36 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
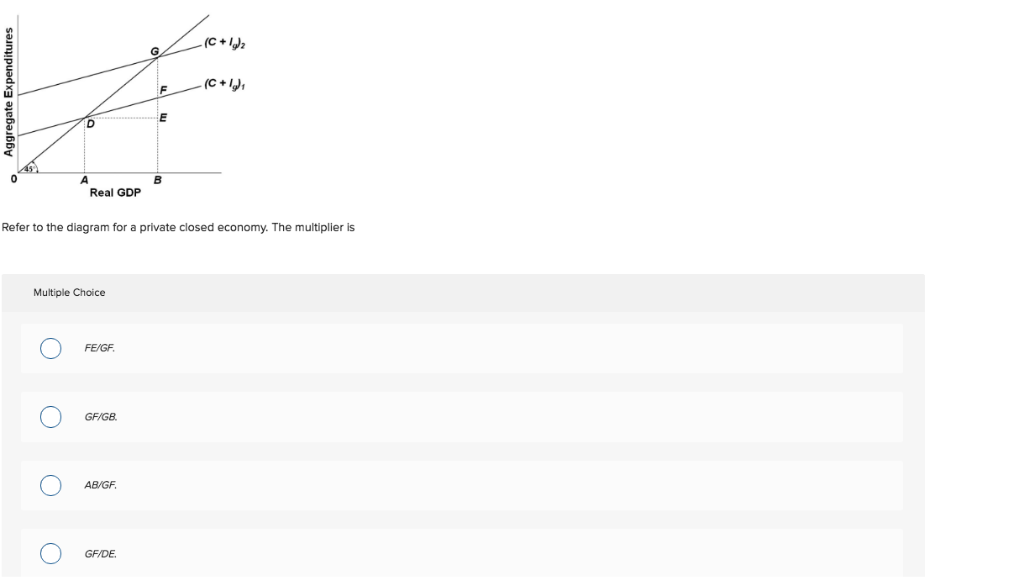
CB/AB. Refer to the given diagram. Consumption will be equal to income at. CD. Refer to the given diagram. Consumption will be equal to income at. An income of E. The relationship between the real interest rate and investment is shown by the. The marginal propensity to consume in economy (1) is.7. 23. Refer to the above diagram. If the multiplier in an economy is 5, a $20 billion increase in net exports will: increase GDP by $100 billion. Refer to the diagram for private closed economy. The marginal propensity to consume is . FE/DE. An increase in expected future income will. increase aggregate demand. Which of the following would shift the investment demand curve from ID1 to ID2? higher expected rates of return on ...
B) the simple multiplier is smaller in a closed economy with no government. C) the marginal propensity to import (m) is larger than the tax rate (t). D) the simple multiplier is larger in a closed economy with no government. E) there is no effect on the simple multiplier from imports or tax rates.
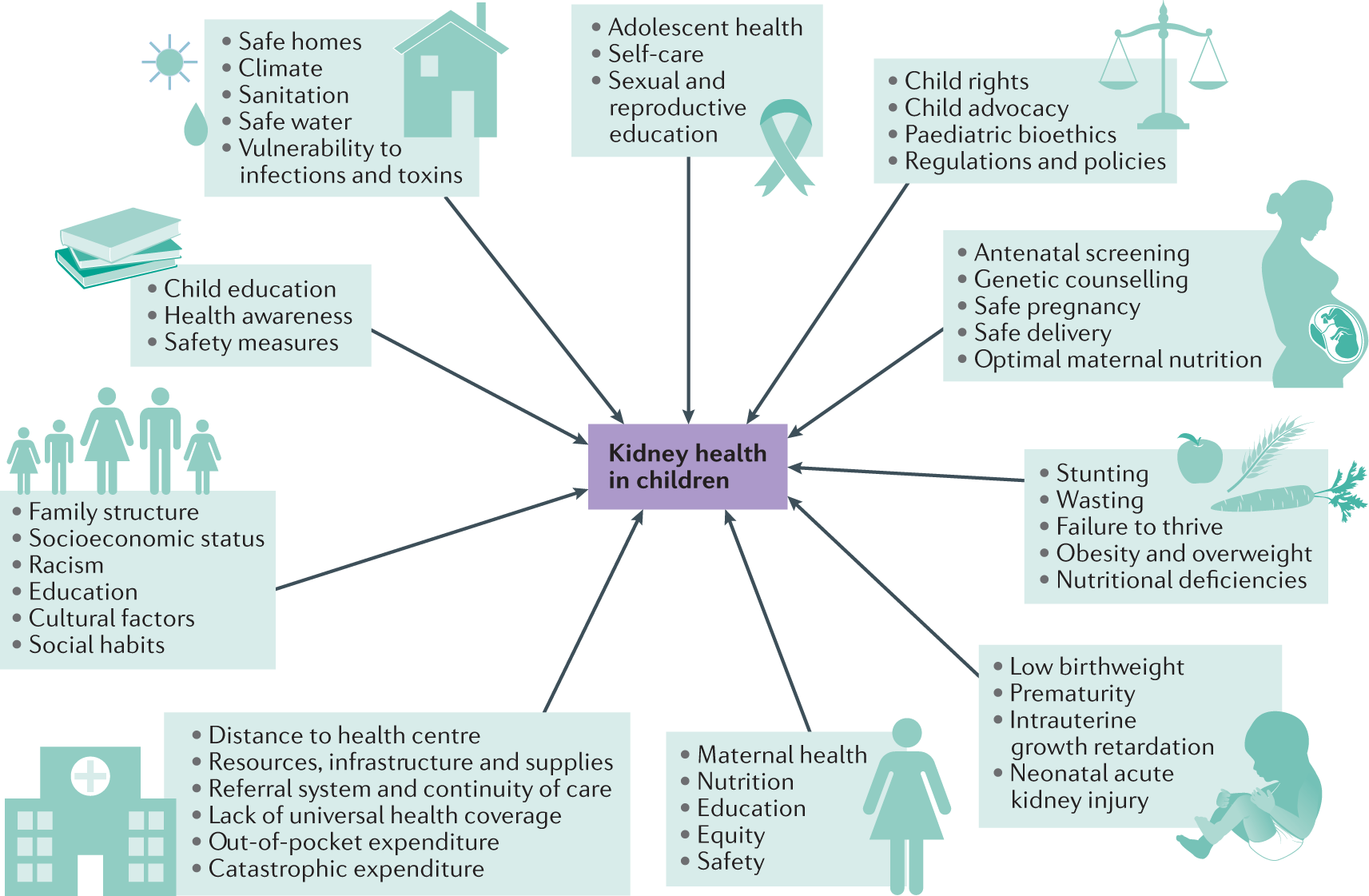
Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
Refer to the above information. If the real interest rate is 9 percent, the equilibrium level of GDP will be: A) $500. B) $600. C) $300. D) $400. If a $50 billion decrease in investment spending causes income to decline by $50 billion in the first round of the multiplier process and by $25 in the second round, the multiplier in the economy is ... Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. Will be 4 units of bicycles. Solved I And Ii Only 6 Which Of The Following Statements Phase Diagram Wikipedia The Economy Unit 1 The Capitalist Revolution Critical Neutral And Positive Statements In The Oireachtas Using Explaining The