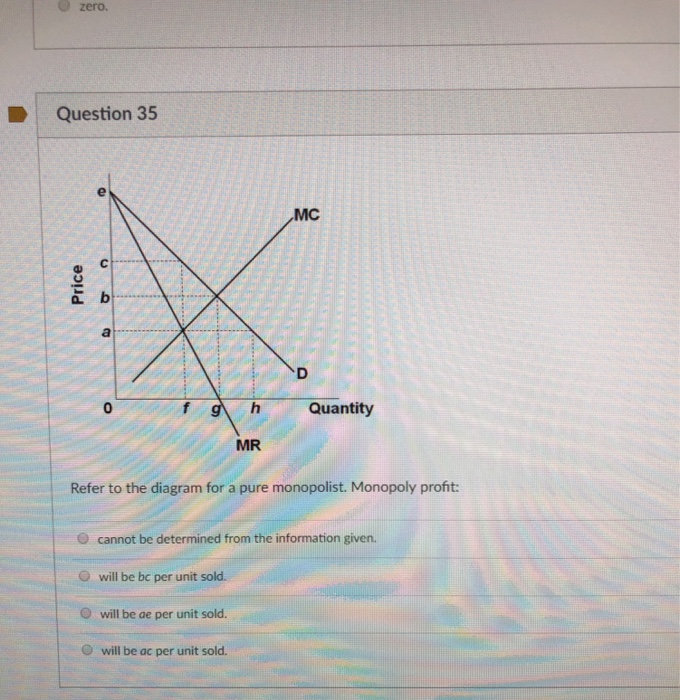
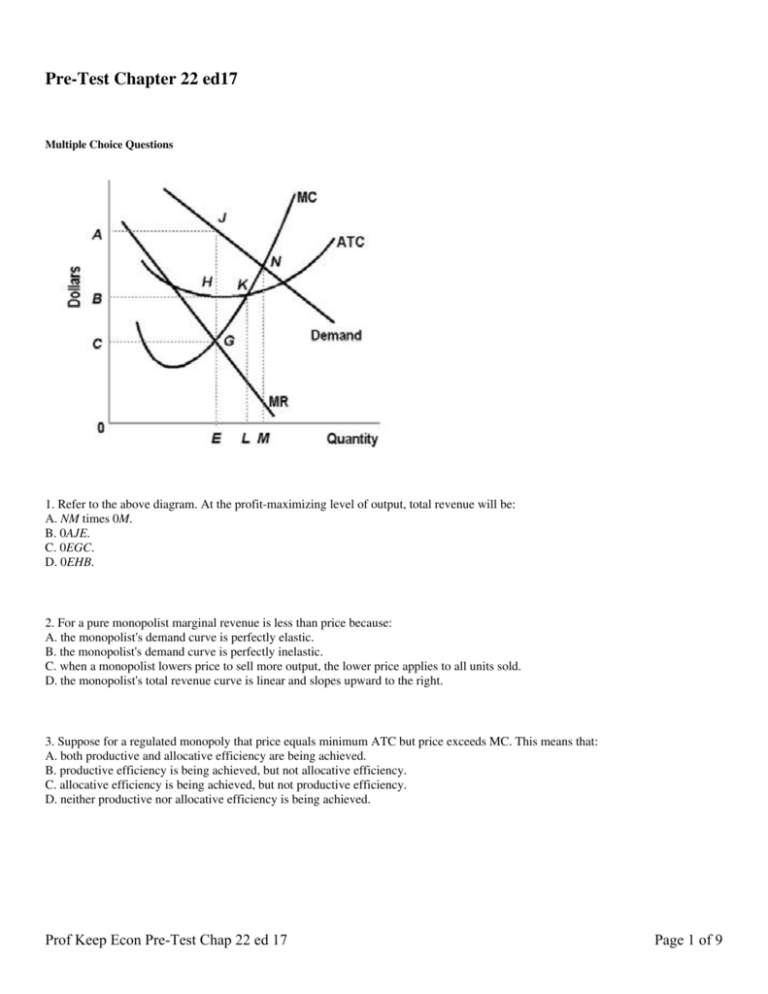
36 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
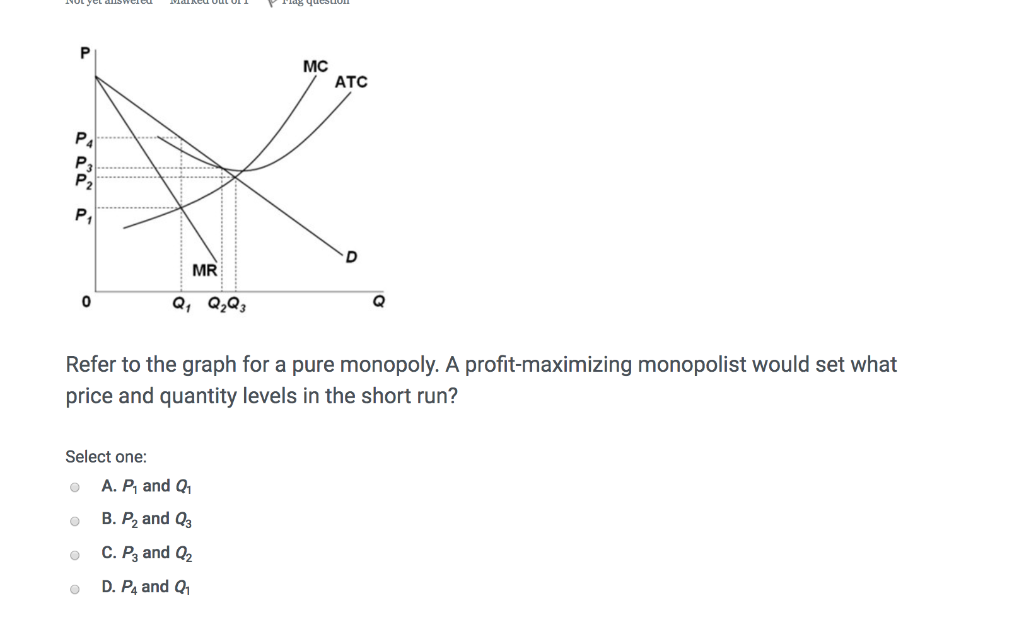
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P 3 and selling a quantity less than Q 3. B. price P 3 and producing output Q 3. C. price P 2 and producing output Q 2. D. price P 1 and producing output Q 1.
`Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at. P1 `refer to the diagram. at the profit maximizing level of output.
