36 match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram fe2+
[Cr(ox) 3] 3- has Cr in the +3 oxidation state, which is d 3, and approximately an octahedral crystal field so LFSE = -12Dq. b) hexacyanoferrate(II) ion [Fe(CN) 6] 4- has Fe in the +2 oxidation state, which is d 6, and a strong octahedral crystal field so LFSE = -24Dq + 2P. c) tetrachloro-η 2 -etheneplatinate(II) ion Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. As a result the splitting observed in a tetrahedral crystal field is the opposite of the splitting in an octahedral complex. The octahedral ion feno 2 6 3 which has 5 d electrons would have the octahedral splitting diagram shown at right with all five electrons in the t 2g level.
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. Metal ion and spin state Octahedral Splitting Diagram High Spin Fe^3+ Low Spin Co^2+ Answer + 20
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram fe2+
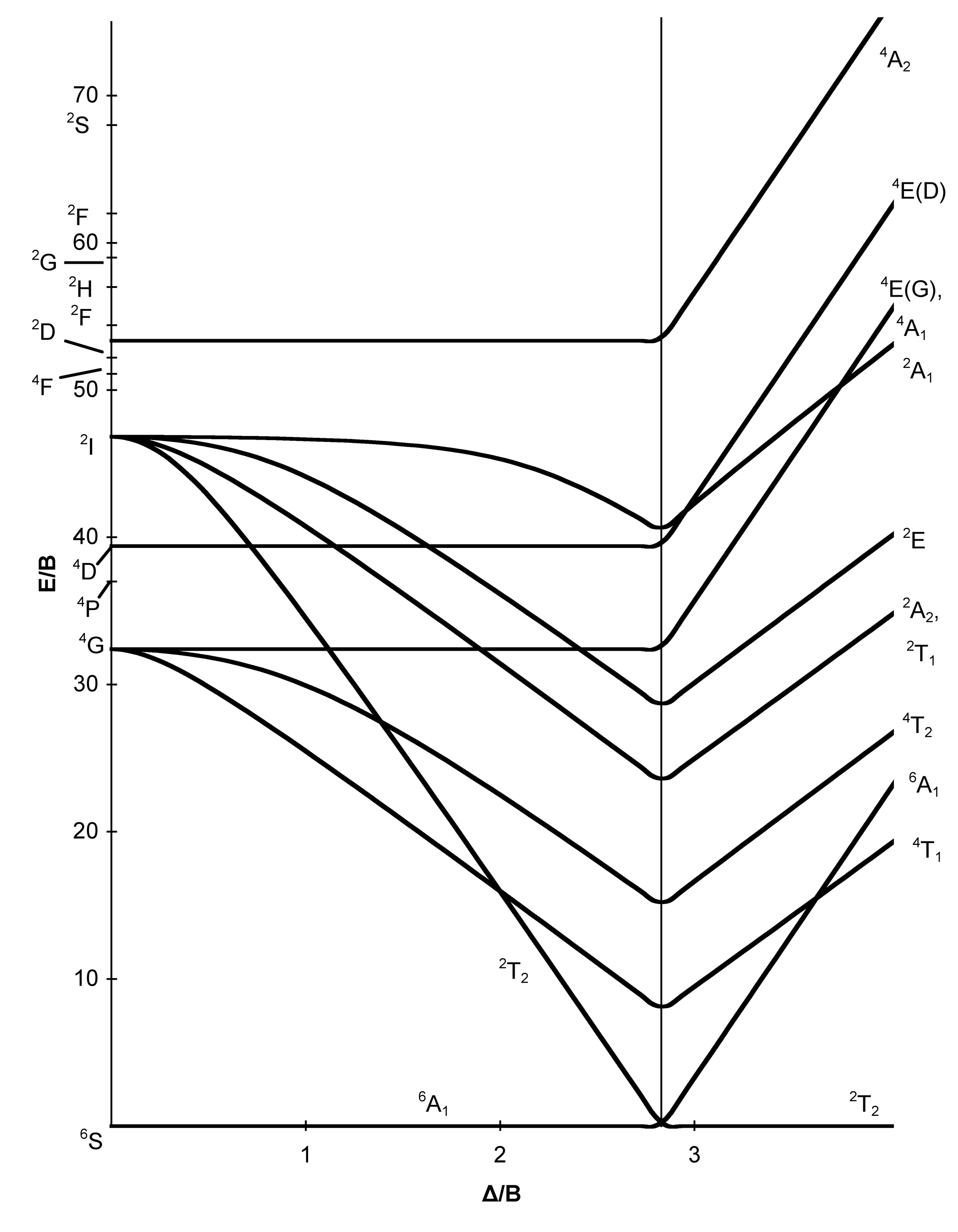
If the splitting of the d-orbitals in an octahedral field is Δ oct, the three t 2g orbitals are stabilized relative to the barycenter by 2 / 5 Δ oct, and the e g orbitals are destabilized by 3 / 5 Δ oct.As examples, consider the two d 5 configurations shown further up the page. The low-spin (top) example has five electrons in the t 2g orbitals, so the total CFSE is 5 x 2 / 5 Δ oct = 2Δ oct. CRYSTAL-FIELD SPLITTING DIAGRAMS All four of these transition metals commonly have coordination numbers of \mathbf(6), however, so let's examine their octahedral complex crystal-field splitting diagrams. HIGH SPIN VS. LOW SPIN High spin = fill all five d orbitals with one electron first, and then double up. Low spin = fill lowest-energy d ... In the model of the crystal field with parameters 10Dq=9500 cm −1 , trigonal splitting C=500 cm −1 , the electronic transition to A g -5 E g at a wavelength of 1.66 μm in the tetrahedron in ...
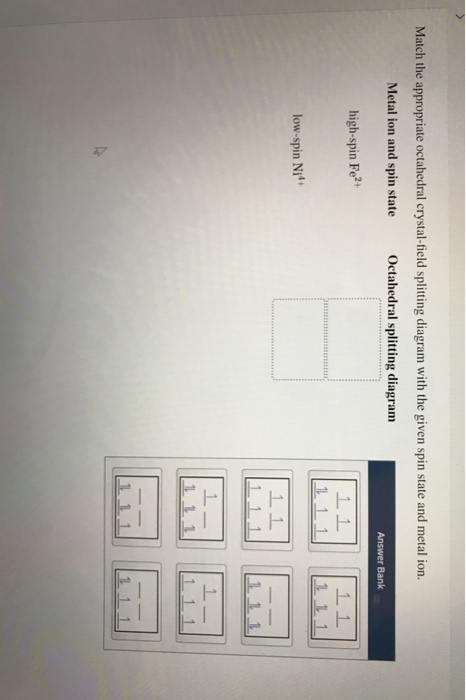
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram fe2+. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram fe2. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. As a result the splitting observed in a tetrahedral crystal field is the opposite of the splitting in an octahedral complex. It then asks how many unpaired electrons and asks to draw a crystal field splitting diagram for this compound. Metal ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank high-spin Fe2+ 2 low-spin Ni'+ 1 111 1 1 1. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. Metal ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank high-spin Ni3+ low-spin Fe4+. Question: Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin state ... Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. Question match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. Fe in the compound is feiii so 23 electrons d5. A d1 octahedral complex is found to absorb visible ... Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with for the ... and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank High-spin Fe2+ 1 1 ... Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the ... and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank high-spin Fe2+ 1 11 11 ... Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram fe2. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. This means that most square planar complexes are low spin strong. Fe in the compound is feiii so 23 electrons d5. Since br is a weak field ligand there isnt too much of a difference in the two ...
(E) Low spin complexes are favoured by strong field ligands. Please explain Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the ... ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank high-spin Fe2+ 1 1 ... Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. The dx2 y2 and dz2 orbitals on the metal ion at the center of the cube lie between the ligands and the dxy dxz and dyz orbitals point toward the ligands. Solved match the appropriate octahedral crystal field spl match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion crystal field ... Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Since the oxalate ligand is fairly low in the series a weak field ligand at this point you may not have studied ligand field theory yet which explains why it is a weak ligand. Cr4 mnh2o62 asked by katie on march 30 2012 chemistry based on crystal field ...
octahedral complexes, it is also typically high spin and also has 3 unpaired electrons; in square planar complexes, it has 1 unpaired electron. The magnetic moments can be calculated as n(n 2) 3.9, 3.9, and 1.7 B, respectivel y. 10.9 For the red compounds (Me and Et at high temperatures, Pr, pip, and pyr at all temperatures), the
The difference between the energies of the t 2g and e g orbitals in an octahedral complex is represented by the symbol o.This splitting of the energy of the d orbitals is not trivial; o for the Ti(H 2 O) 6 3+ ion, for example, is 242 kJ/mol. . The magnitude of the splitting of the t 2g and e g orbitals changes from one octahedral complex to another. It depends on the identity of the metal ion ...
The d-orbital splitting diagram is the inverse of that for an octahedral complex. 6. 7. Page 7 of 33 Crystal Field Splitting Parameters In an octahedral or a tetrahedral crystal field, the d-orbitals are split into two sets. The energy separation between them is called the crystal field splitting parameter.
question match the appropriate octahedral crystal field question match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion high spin cr 2 low spin fe 3 please give the octahedral splitting diagrams for each ion. crystal field stabilization energy Calculation of the LFSE of tetrachloridocobaltate II.
Answer to: Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin stale and metal ion with given spin state. [{Image...
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. High-spin Mn^3+ Low-spin Fe^3+. Sign up to view answer. Our mission is to help you succeed in your Chemistry class. Sign up for free to see the solution.
This photo about: Match the Appropriate Octahedral Crystal-field Splitting Diagram, entitled as Ligand Field Theory Advanced Inorganic Chemistry Lecture Slides Match The Appropriate Octahedral Crystal Field Splitting Diagram - also describes Ligand Field Theory Advanced Inorganic Chemistry Lecture Slides and labeled as: match the following phrases about colour,match the phrases,match the ...
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram fe2. A none of the 3d orbitals point directly at ligands b t2 orbitals are more stable than e orbitals c a small crystal field splitting. Tetrahedral crystal field splitting barycenter spherical field t 2 orbitals point more directly at ligands and are destabilized. Ni2 in the presence of strong field ligands such as cn forms a ...
Metal ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram high-spin Fe2+ 1 1 Answer Bank 1 1 low-spin Ni4+ 1 1 incorrect. This problem has been solved! See the ...
an crystal field splitting diagrams to show orbital occupancies in both weak and strong octahedral fields, and (ii) indicate the number of unpaired electrons in each case. Label . the diagrams (iii) weak or strong field, (iv) high spin or low spin (as appropriate), (v) with the names of the d-orbitals, and (vi) with the appropriate orbital sets ...
Metal ion and spin state Octahedral Splitting Diagram 1L 11 1 High Spin Fe2+ Low Spin Ni3 1L 11 1L 111. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Crystal Field Splitting Spin Pairing Δ P vs. ... Octahedral Crystal Field d6 High Spin (i.e. Co3+) t 2g e g d6 Low Spin (i.e. Co3+) t 2g e g. Color of Transition Metal Complexes The color of these compounds comes from the absorption of light that causes an excitation of an electron from one
Electrons in Orbitals. According to the Aufbau principle, electrons are filled from lower to higher energy orbitals (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).For the octahedral case above, this corresponds to the d xy, d xz, and d yz orbitals. Following Hund's rule, electrons are filled in order to have the highest number of unpaired electrons.For example, if one had a d 3 complex, there would be three ...
Met ion and spin state Octahedral Splitting Diagram HighSpinNi3+ Low spin Fe2+. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Question match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram with the given spin state and metal ion. A left handed propeller will pull the stern to starboard right when in reverse. Given this is an octahedral complex your splitting diagram will have 2 degenerate states. Crystal field splitting in an octahedral field eg energy 35 o ...
So the octahedron from crystal field splitting takes place like this two off. The orbital's going higher and adjusted, and in the ground state, and three of them come to a lower energy state and then the ground state. We call them Tito cheer pickles. And this as each your vittles. So for chromium three plus, we have for chromium. We know the chromium silica reconfiguration is like this are ...
Tetrahedral crystal field splitting barycenter spherical field t 2 orbitals point more directly at ligands and are destabilized. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram fe2. When to expect square planar geometry. Consider ions to be from first row transition metals. Consider ions to be from first row transition metals.
Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)63+ Co (CN)63 - Mn (H2O)62+. A d1 octahedral complex is found to absorb visible light, with the absorption maximum occcurring at nm. a) Calculate the crystal-field splitting energy, Δ, in.
Show transcribed copy text Match the misspend octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the consecrated incline narrate and metal ion. Metal ion and incline narrate Xdahedral Splitting Diagram High Incline Co3* Low Incline Fe* 1L 1 1 Match the misspend octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with the consecrated incline narrate and metal ion. Metal ion and incline […]
This is analogous to deciding whether an octahedral complex adopts a high- or low-spin configuration; where the crystal field splitting parameter \(Δ_o\) \(ΔE\) does above. Unfortunately, unlike \(Δ_o\) in octahedral complexes, there is no simple graphical way to represent \(ΔE\) on the diagram above since multiple orbitals are changed in ...
Chemistry questions and answers. Match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram with for the metal ion with the given spin state. Metal ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank High-spin Fe2+ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Low-spin Fe2+ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1. Question: Match the appropriate octahedral ...
Metal ion and spin state Octahedral splitting diagram Answer Bank high-spin Fe2+ 1 1 1 1 1 low-spin Cr2+ 11 11 11 1 1 1 1. This problem has been solved! See the ...
Match The Appropriate Octahedral Crystal Field Splitting Diagram. Conversely the dconversely the dx2 y22 and the dxy orbitals increase in energy the splitting orbitals increase in energy. Match …. Written By Maria M Beus Friday, July 28, 2017 Add Comment. Edit.
Match the appropriate octahedral crystal field splitting diagram. A none of the 3d orbitals point directly at ligands b t2 orbitals are more stable than e orbitals c a small crystal field splitting energy results in a paramagnetic complex d the low spin case gives maximum unpaired electrons e for a given ligand.
In the model of the crystal field with parameters 10Dq=9500 cm −1 , trigonal splitting C=500 cm −1 , the electronic transition to A g -5 E g at a wavelength of 1.66 μm in the tetrahedron in ...
CRYSTAL-FIELD SPLITTING DIAGRAMS All four of these transition metals commonly have coordination numbers of \mathbf(6), however, so let's examine their octahedral complex crystal-field splitting diagrams. HIGH SPIN VS. LOW SPIN High spin = fill all five d orbitals with one electron first, and then double up. Low spin = fill lowest-energy d ...
If the splitting of the d-orbitals in an octahedral field is Δ oct, the three t 2g orbitals are stabilized relative to the barycenter by 2 / 5 Δ oct, and the e g orbitals are destabilized by 3 / 5 Δ oct.As examples, consider the two d 5 configurations shown further up the page. The low-spin (top) example has five electrons in the t 2g orbitals, so the total CFSE is 5 x 2 / 5 Δ oct = 2Δ oct.




















0 Response to "36 match the appropriate octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram fe2+"
Post a Comment