39 monty hall tree diagram
Nov 13, 2006 — The set of all possible outcomes is called the sample space for the experiment. A tree diagram is a graphical tool that can help us work through ...17 pages Test your logic with 25 logic puzzles, including easy word logic puzzles for kids, and hard logic puzzles for adults. Solve these word problems, with answers included.
Monty Hall problem decision tree according to conditional probability According to Figure 5, in case the host opens door 3 and the contestant changes ...

Monty hall tree diagram
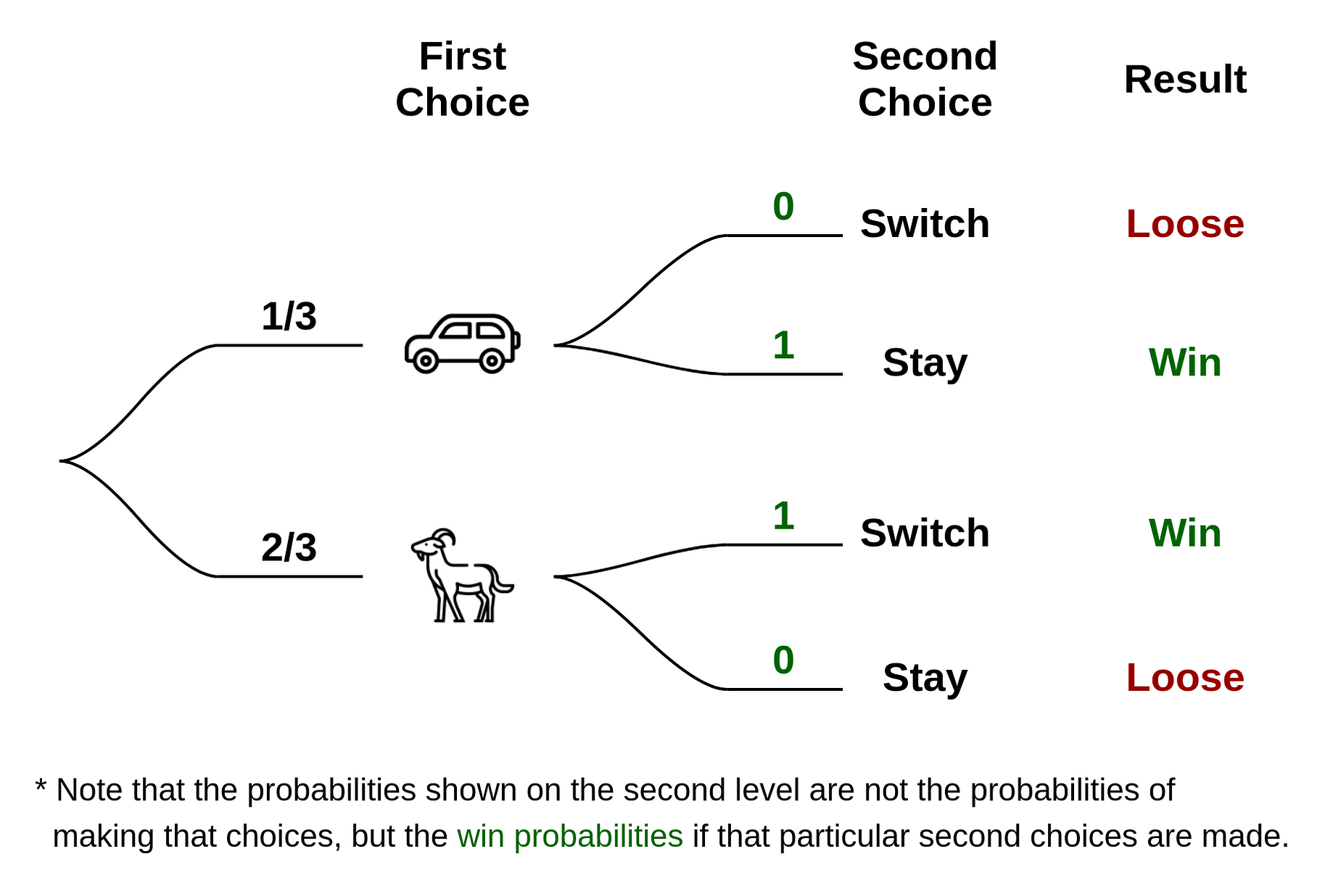
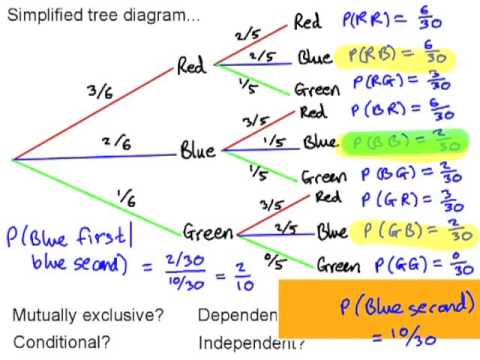
