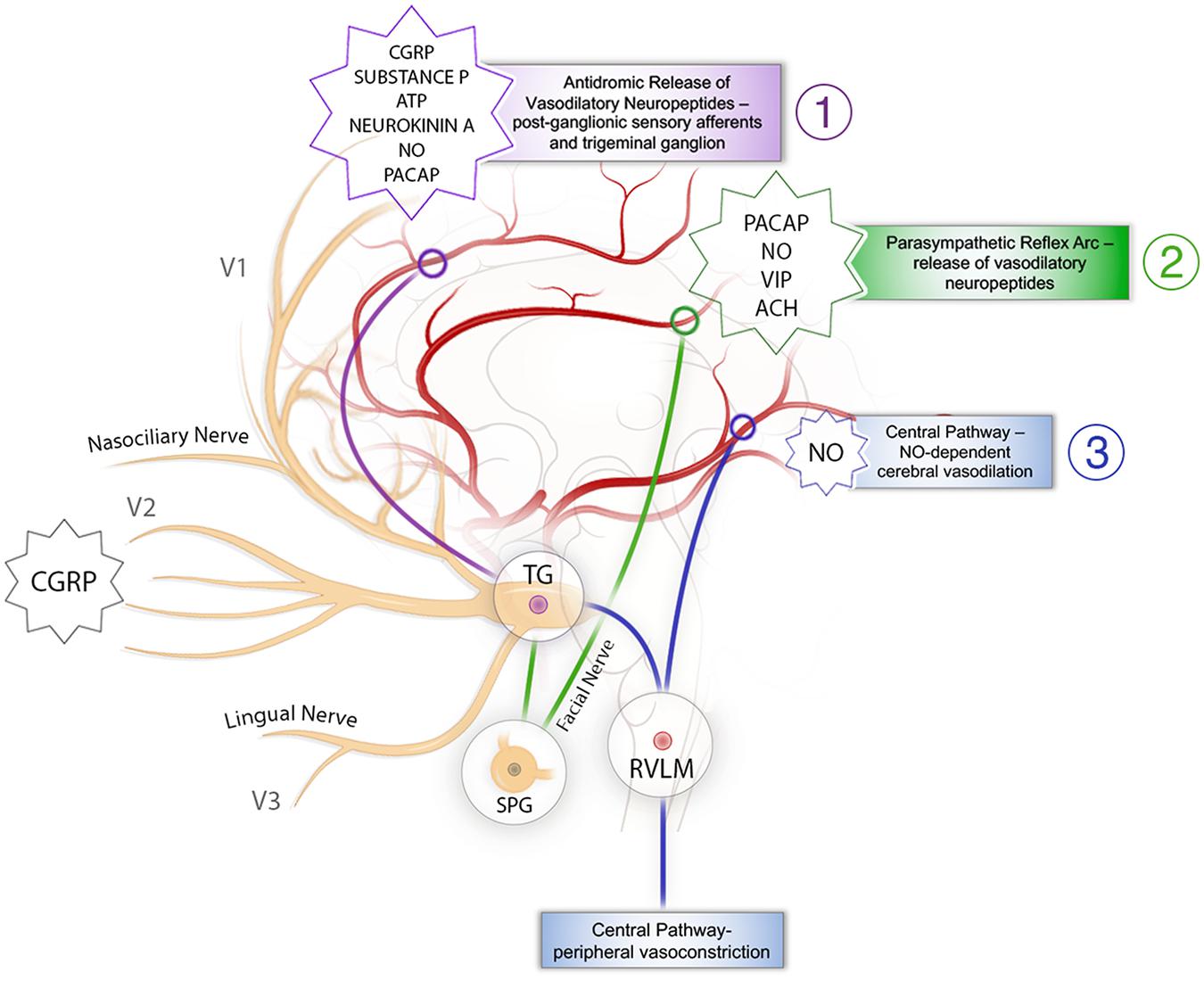
Diagram shows trigeminal nerve (TGN), trigeminal ganglion, and peripheral divisions and their branches. From fora-men rotundum ossis sphenoidalis, maxil-lary nerve (thin underline) gains access to pterygopalatine fossa and continues in floor of orbit as infraorbital nerve. Inferior alveolar and lingual nerves ( thick underline )
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram
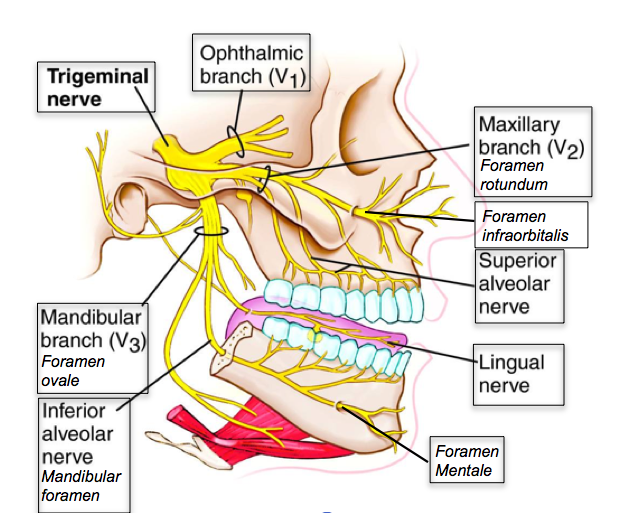
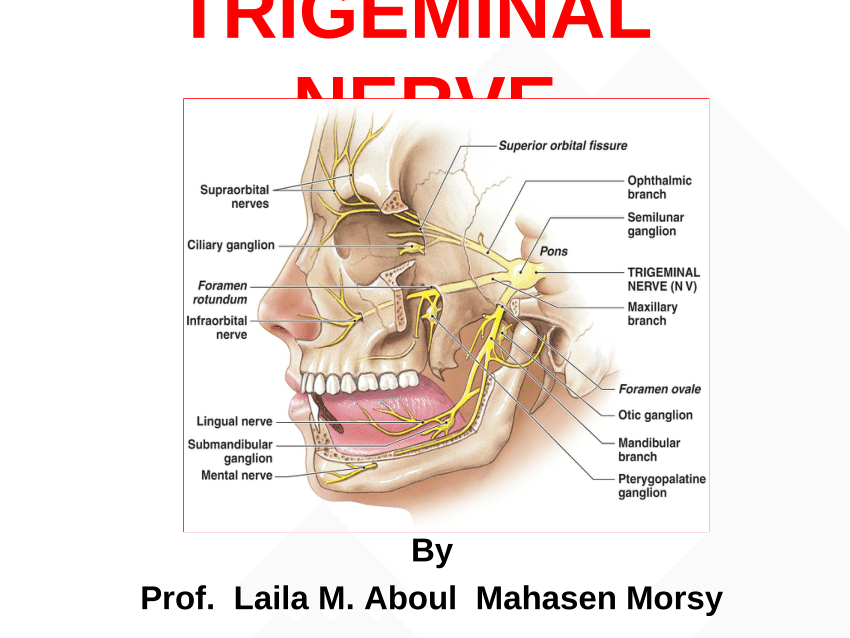
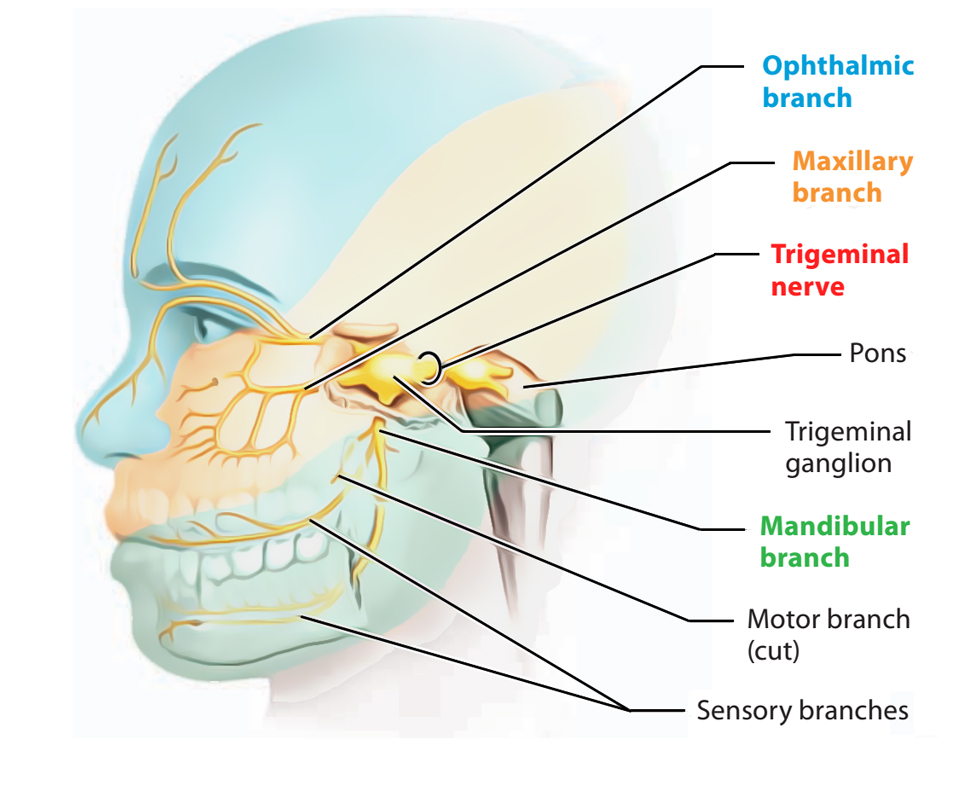
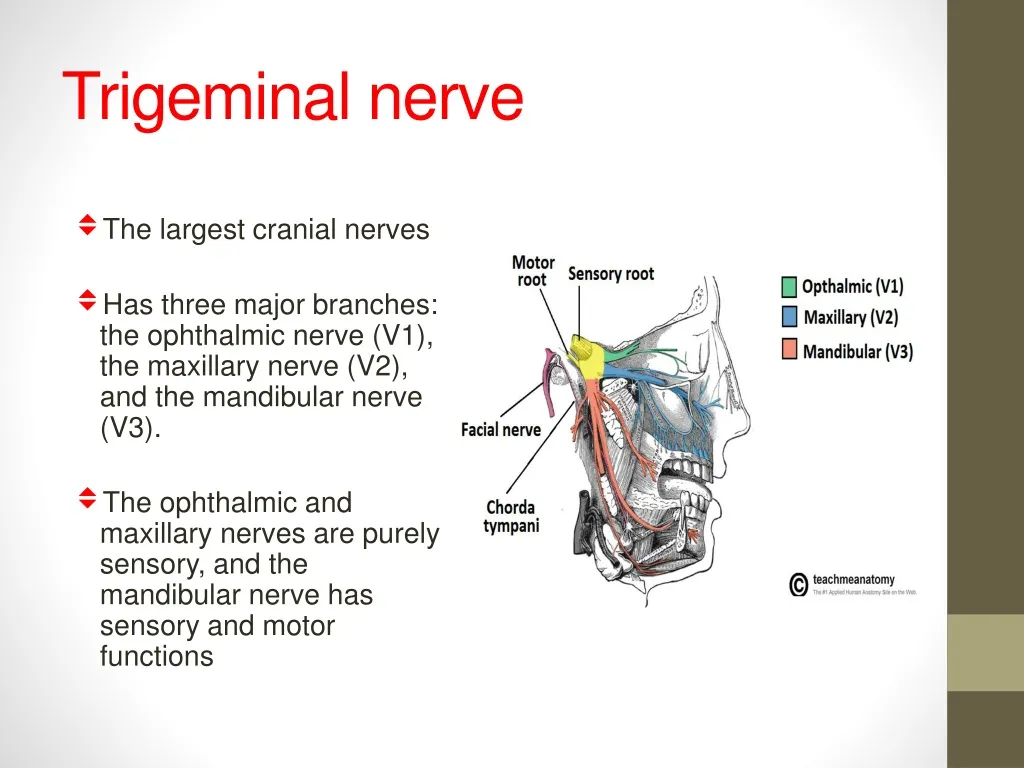
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. 2. Three nerve roots give rise to: a. Ophthalmic nerve, (CN V-1) b. Maxillary nerve, (CN V-2) c. Mandibular nerve, (CN V-3) 3. Peripheral distribution of three branches. Back of head and the angle of the jaw are not supplied by the trigeminal (Areas around ear supplied by CNs Symptoms. Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include one or more of these patterns: Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock. Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks ...
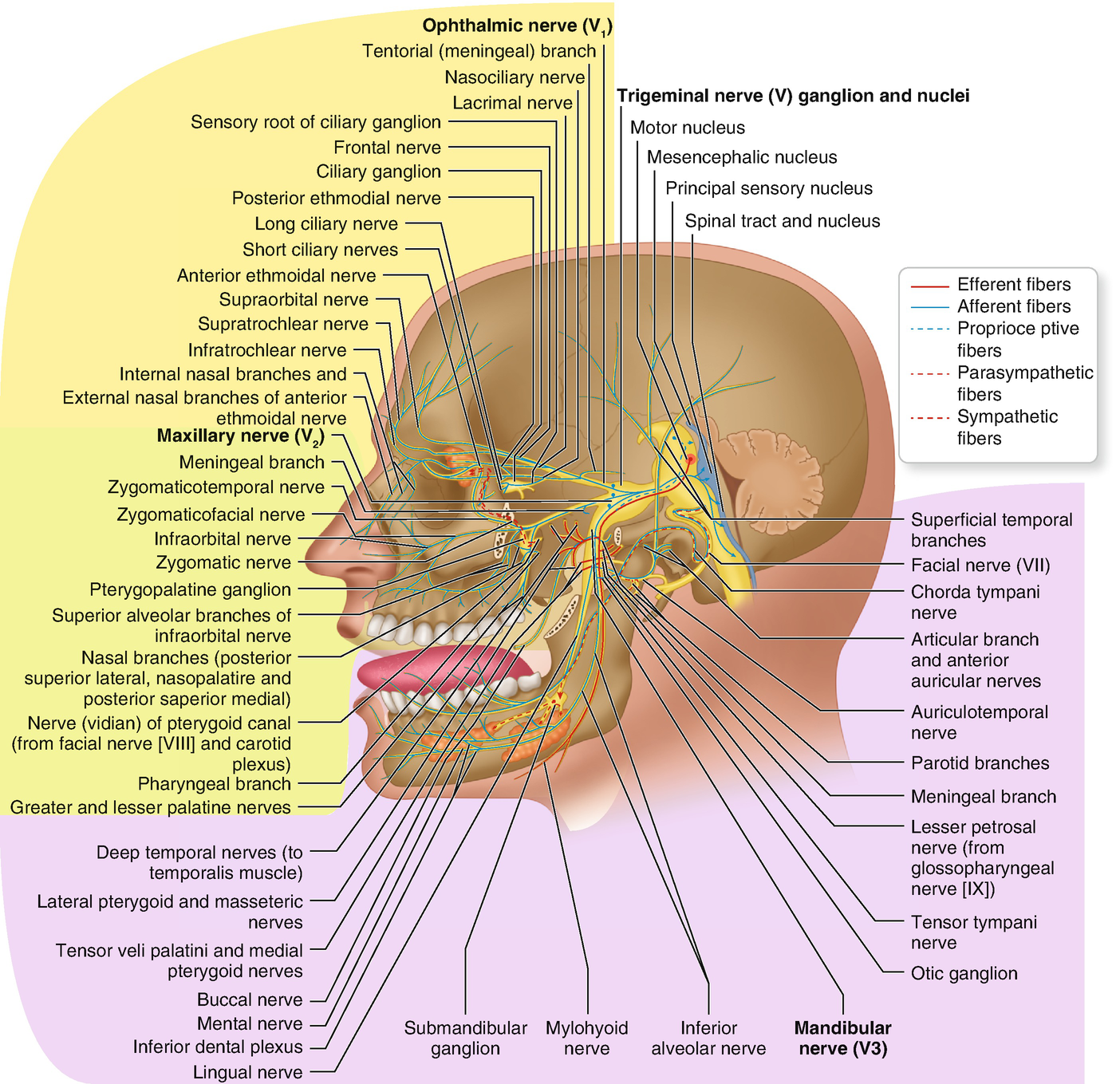
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram. The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth (or V) cranial nerve, is a cranial nerve and its primary role is relaying sensory information from the face and head, although it does provide motor control to the muscles of mastication.It is both large and complicated and has multiple brainstem nuclei (sensory and motor) as well as many interconnections with other cranial nerves. The ophthalmic branch is the first division of the trigeminal nerve. It is a purely sensory nerve that carries afferent stimuli of pain, light touch, and temperature from the upper eyelids and supraorbital region of the face, up to the vertex of the head. The nerve also acts as a conduit for sympathetic fibers that require access to the ciliary body, lacrimal glands, cornea, and conjunctiva ... The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves.Its name ("trigeminal" = tri-, or three, and - geminus, or twin: thrice-twinned) derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic ... The ophthalmic nerve (CNV1) is a terminal branch of the trigeminal nerve (along with the maxillary and mandibular nerves).. It provides sensory innervation to the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the upper face and scalp.. In this article, we will look at the anatomy of the ophthalmic nerve - its anatomical course, sensory functions and autonomic functions.
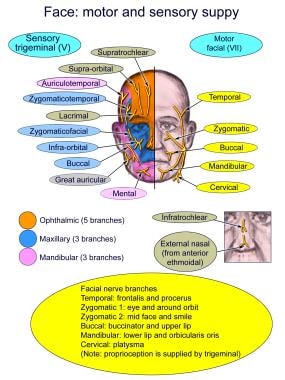
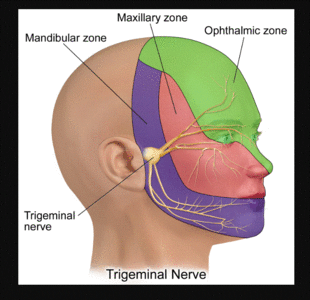
The trigeminal nerve contains three branches (that's why it's called trigeminal). The mandibular branch takes sensory data from the lower jaw area, all the way from the chin up to the area in front of the ear. The maxillary branch covers the area of the upper jaw, including the lower part of the nose and up to the area right below the eye. Understanding cranial nerves can easily be a problem that is hard to overcome in the process of studying anatomy. Since the matter is complex, students can easily forget why they even have to know all of that information. The maxillary nerve is one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, otherwise known as the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Supplying sensory innervation to certain parts of the ... sensation includes: maxillary distal root of the 1st molar, maxillary 2nd and 3rd molars, periodontium and buccal gingiva, and part of the maxillary sinus. Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3) -mixed (motor and sensory) -largest of the 3 branches. -joins V2 at the trigeminal ganglion. -passageway through the foramen ovale. Jul 27, 2018 · The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the 12 cranial nerves. Its main function is transmitting sensory information to the skin, sinuses, and mucous membranes in the face.
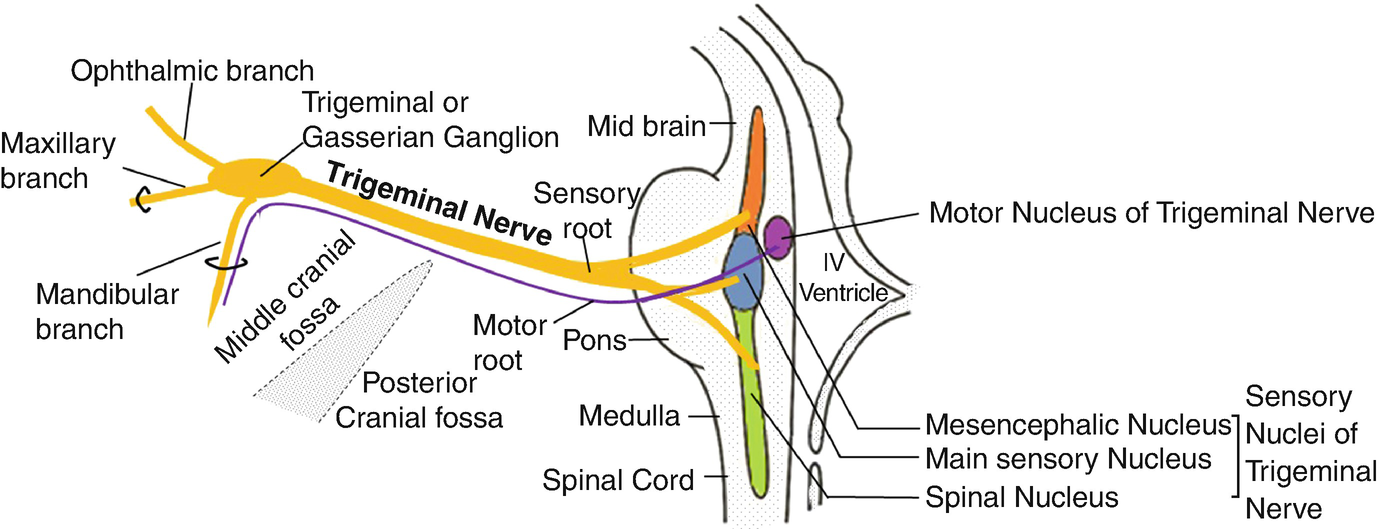
The fifth cranial nerve, the trigeminal nerve, has three branches which are the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The third branch is called mandibular nerve (V3). It is the largest of the three divisions and carries both afferent and efferent fibers. The first two branches of the trigeminal nerve carry only afferent fibers. The mandibular nerve innervates the lower face including the ... The mandibular nerve is a terminal branch of the trigeminal nerve (along with the maxillary and ophthalmic nerves).. It has a sensory role in the head, and is associated with parasympathetic fibres of other cranial nerves. However unlike the other branches of the trigeminal nerve, the mandibular nerve also has a motor function.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the mandibular ... The trigeminal nerve roots. Both motor and sensory components of the trigeminal nerve complex exit the ventral mid-pons as distinct nerves.. The larger, more medial nerve is the trigeminal sensory root; and a smaller, more lateral nerve is the trigeminal motor root named portio minor (the minor portion of the trigeminal nerve; the fourth branch). These two nerve roots come together to form a ... Branches of the trigeminal nerve. Print. Sections. Products and services. Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Diagram of the third branch (mandibular) of the trigeminal nerve with its branches. View Media Gallery The mandibular nerve carries sensory information from the lower lip, the lower teeth, gums, the chin and jaw (except the angle of the mandible, which is supplied by C2-C3), parts of the external ear, and parts of the meninges.
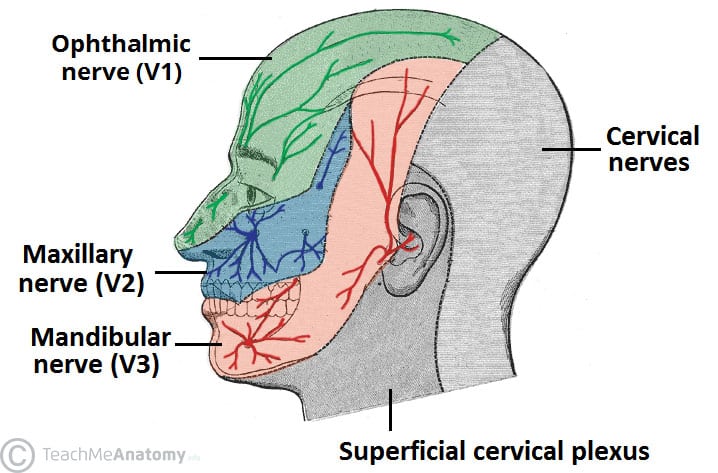
Trigeminal nerve. The large trigeminal nerve or 5th cranial nerve has three branches: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) divisions. Trigeminal nerve is a mixed nerve providing sensations of the face for touch, temperature, and pain from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain.
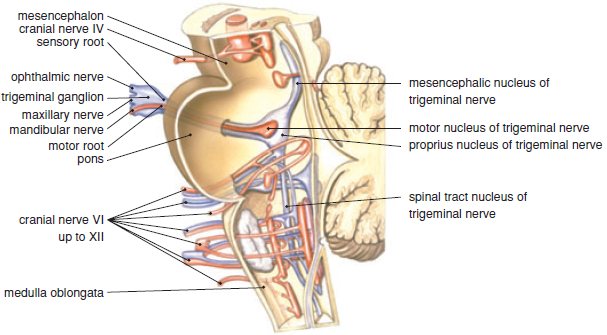
The trigeminal nerve is the largest cranial nerve and is the great sensory nerve of the head and face, and the motor nerve of the muscles of mastication.: It emerges from the side of the pons, near its upper border, by a small motor and a large sensory root—the former being situated in front of and medial to the latter.: Motor Root.—The fibers of the motor root arise from two nuclei, a ...
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth (or V) cranial nerve, is a cranial nerve and its primary role is relaying sensory information from the face and head, although it does provide motor control to the muscles of mastication.It is both large and complicated and has multiple brainstem nuclei (sensory and motor) as well as many interconnections with other cranial nerves.
The maxillary nerve (V2) is the branch of the trigeminal nerve that innervates the nasal region along with the maxillary teeth and maxillary sinus.It is a sensory branch of the trigeminal nerve.
The trigeminal nerve is associated with derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch. Sensory: The three terminal branches of CN V innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of the face.Their distribution pattern is similar to the dermatome supply of spinal nerves (except there is little overlap in the supply of the divisions).
Trigeminal Nerve. Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Trigeminal Nerve in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own.
Link to PayPal donation https://paypal.me/studentlamedicina?locale.x=en_US#anatomy #cranialnerve#maxillaryhttps://www.instagram.com/anatomy.knowledge/Anatomy...
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head.
The mandibular nerve (third division of fifth cranial nerve, third division of trigeminal nerve, mandibular division of trigeminal nerve, CN V3, Latin: nervus mandibularis) is the third branch of the trigeminal nerve, a mixed nerve consisting of general somatic efferent (motor) and general somatic afferent (sensory) fibers.The sensory fibers of the mandibular nerve innervate several skin ...
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Its primary function is to provide sensory and motor innervation to the face. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face. These branches join at the trigeminal ganglia which are located within the Meckel cave of the cranial cavity. The different branches are namely the ...
The motor nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve is smaller than the sensory branches and exits from the brainstem through the root of the trigeminal nerve. Location . The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion, like those of other cranial nerves, are located right outside the brainstem. The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that serves as ...
The trigeminal nerve is one of 12 pairs of nerves that are attached to the brain. The nerve has three branches that conduct sensations from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain. The ophthalmic, or upper, branch supplies sensation to most of the scalp, forehead, and front of the head.
Symptoms. Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include one or more of these patterns: Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock. Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks ...
2. Three nerve roots give rise to: a. Ophthalmic nerve, (CN V-1) b. Maxillary nerve, (CN V-2) c. Mandibular nerve, (CN V-3) 3. Peripheral distribution of three branches. Back of head and the angle of the jaw are not supplied by the trigeminal (Areas around ear supplied by CNs
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nucleus-principalis-nervi-trigemini/trj4f9Y96F8ZxnclYEC0g_Principle_nucleus_of_trigeminal_nerve_02.png)


















0 Response to "37 trigeminal nerve branches diagram"
Post a Comment