40 co molecular orbital diagram
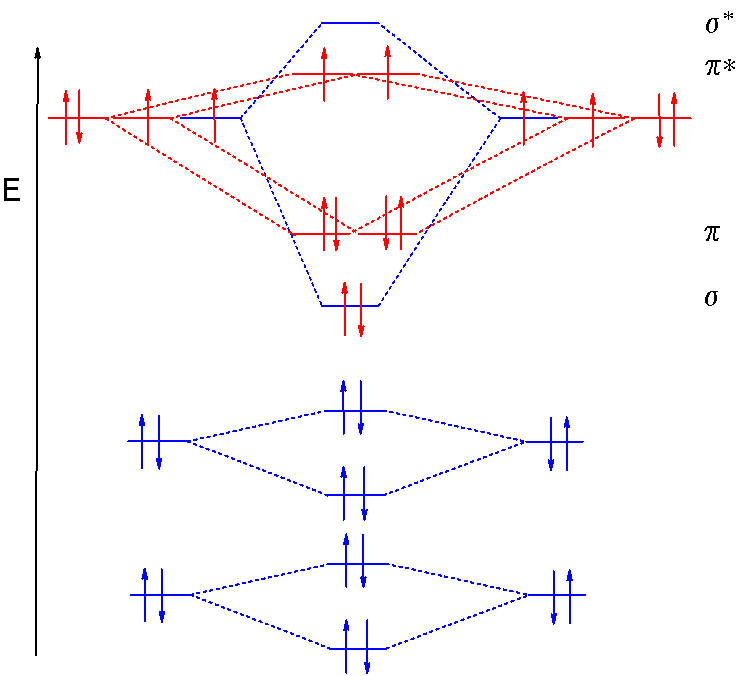
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. A molecular orbital diagram of ethene is created by combining the twelve atomic orbitals associated with four hydrogen atoms and two sp 2 hybridized carbons to give twelve molecular orbitals. Six of these molecular orbitals (five sigma & one pi-orbital) are bonding, and are occupied