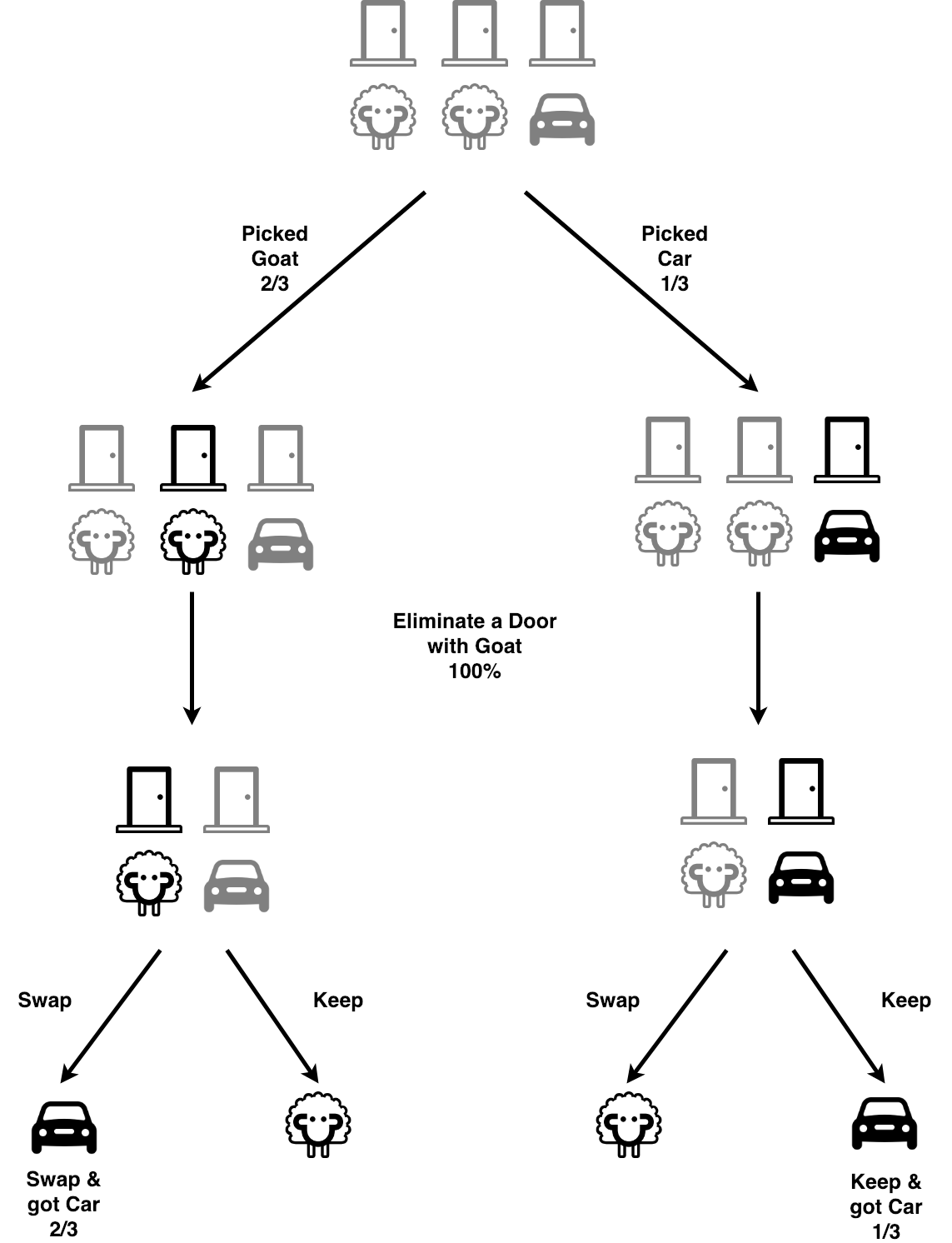
Nov 6, 2018 — As you read the tree diagram, it starts to make sense why you should always switch, and why it is much more complicated than just a coin ... For the addition exercise, the 9 fractions represent the 9 probabilities associated with the 9 different outcomes from the tree diagram. The first three are the probabilities of the three outcomes that are the same colour, P ( R R) = 9 100, P ( B B) = 1 25 = 4 100, P ( G G) = 1 4 = 25 100. T h e y a d d u p t o 19 50, t h e o t h e r s a d d u ... Solution To Monty Hall Problem · 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or ...