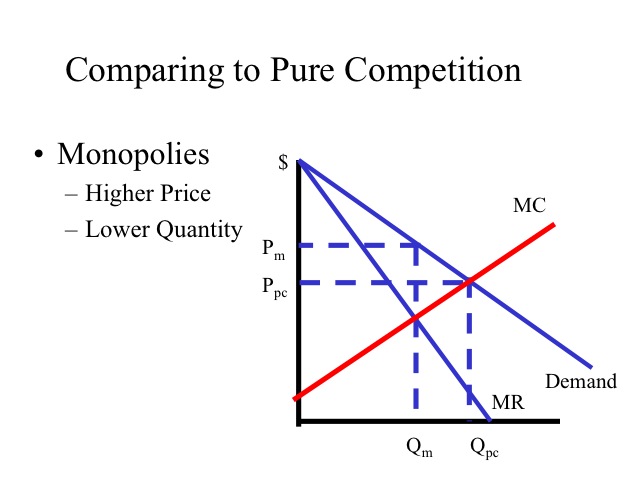
Monopoly Graph. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC. This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q. Blue area = Deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus ...
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
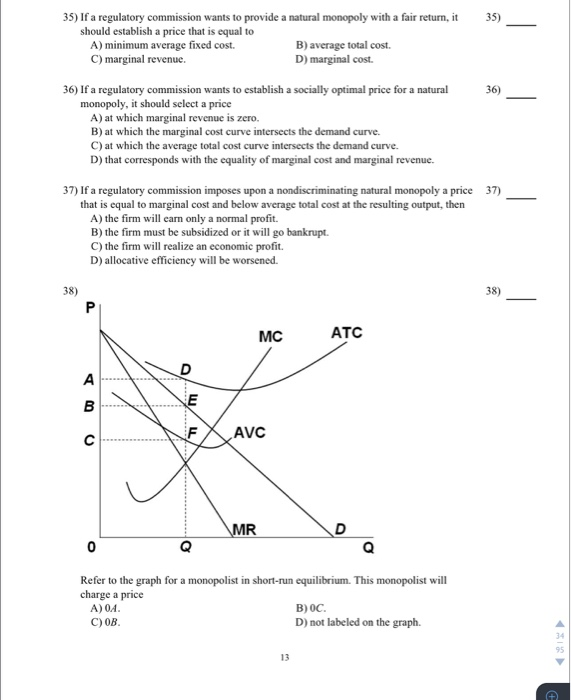
Refer to the graph for a monopolist in short-run equilibrium. This monopolist has total cost equal to area. ... One major barrier to entry under pure