by the twelve available valence shell electrons. The remaining six molecular orbitals are antibonding, and are ...
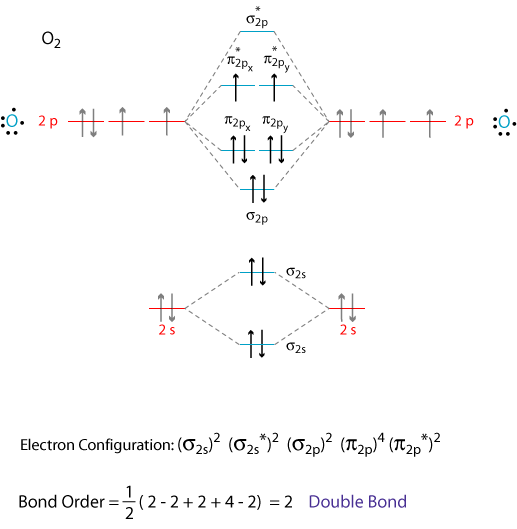
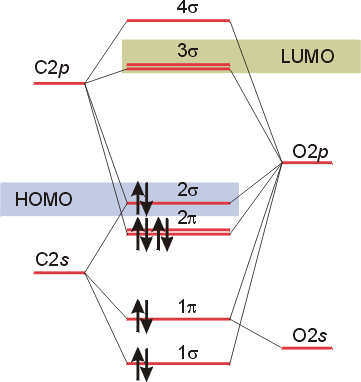
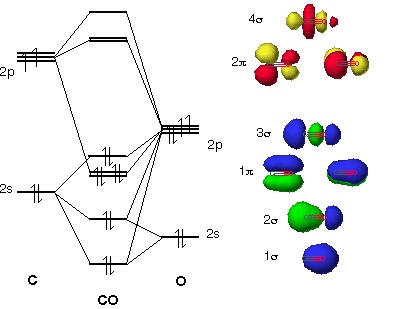
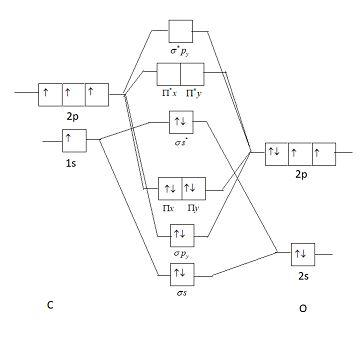
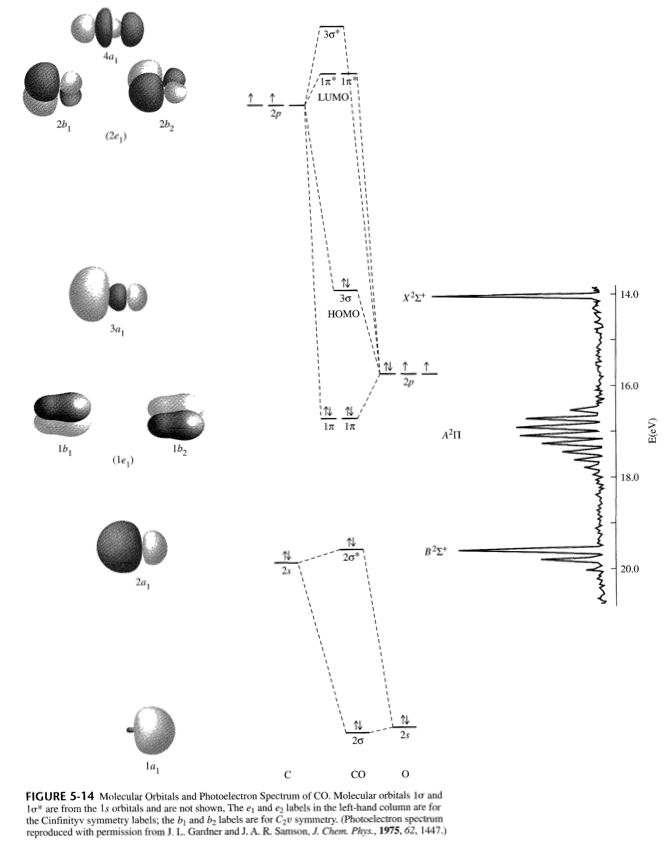
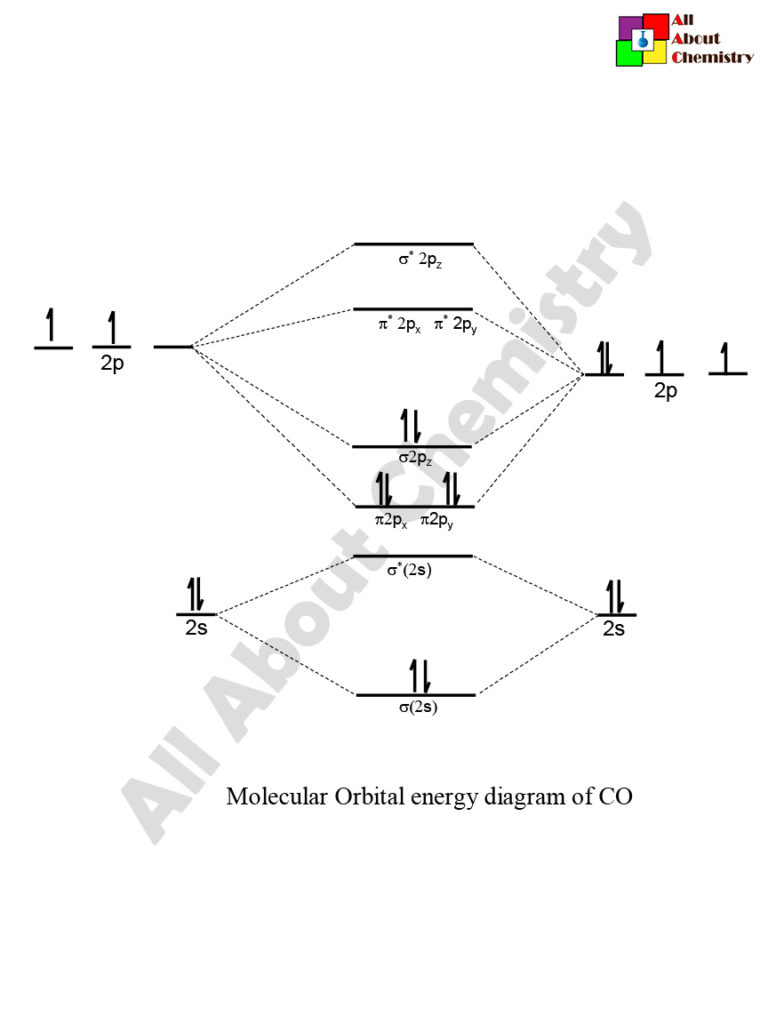
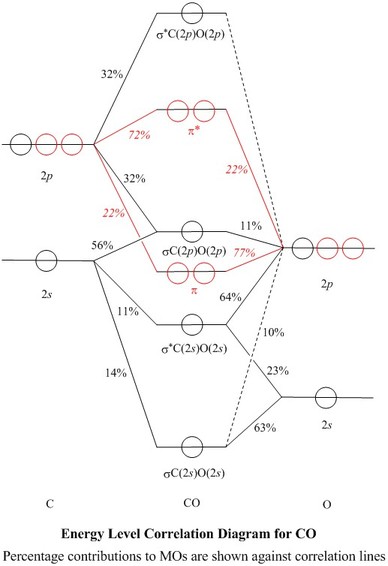