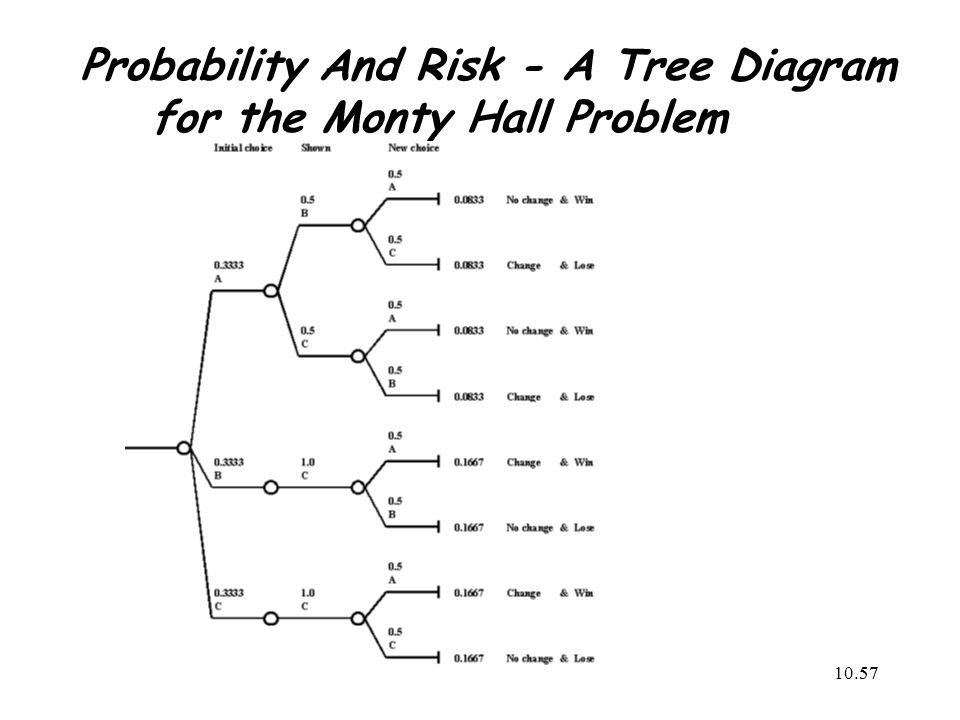
Monty hall tree diagram. Figure 1 — Tree diagram showing the probabilities associated with the Monty Hall Problem (Diagram by the Author) When you are asked to make your first choice, there is an equal probability that the car is behind any one of the three doors. So you have a 1/3 chance of guessing it correctly. This implies that 2/3 of the times your guesses are ... Talk:Monty Hall problem/Archive 14#The MHP in economics and game theory. "The basis to my solution is that Monty Hall knows which box contains the keys and when he can open either of two boxes without exposing the keys, he chooses between them at random." - Steve Selvin. Kruskal's algorithm is a strategy for discovering a minimal spanning tree from a graph, a tree containing all vertices of the graph and V-1 edges with minimal cost. The complexity of this graph is (VlogE) or (ElogV). The disjoint sets provided as output by this computation are used in most link organizations to distribute links between urban ... 1999 dual battery wiring diagram chevrolet 1999 silverado 1500 question… Written By Anonymous Tuesday, August 31, 2021 Add Comment Edit. 03 ford expedition fuse box diagram. 35 03 Ford Expedition Fuse Box Diagram. Here is a picture gallery about 03 expedition fuse box complete with th…
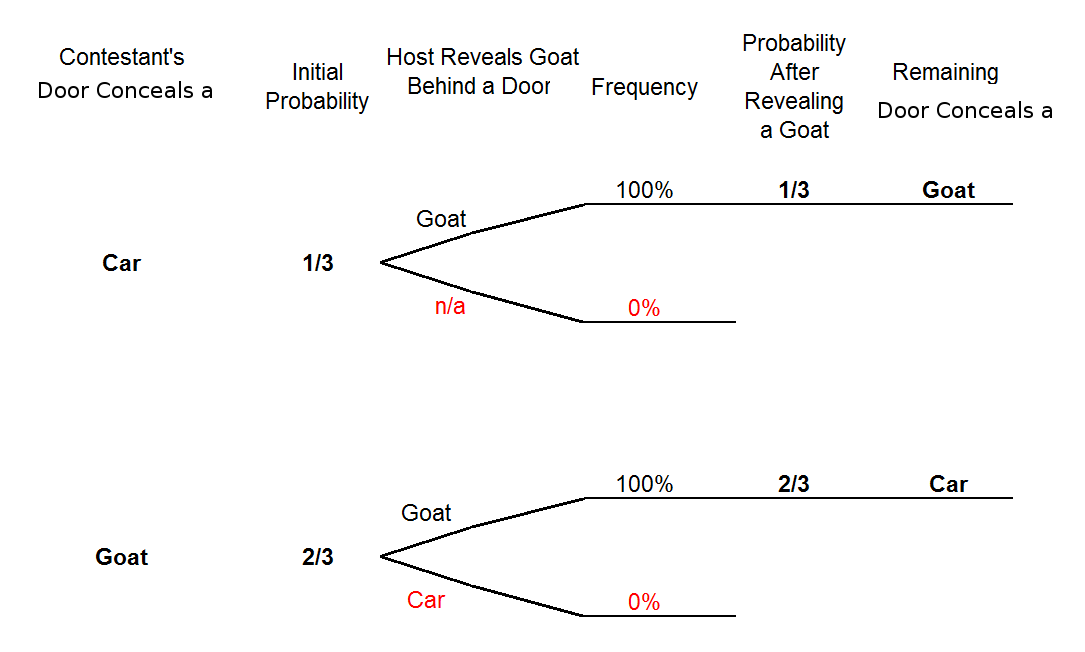
The Monty Hall problem is a famous problem in probability (chance). The problem is based on a television game show from the United States, Let's Make a Deal.It is named for this show's host, Monty Hall. In the problem, there are three doors. A car (prize of high value) is behind one door and goats (booby prizes of low value) are behind the other two doors. In my tree diagram I haven't included the host revealing a door, so could this be a factor as to why my answer is wrong? Share.4 answers · Top answer: It's simply because your diagram assumes you stay with probability 1/2. In that case the probability ... In our tree diagrams, each branch-point always uses a set of possibilities that is both exclusive and exhaustive. The first split on the three doors covers all ... The Monty Hall problem (or "three-door problem" or "goat problem"), which had not yet been formulated at the time of Tversky and Kahneman's first publications but today is one of the most famous examples of a cognitive illusion, ... 2015), tree diagrams (e.g., Sedlmeier and Gigerenzer, 2001; Budgett et al., ...
This is a list of pages in the scope of Wikipedia:WikiProject Mathematics along with pageviews.. To report bugs, please write on the Community tech bot talk page on Meta.. List. Period: 2021-01-01 to 2021-01-31 . Total views: 53,972,868 . Updated: 18:31, 5 February 2021 (UTC) Monty hall problem tree diagram The monty hall problem is a brain teaser in the form of a probability puzzle loosely based on the american television game show lets make a deal and named after its original host monty hallthe problem was originally posed and solved in a letter by steve selvin to the american statistician in 1975. Geometric distribution. Phylogenetic trees and time to the most recent common ancestor. Mitochondrial Eve, Y-chromosome Adam and ancestry of nuclear DNA. Lecture10.pdf. 11. Sep 28. Mitochondrial Eveen (continued) Negative Binomial Distribution. Feb 10, 2019 — The probability tree diagram is consisted of 3 parts, the branch which leads to the possible outcomes, the probability of the event occurring ...
Bits will be missing because, just like living trees, tree diagrams are rarely square. From top left to right, we have Darwin's tree of life 1859, a syntax tree, a family tree template, Phylogenetic tree of Theropods respiratory system, Haeckel's foundations of science tree 1866, and one and a half medieval trees of knowledge.

Https Probabilityandstats Wordpress Com 2017 09 04 Bayes Formula Gives Better Perspective On Medical Testing Https Probabilityandstats Files Wordpress Com 2017 09 Bayes Tree Medical Test Version 5 Jpg Bayes Tree Medical Test Version 5 Https
Lecture 4: Compound events example with tree diagram. Lecture 5: Dependent probability example 2. Lecture 6: Getting exactly two heads (combinatorics) ... Lecture 22: Probability and the Monty Hall problem. Lecture 23: Probability using combinations. Lecture 24: Factorial and counting seat arrangements.
The Monty Hall problem involves a classical game show situation and is named after Monty Hall the long-time host of the TV game show Lets Make a Deal. ... obtaining a sum conditional probability video lessons examples and solutions lesson explainer conditional probability tree diagrams nagwa games for teaching probability 3 conditional ...
Riddles Bend Baptist Church was live. Jan 20 2017 This weeks riddle originally posted by Ted-Ed has number of similarities to the famous Monty Hall problem so you might want to brush up. Feb 01 2021 Sen. Providing Certainty in Uncertain Times. Week 3 Beneath the Wanderers Heel. As Israel is rejecting him more and more and more.

Https Probabilityandstats Wordpress Com 2017 09 04 Bayes Formula Gives Better Perspective On Medical Testing Https Probabilityandstats Files Wordpress Com 2017 09 Bayes Tree Medical Test Version 5 Jpg Bayes Tree Medical Test Version 5 Https
This answer is not useful. Show activity on this post. B) The probability that Terry will not be the champion is. ( 1 − p) + 0.4 p = 1 − 0.6 p. Solving, 1 − 0.6 p = 0.58 p = 0.7. C) The answer is. 1 − p 1 − 0.6 p = 0.3 0.58 = 15 29. The events are not independent, since the event "Terry loses in the semi-final" is a subset of the ...
Mythbusters did that one: When presented with the Monty Hall Problem, people tend to stick with their first choice.. CONFIRMED. After they built a game show mock-up set at a local theater, Adam acted as a game-show host and had 20 volunteers play a game of "Pick a Door".

Monty Hall This Is A Old Problem But It Illustrates The Concept Of Conditional Probability Beautifully References To This Problem Have Been Made In Much Ppt Download
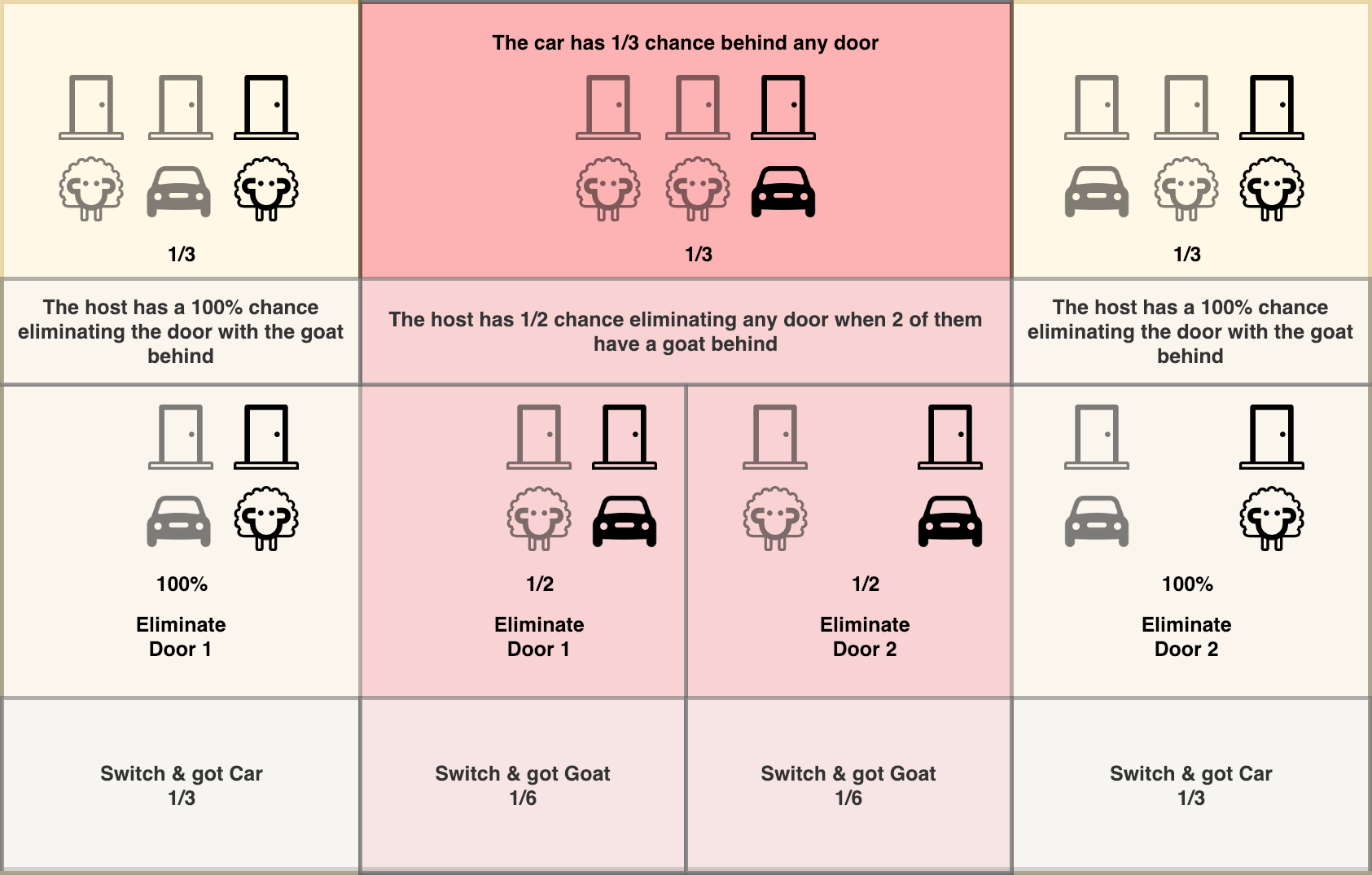
Monty Hall randomly selects one of the three doors and puts a prize behind it. The other two doors hide nothing. A contestant, who does not know where the prize is, selects one of the three doors. This door is not opened yet. Monty chooses one of the three doors and opens it. The door that Monty opens (a) does not hide the prize, and (b) is not ...
Ever since I read about Monty Hall problem in "The Drunkard's Walk: How Randomness Rules Our Lives" book by Leonard Mlodinow from of the California Institute of Technology, I always wanted to try and run a simulation to see that the math is correct. It is one of those problems, where the first answer that comes to mind is usually wrong, and the correct answer to the problem is ...
The Monty Hall problem. Three-pointer vs free-throw probability. Transforming polygons using matrices. Transforming vectors using matrices. Unit vectors intro. Vectors word problem: tug of war. Visual representation of transformation from matrix. Worked example: Scaling unit vectors. Worked example: finding unit vector with given direction
The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ...
