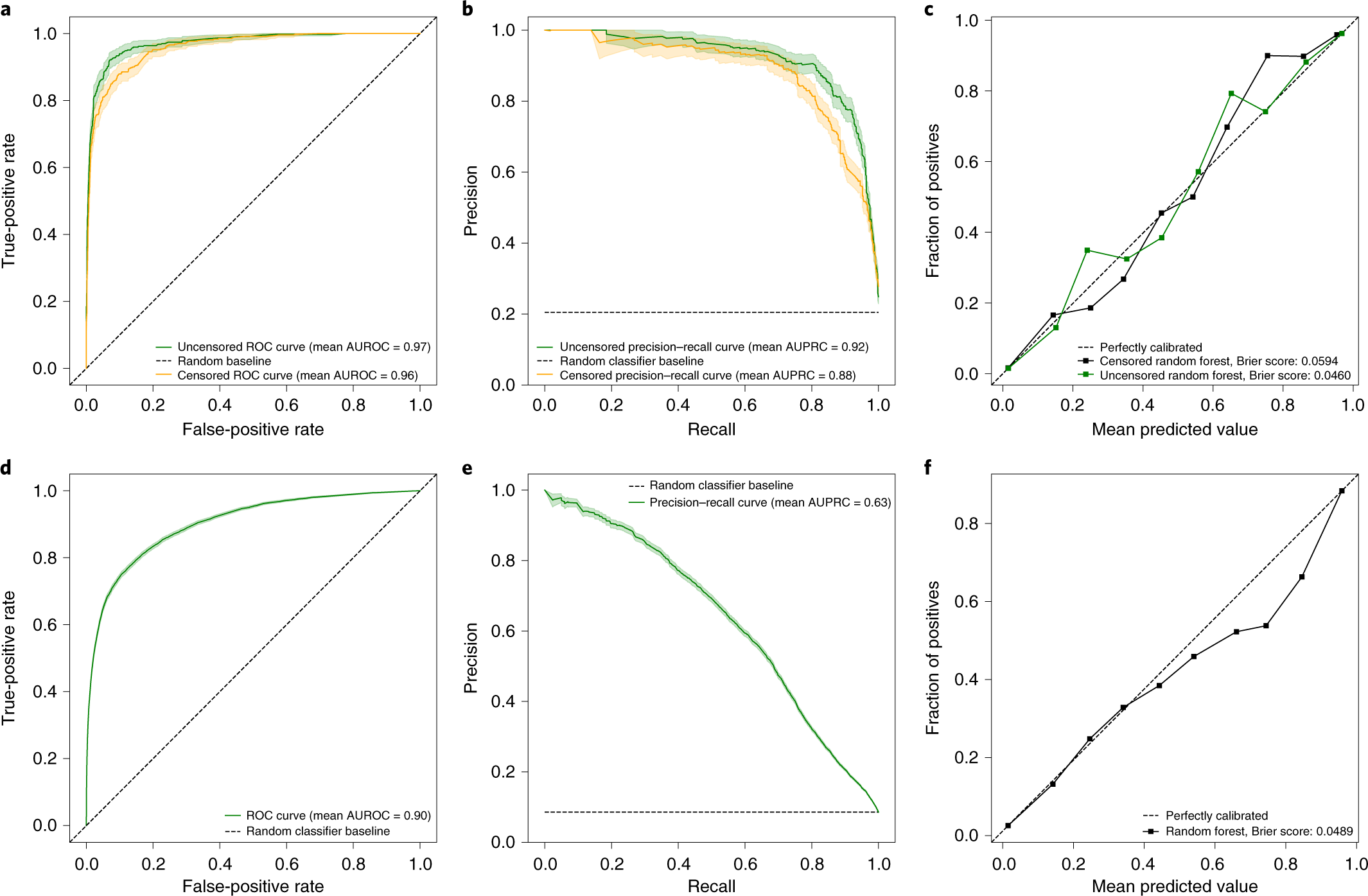
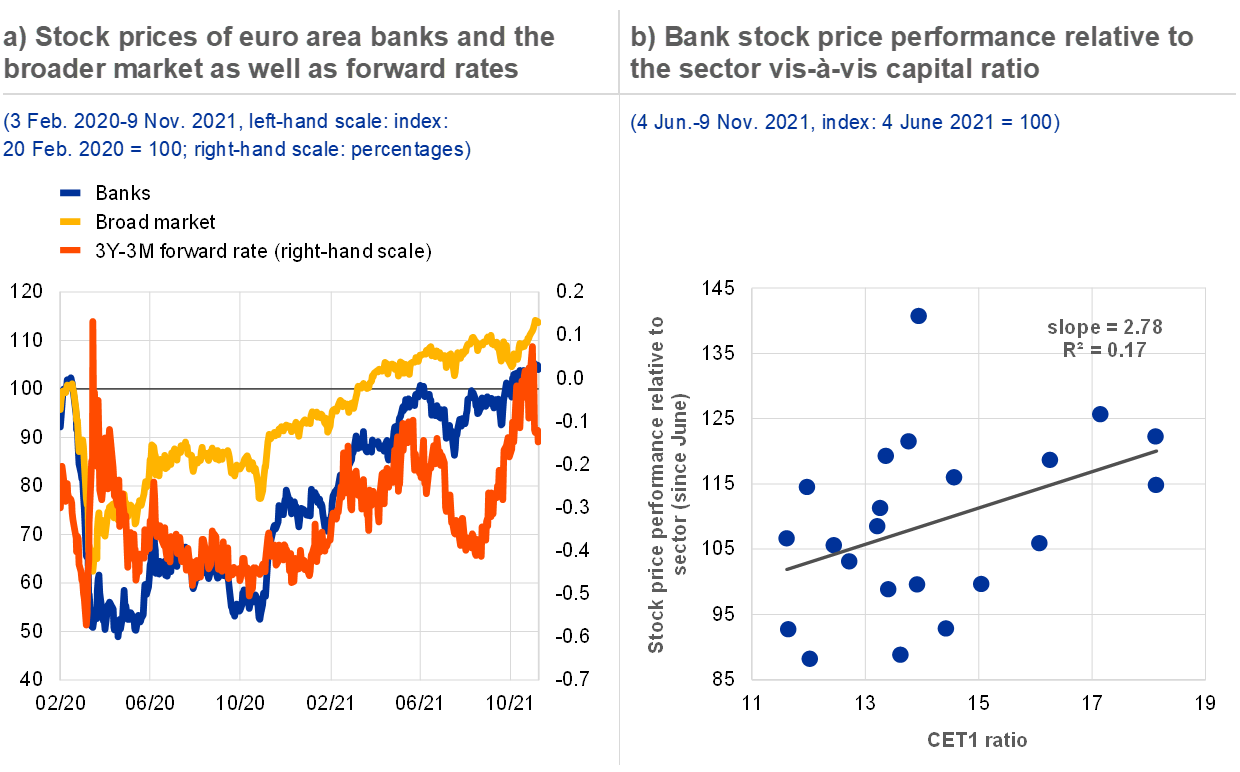
37 refer to the diagram to the right. curve g approaches curve f because
use a taper offset with a simple curve, a 2-centered or a 3-centered symmetrical or asymmetrical compound curve. The details of the recommended curve layouts and how they accommodate the design vehicles are discussed in Sections 5-2.0 and 5-3.0 of this manual, and in MnDOT’s Traffic Engineering Manual.
Curve Fitting using Reciprocal Terms in Linear Regression. When your dependent variable descends to a floor or ascends to a ceiling (i.e., approaches an asymptote), you can try curve fitting using a reciprocal of an independent variable (1/X). Use a reciprocal term when the effect of an independent variable decreases as its value increases.
Young's modulus, E, is the most important of the elastic constants and can be derived from the slope of the strain–stress curve obtained when a rock specimen is subjected to unconfined compression (i.e., static loading), it being the ratio of stress to strain.The strains are measured by attaching strain gauges to the test specimens, or by displacement transducers, and recording …

Refer to the diagram to the right. curve g approaches curve f because
1. Long-run cost curves are U-shaped because. of economies and diseconomies of scale. 1. Marginal cost is equal to the. change in total cost divided by the change in output. 1. One reason why, in the short run, the marginal product of labor might increase initially as more workers are hired is that.
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve (sigmoid curve) with equation = + (),where , the value of the sigmoid's midpoint;, the curve's maximum value;, the logistic growth rate or steepness of the curve. For values of in the domain of real numbers from to +, the S-curve shown on the right is obtained, with the graph of approaching as approaches + and …