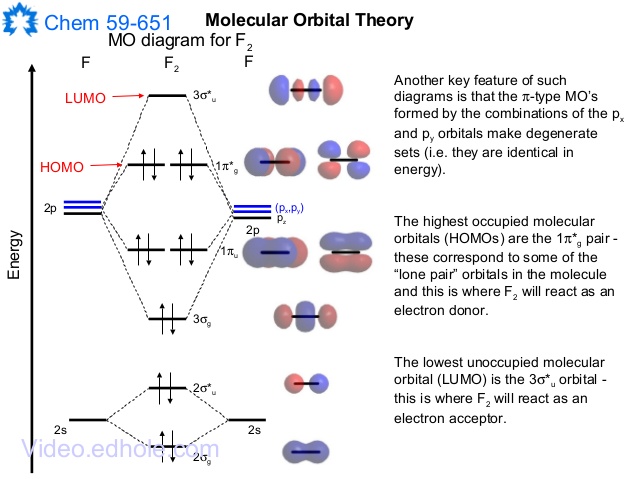
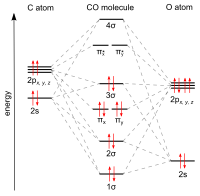
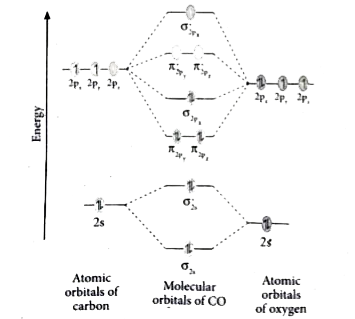
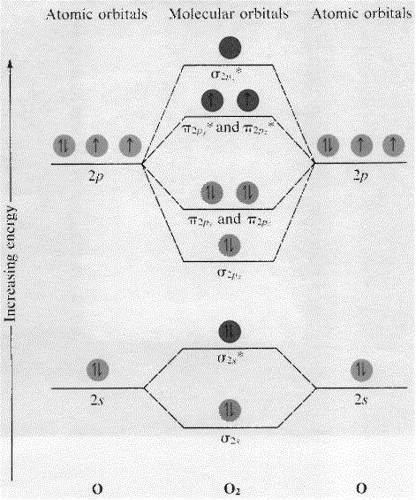
In the case of CO, the 2s atomic orbital on Oxygen is much lower in energy than the 2s atomic orbital in carbon. The discrepancy in energies allows the π2px & π2py bonding molecular orbitals to sink lower in energy than the “ σ*2s MO” in the MO diagram of CO.