monopoly arises from. ... Refer to the diagrams. The price will be _____ and the quantity will be _____ with the industry structure represented by diagram (B) compared to the one represented in (A
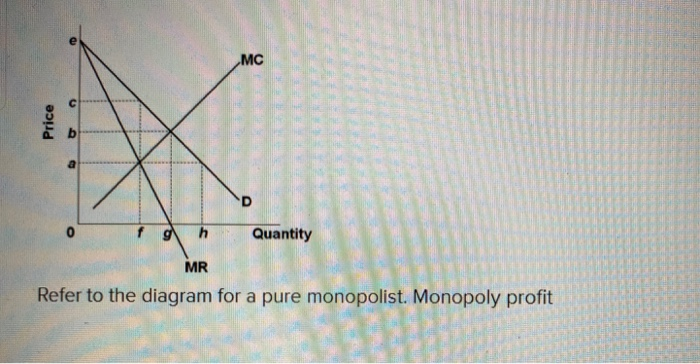
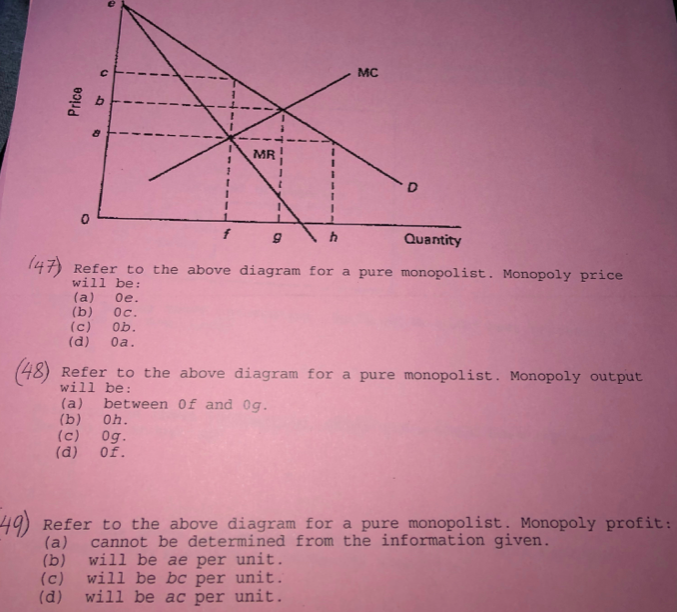
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: Answer cannot be determined from the information given. will be ae per unit sold. will be bc per unit sold. will be ac per unit sold. 2.667 points Question 2 A profit-maximizing