Multiplier Effect Tutor2u Economics Hr Diagram Syllabus: Use the multiplier to calculate the effect on GDP of a change in an injection in investment, government spending or exports (I,G,X). Syllabus: Draw a Keynesian AD/AS diagram to show the impact of the multiplier. Figure 1 Diagram to show Multiplier effect. Figure 1 AD shifts due to the initial injection and then has a greater shift due to multiplier effect - I don´t know why it says ...
Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is. making the complex multiplier less than the simple multiplier. 10-3 Graphically depict the aggregate expenditures model for a private closed economy. Next, show a decrease in the aggregate expenditures schedule and explain why the decrease in real GDP in your diagram is greater than the initial decline in aggregate expenditures. Refer to the above diagram that applies to a private closed economy. In this economy the value of the multiplier is equal to: HJ/BF FD/BF FD/LK All of the above None of the above. Click HERE to order a unique plagiarism free paper done by professional writers and delivered before your deadline. In the dynamic world we currently live in, it's ... 120. Refer to the above diagram. The multiplier in this economy is: A) 0E/0A. B) BD/FG. C) FG/BD. D) BD/AD. Answer: B . Type: G Topic: 3 E: 179-180 MA: 179-180 121. Refer to the above diagram. If aggregate expenditures in this economy are C + I g + X n2), then the equilibrium levels of GDP and aggregate expenditures respectively will be: A) 0A and 0E. B) 0B and 0F. C) 0A and AH . D) 0D and DJ ... The actual multiplier effect in the U.S. economy is less than the multiplier effect in the text examples because: A. the real-world MPS is larger than the MPS in the examples. ... Refer to the above diagram. The simple multiplier for this economy is: A. 1.0 B. 1.5 C. 2.0 D. 2.5.