Co molecular orbital diagram
The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ... Molecular orbital diagram of co. Tricky chemistry basics. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic ... In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Co molecular orbital diagram. Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. 23:32In this video we are discuss about MO Diagram and Characteristics of CO Molecule MO diagrams of ...19 Oct 2019 · Uploaded by Chem Academy The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- 2p ... In carbon monoxide (CO, isoelectronic with dinitrogen) the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital and therefore the degree of ...
19 Mar 2021 — Carbon monoxide MO diagram ... Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The ... The following diagram uses metallic radii for metallic elements, covalent radii for elements that form covalent bonds, and van der Waals radii for those (like the noble gases) which don't form bonds. Trends in atomic radius in Periods 2 and 3. Trends in atomic radius down a group. It is fairly obvious that the atoms get bigger as you go down groups. The reason is equally obvious - you are ... Point out key differences between the diagrams and use the diagram to explain why $\ce{CO}$ acts as a two-electron donor through carbon rather than through oxygen. Understandably, the key difference between these molecules is that $\ce{CO}$ is heteronuclear, and thus will have differences in energy between the molecular orbital and the atoms. Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics 31.08.2021 · Discover what a phase diagram is and how it graphs a substance's states of matter using temperature and pressure. Learn how to define and locate phase equilibrium lines, triple points, critical ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural ...

By Writing Molecular Orbital Configuration For No Co O2 Molecules Calculate The Bond Order And Also Determine Whether It Is Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic Socratic
Molecular orbital diagram of CO and charge localisation. Ask Question Asked 1 year, 5 months ago. Active 1 year, 5 months ago. Viewed 110 times ... My question concerns the interpretation of the Molecular Orbital of CO. I think I find it clear how you build it but I have some concerns about how you rationalize it.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find it to be informative, pls share it and visit our website.

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Indicate The Point Group Symmetry And Draw With Bonding And Homeworklib
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence ...
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Molecular orbital diagram of co. Tricky chemistry basics. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic ...
The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ...

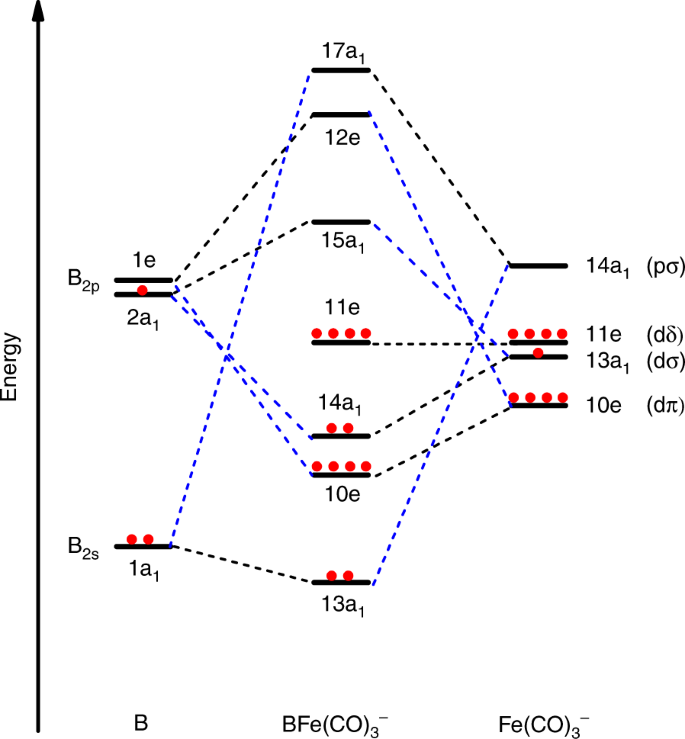
How To Rationalise With Mo Theory That Co Is A Two Electron Donor Through Carbon Chemistry Stack Exchange














0 Response to "40 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment