39 consider the flasks in the following diagram. what are the final partial pressures of h2 and n2
Question: N2 16. Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2, and the total pressure, after the valve between the two flasks is opened, and the gases are allowed to mix? (Assume the final volume is 3.00 L.) 2.00 L H2 475 torr 1.00 L N2 0.200 atm A. PH2 317 torr, PN2 50.7 torr, Ptotal 368 torr ... Consider the flasks in following diagram: voton w. Yclame . ... What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks ...2 pages
What is the total pressure in a 6.00-L flask which contains 0.127 mol of H2(g) and 0.288 mol of N2(g) at 20.0°C? 1.66 atm How many molecules of N2 are in a 500.0 mL container at 780 mm Hg and 135°C?

Consider the flasks in the following diagram. what are the final partial pressures of h2 and n2
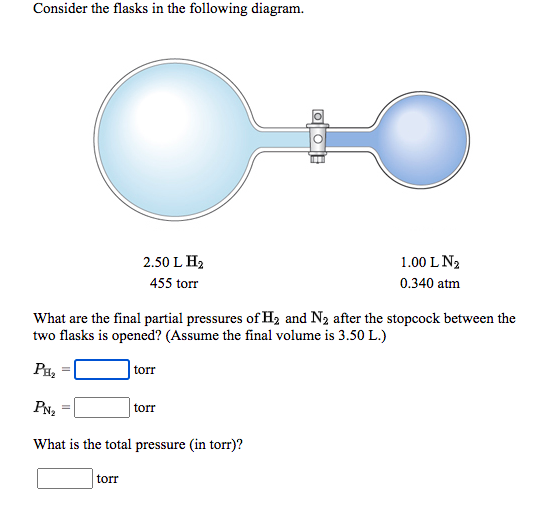
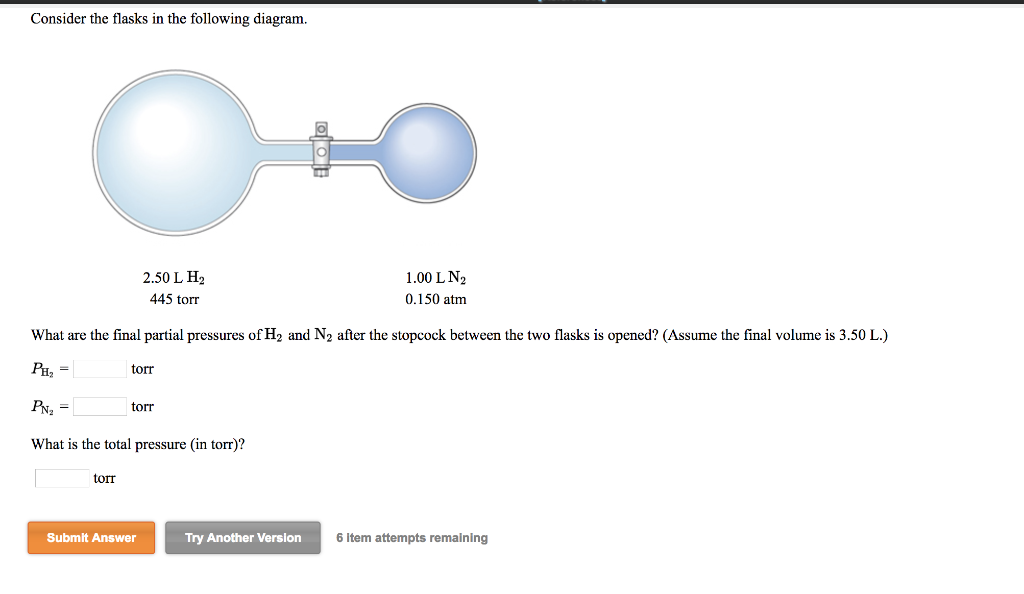
Chemistry Q&A Library Consider the flasks in the following diagram. 2.50 L 1.00 L 435 torr 0.260 atm What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume is 3.50 L.) H2 = torr N2 = torr What is the total Question: Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume in 3.00L) What is the total pressure in torr? One side of the bulb is H2 and it has 2.0L H2 and 475 torr. The other side is N2 and has 1.0L N2 and .200 atm. Answer to: Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H_2 and N_2 after the stopcock between the two...
Consider the flasks in the following diagram. what are the final partial pressures of h2 and n2. Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste · 2020 · ScienceConsider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? Problem: Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H 2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? ( ...1 answer · Top answer: Recall: The ideal gas law is as follows:We can see that the pressure and volume of a gas are related to the number of moles of gas, the universal gas constant, ... Consider the following reaction: H2(g)+I2(g)⇌2HI(g) Complete the table. Assume that all partial pressures are equilibrium values and in bar. T/K PH2 PI2 PHI K 298 0.0302 0.0388 0.922 − 600 0.0428 − 0.387 78.2 515 0.0540 0.382 − 33.0 81. Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H, and N2 after the stopcock between two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume is 3.00 L.) What is the total pressure (in torr)? 2.00 LH 475 torr 1.00 L N 0.200 atm ; Question: 81. Consider the flasks in the following diagram.
Consider the flask diagramed below with the following pressures 492 torr for H2 and 0.376 atm for N2. What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 ...3 pages Consider the flasks in the following diagram. (a) What are the final partial pressures of He and Ar after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume that the final volume is 4.00 L.) (b) What is the total pressure (in torr)? 3.00 L He 632 torr 1.00 L Ar 103 torr 19. Sketch graphs of the following ideal gas relationships for a given ... Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl · 2013 · ScienceConsider the flasks in the following diagrams. ... What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? Consider two flasks. What are the final partial pressure of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? Assume the final volume is 3.00 L. What is the total pressure in torr? Flask 1: 2.00 L H2, 475 torr Flask 2: 1.00 L N2, 0.200 atm Imagine two round flasks filled with gas that are connected to each other, with a stopcock in the middle.