The numerical value of the multiplier will be smaller the: ... Refer to the diagram that applies to a private closed economy. If aggregate expenditures are ... Rating: 5 · 1 review When economists refer to "investment," they are describing a situation where: ... promote economic growth by helping to direct household saving to ... Transcribed image text: Real GDP (Billions) 15 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium GDP is 00:54:39 Multiple Choice O $60 billion at all levels of GDP. $60 billion. between $60 and $180 billion. O $180 billion. 45. Refer to the above table. The marginal propensity to consume is: A) .5 B) .75 C) .8 D) .9 46. Refer to the above table. The total change in income resulting from the initial change in investment will be: A) $5 B) $10 C) $15 D) $20 47. Refer to the above table. The multiplier in this economy is: A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5
Which aggregate expenditure schedule(s) AE in the diagram for a private closed economy ... Refer to the diagrams. ... The multiplier in this economy is:. Rating: 5 · 1 review Refer to the diagram below. The multiplier in this economy is: A. 0E/0A . B. BD/FG . C. FG/BD . D. BD/AD . Difficulty: Hard Learning Objective: 11-05 Analyze how changes in equilibrium GDP can occur in the aggregate expenditures model and how those changes relate to the multiplier. Multiplier is one of the most important concepts developed by J.M. Keynes to explain the determination of income and employment in an economy. The theory of multiplier has been used to explain the cumulative upward and downward swings of the trade cycles that occur in a free-enterprise capitalist economy. To understand how the multiplier effect works, return to the example in which the current equilibrium in the Keynesian cross diagram is a real GDP of $700, ...
An economy is employing 2 units of capital, 5 units of raw materials, and 8 units of labor to produce its total output of 640 units. Each unit of capital costs $10; each unit of raw materials, $4; and each unit of labor, $3. Refer to the information. The per-unit cost of production in this economy is: $0.10.
A multiplier refers to an economic factor that, when applied, amplifies the effect of some other outcome. A multiplier value of 2x would therefore have the result of doubling some effect; 3x would ...
The formula for the multiplier in a closed economy with no government is 1/marginal propensity to save or 1/(1-marginal propensity to consume) We can infer from the information that the value of the multiplier = 5. Therefore the marginal propensity to save must be 0.2. Because MPS + MPC always equals 1 . Then the MPC = 1-0.2 = 0.8. 7. Revision Flashcards for A Level Economics Students ...
Refer to the given diagram, which shows consumption schedules for economies A and B. We can say that the ... Which economy has the largest multiplier? Rating: 5 · 3 reviews
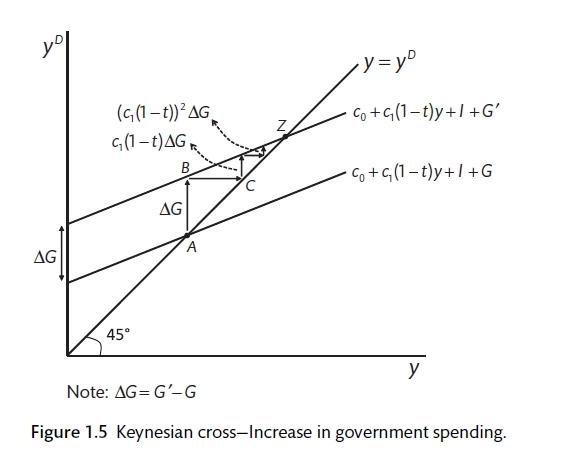
An initial change in aggregate demand can have a much greater final impact on the level of equilibrium national income. This is known as the multiplier effect - the multiplier is explained in our short revision video below. Practice MCQ Revision Video on the Multiplier. Quizlet revision resource on the multiplier and the accelerator effects.
Refer to Figure 24-2. Suppose the economy is in a short-run equilibrium at Y1. A contractionary fiscal policy would restore the economy to potential output (Y*) by shifting the A) AS curve to the left to intersect AD at C. B) AS curve to the right. C) potential GDP and the AS curve to the left. D) AD curve to the right.
Refer to the above diagram. The multiplier in this economy is: A) 0E/0A. B) BD/FG. C) FG/BD. D) BD/AD. Answer: B 23. Refer to the above diagram. If aggregate expenditures in this economy are (C + Ig + Xn2), then the equilibrium levels of GDP and aggregate expenditures respectively will be: A) 0A and 0E. B) 0B and 0F. C) 0A and AH . D) 0D and DJ . Answer: D 24. Refer to the above diagram. The ...
24. The Council of Economic Advisers has estimated that the actual multiplier for the U.S. economy is approximately: A) 4. B) 3.5. C) 3. D) 2. Answer: D Use the following to answer questions 25-29: The following schedule contains data for a private closed economy. All figures are in billions. Use these data in answering the next question(s ...
An economy is currently in equilibrium and the following figures refer to elements in its national accounts. At income of 200 how much is the consumption. Refer to the above diagram the value of the. This is a preview content. The equilibrium level of gdp is. Refer to the above diagram where t is tax revenues and g is government expenditures.
Refer to the above diagram The multiplier in this economy is A 0 E 0 A B BD FG C from ECON 210 at Adrian College.
The multiplier effect in an open economy. As well as calculating the multiplier in terms of how extra income gets spent, we can also measure the multiplier in terms of how much of the extra income goes in savings, and other withdrawals. A full ‘open’ economy has all sectors, and therefore, three withdrawals – savings, taxation and imports. This is indicated by the marginal propensity to ...
Refer to the diagram. The multiplier in this economy is: ... Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium GDP is: inflationary expenditure gap is ei. Refer to the diagram. If the full-employment level of GDP is B and aggregate expenditures are at AE1, the:
AACSB: Analytical Skills Bloom's: Analysis Learning Objective: 28-3 Topic: Open economy 109. Refer to the above table. For the open economy the equilibrium GDP and the multiplier are: A. $300 and 2.5. B. $450 and 5. C. $400 and 4. D. $400 and 5.
Einstein The multiplier in an economy with a government and foreign trade. We can again use the fact that there is equilibrium in the goods market when output is equal to aggregate demand to find the multiplier (equilibrium is where the aggregate demand line crosses the 45-degree line in the multiplier diagram).
3. (Refer to the image to the left). Suppose that the level of GDP associated with point N is potential GDP. If the U.S. economy is currently at point K, a) Firms are operating above capacity. b) The economy is at full employment. c) The economy is in recession. d) The level of unemployment is equal to the natural rate.
2) Refer to Table 8-1. Suppose that a simple economy produces only four goods and services: sweatshirts, dental examinations, coffee drinks, and coffee beans. Assume all of the coffee beans are used in the production of the coffee drinks. Using the information in the above table, nominal GDP for this simple economy equals A) 3,090 units. B) $7,250.
The MPC for an economy is: the slope of the consumption schedule or line. Refer to the given diagram, which shows consumption schedules for economies A and B. We can say that the: MPC is greater in A than in B. If Trent's MPC is .80, this means that he will: spend eight-tenths of any increase in his disposable income.
11. Refer to the above diagram that applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment is Ig1, the equilibrium GDP and the level of consumption will be: A. H and HB respectively. B. J and JI respectively. C. J and JK respectively. D. H and HF respectively. 12. Refer to the above diagram that applies to a private closed economy. In this ...
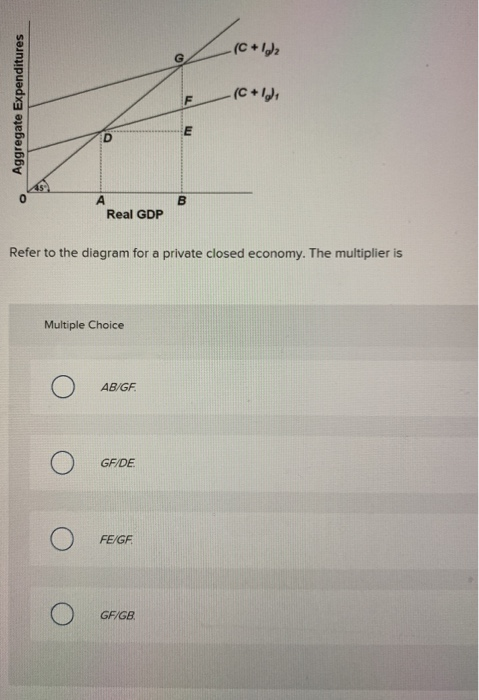
Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. The multiplier is: AB/GF. other things equal, an increase in an economy's exports will: increase expenditures and therefore increase its equilibrium GDP. In an inflationary expenditure gap, the equilibrium level of real GDP would be: Greater than full-employment GDP . John Maynard Keynes developed the ideas underlying the aggregate ...
Syllabus: Use the multiplier to calculate the effect on GDP of a change in an injection in investment, government spending or exports (I,G,X). Syllabus: Draw a Keynesian AD/AS diagram to show the impact of the multiplier. Figure 1 Diagram to show Multiplier effect. Figure 1 AD shifts due to the initial injection and then has a greater shift due to multiplier effect - I don´t know why it says ...
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. Will be 4 units of bicycles. Solved I And Ii Only 6 Which Of The Following Statements Phase Diagram Wikipedia The Economy Unit 1 The Capitalist Revolution Critical Neutral And Positive Statements In The Oireachtas Using Explaining The Multiplier Effect Tutor2u Economics Hr Diagram
Refer to the above information. If the real interest rate is 9 percent, the equilibrium level of GDP will be: A) $500. B) $600. C) $300. D) $400. If a $50 billion decrease in investment spending causes income to decline by $50 billion in the first round of the multiplier process and by $25 in the second round, the multiplier in the economy is ...


















0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is"
Post a Comment