monopolist will set its price: Answer as far above ATC as possible. along the elastic portion of.
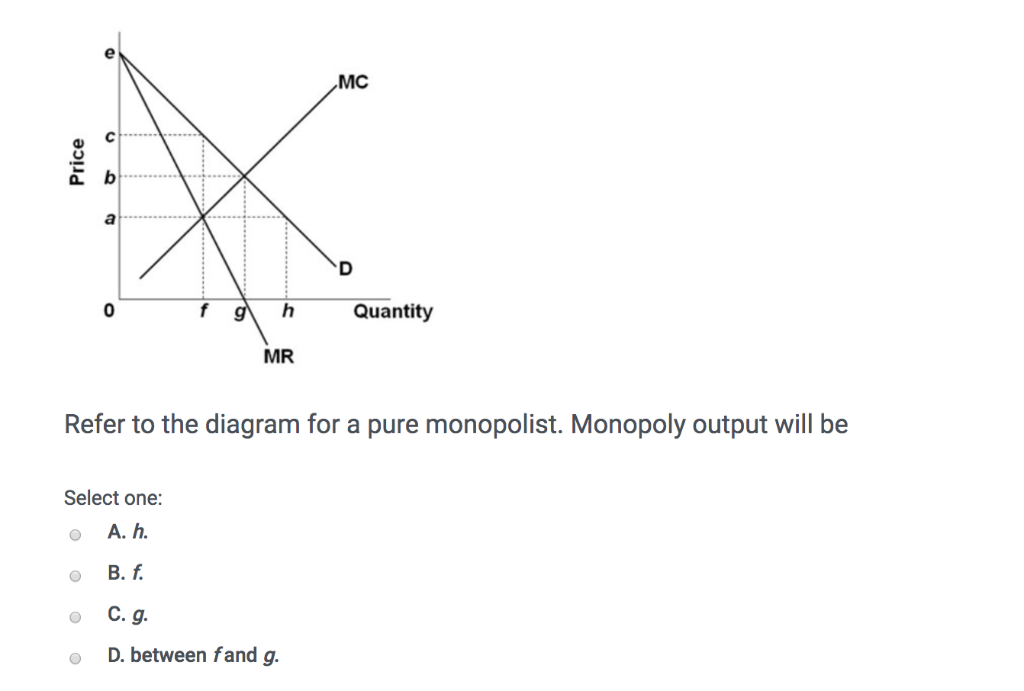
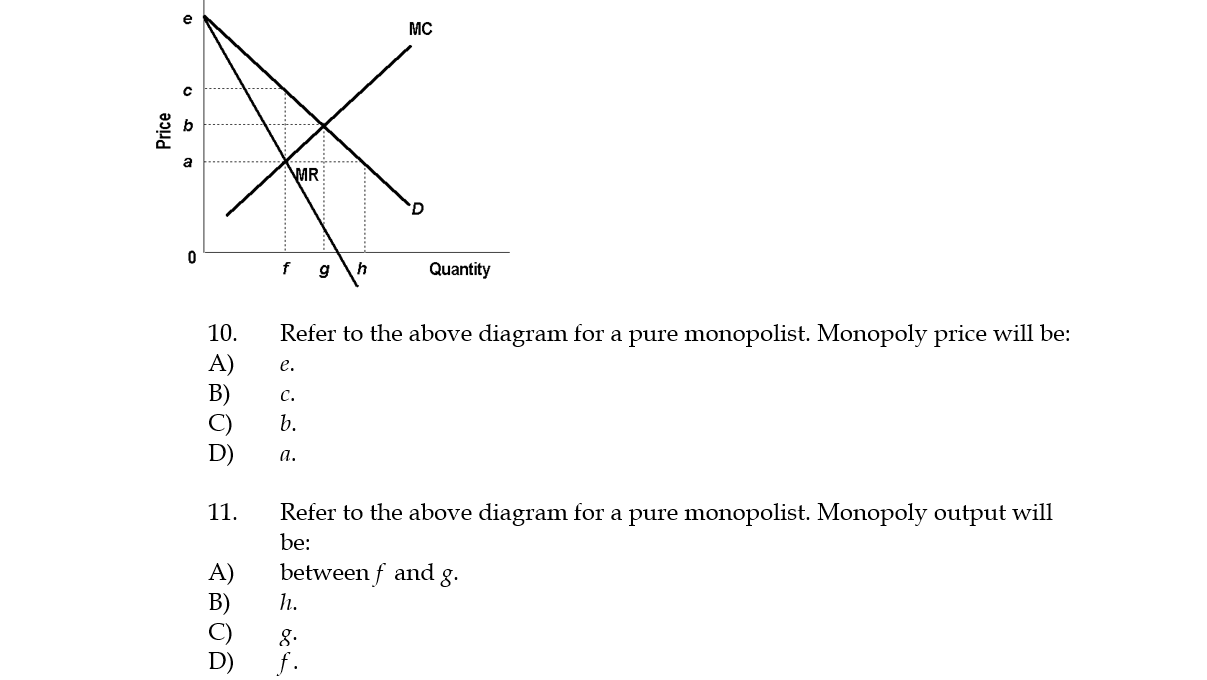
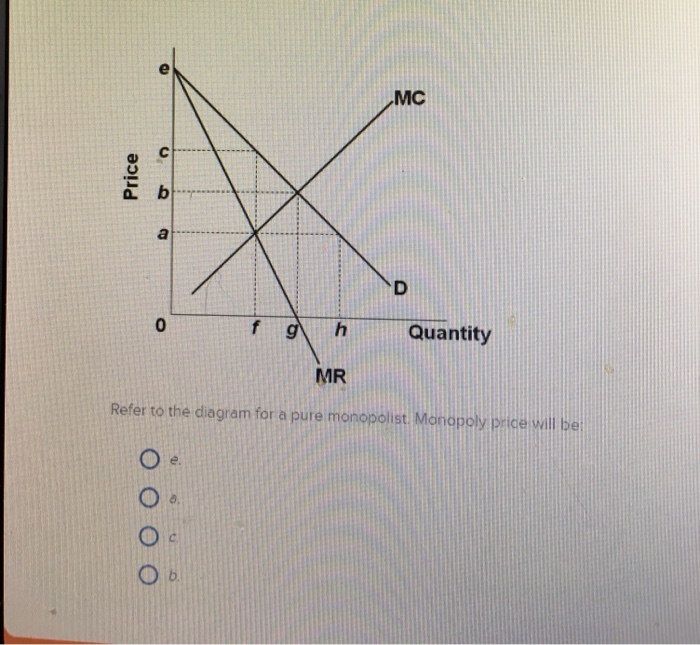
Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be.
Assume a pure monopolist is charging price P and selling output Q, as shown on the diagram. On the basis of this information, we can say that if marginal costs were somehow zero, the firm would be maximizing its profits.
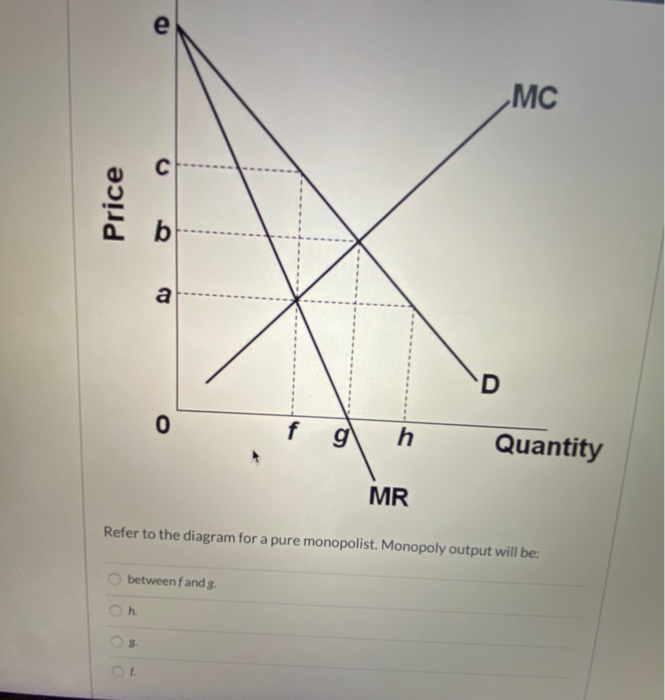
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. A single-price monopoly is economically inefficient because, at the profit-maximizing output, society values additional units of the monopolized product more highly than it does the alternative products those resources could otherwise produce.
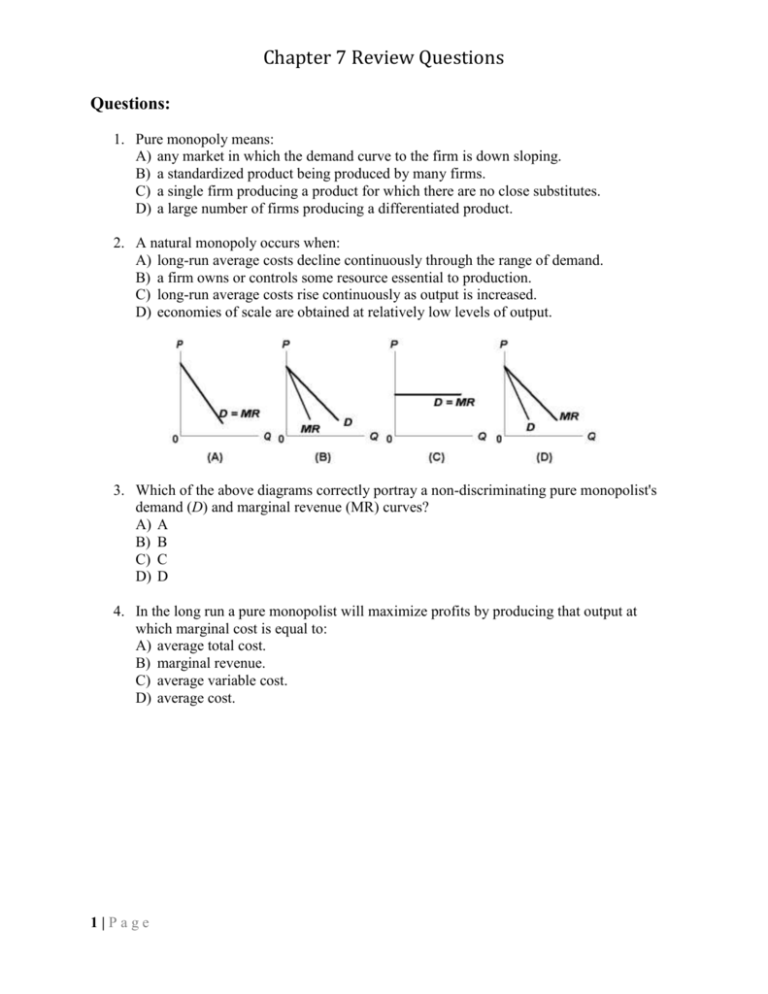
For a pure nondiscriminating monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because; When a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. Refer to the diagram for a non discriminating monopolist.
This problem has been solved! Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P 3 and selling a quantity less than Q 3. B. price P 3 and producing output Q 3. C. price P 2 and producing output Q 2. D. price P 1 and producing output Q 1.















0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be"
Post a Comment