What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume is 3.00 L.) What is the total ... 2.50 L 1.00 L 405 torr 0.260 atm What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume ...4 answers · Top answer: problem. Anyone says to consider the flasks and the following diagram. So here's my somewhat ... Answer to: Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H_2 and N_2 after the stopcock between the two... Question: Consider the flasks in the following diagram. What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume in 3.00L) What is the total pressure in torr? One side of the bulb is H2 and it has 2.0L H2 and 475 torr. The other side is N2 and has 1.0L N2 and .200 atm.
Chemistry Q&A Library Consider the flasks in the following diagram. 2.50 L 1.00 L 435 torr 0.260 atm What are the final partial pressures of H2 and N2 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened? (Assume the final volume is 3.50 L.) H2 = torr N2 = torr What is the total
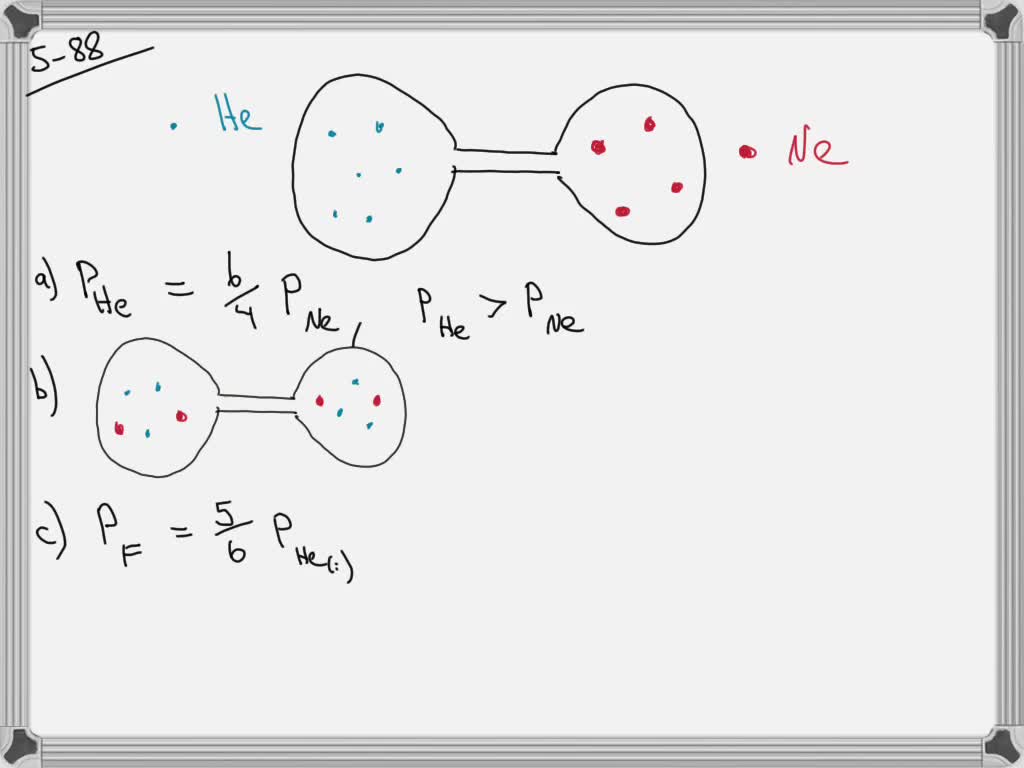
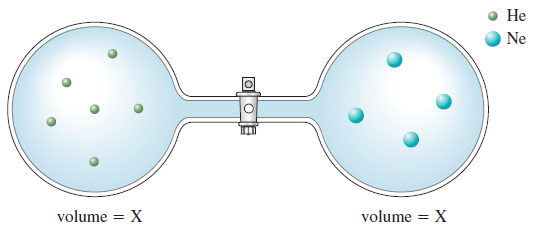
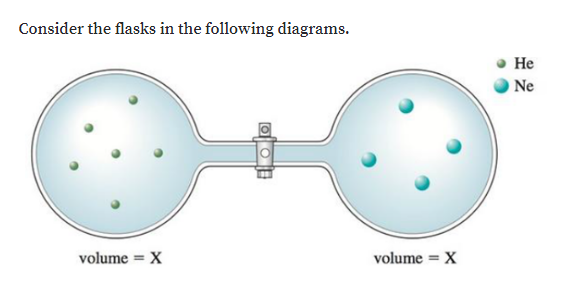
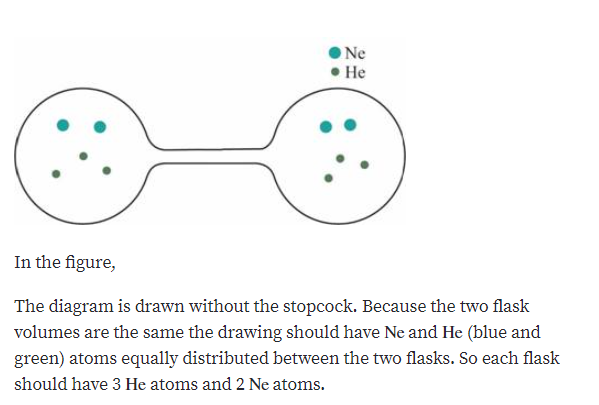
Solved Consider The Flasks In The Following Diagrams A Which Is Greater The Initial Pressure Of Helium Or The Initial Pressure Of Neon How Much Greater B Assuming The Connecting Tube Has Negligible

Solved Consider The Flasks In The Following Diagram What Are The Final Partial Pressures Of Mathrm H 2 And Mathrm N 2 After The Stopcock Between The Two Flasks Is Opened Assume The Final Volume Is 3 00

Solved Consider The Flasks In The Following Diagram What Are The Final Partial Pressures Of Mathrm H 2 And Mathrm N 2 After The Stopcock Between The Two Flasks Is Opened Assume The Final Volume Is 3 00

Two Flask Of Equal Volume Have Been Joined By A Narrow Tube Of Negligible Volume Initially Both Flasks Are At 300k Containing 0 60 Mole Of O2 Gas At 0 5atm Pressure One Of
Solved The Questions Are A Which Is Greater The Initial Pressure Of Helium Or The Initial Pressure Of Neon How Much Greater Course Hero
.png)














0 Response to "39 consider the flasks in the following diagram. what are the final partial pressures of h2 and n2"
Post a Comment