Here's my visual representation of the classic Monty Hall game. It extends the traditional probability tree by framing the contestant's winning decision as the third trial of the probability experiment. Here—without loss of generality ♪ —the contestant has chosen Door $1.$ From the diagram: the sample space is $\{12c,121,13c,131,23c,231 ...
Part 4 - The tree Diagram - Link it all together, use the sample space diagram to help you build a tree diagram and see the links between the previous activities. For computers. Part 5 - Practice! - Put what you have learned in to practice with these fill in the gap probability tree diagrams. (you are given a little bit less information each time.
Search: Custom Cursor Top Pack. If you are searching for Custom Cursor Top Pack, simply look out our text below :

Mathematical Circle Master Angela Dr Pinheiro And The Monty Hall Puzzle Part 2 Discussing Dr Pinheiro S Solution
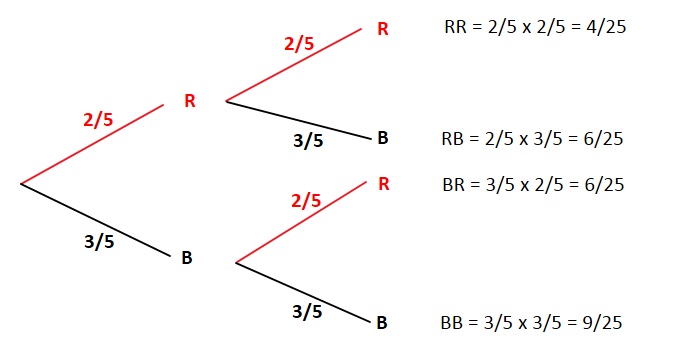
Answer: Starting at the left side of the page, draw two branches diverging towards the right. Label one B and the other one G. This represents the possible genders for the first child. On each branch draw another similar system. That's for the second child. Again for the third, and again for the ...
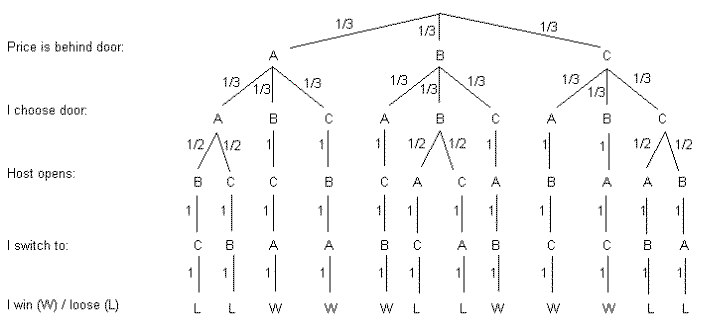
According to the tree diagram, the probability of winning the prize if the choice is switched from the first door to one of the two remaining doors is: The general case of the 'Monty Hall' problem The tree diagram allows us to classify the available data into groups and to predict dependent variables based on known independent variables.
A tree diagram of the monty hall problem under the marilyn vos savant assumptions. Door a door b and door c. Probability tree diagram of monty hall problem as we can see from the diagram the only place where there is a random event involved is during the initial pick the elimination process is actually.
Solution To Monty Hall Problem · 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or ...
For the addition exercise, the 9 fractions represent the 9 probabilities associated with the 9 different outcomes from the tree diagram. The first three are the probabilities of the three outcomes that are the same colour, P ( R R) = 9 100, P ( B B) = 1 25 = 4 100, P ( G G) = 1 4 = 25 100. T h e y a d d u p t o 19 50, t h e o t h e r s a d d u ...
Nov 6, 2018 — As you read the tree diagram, it starts to make sense why you should always switch, and why it is much more complicated than just a coin ...
Games Puzzles And The Real World 2a Monty Hall S Doors Bertrand S Boxes And The Three Prisoners Goss Blog

Probability Activities Tree Diagrams Sequences Summation Notation Dice Rolling Rock Paper Scissors And The Monty Hall Problem Ppt Download




















0 Response to "39 monty hall tree diagram"
Post a Comment