G average variable cost curve. G average variable cost curve h marginal cost curve b e marginal cost curve. 6 refer to figure 10 7. Identify the curves in the diagram. Suppose the price of pilates sessions rise to 30 while income and the price of yoga sessions remain unchanged. Identify the curves in the diagram. F average total cost curve. B a ...
Refer to the diagram to the right. curve g approaches curve f because.
Materials fatigue performance is commonly characterized by an S-N curve, also known as a Wöhler curve.This is often plotted with the cyclic stress (S) against the cycles to failure (N) on a logarithmic scale.S-N curves are derived from tests on samples of the material to be characterized (often called coupons or specimens) where a regular sinusoidal stress is applied by a testing …
Shift curve a to the left and shift curve b downward. Refer to the diagram to the right curve g approaches curve f because. A firm finds that at its mrmc output its tc 1000 tvc 800 tfc 200 and total revenue is 900. Curve g approaches curve f because a fixed cost falls as capacity rises.
Refer to the diagram to the right. Curve G approaches curve F because A. average fixed costs falls as output rises. B. fixed costs falls as capacity rises. C. total costs fall as more and more is produced. D. marginal costs are above average variable costs.
Answer is D) E represents marginal cost as it increases with increase in output due to diminishing returns (when the marginal cost cur …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. E=average fixed cost curve, F=average total cost curve, G= average variable cost curve, H ...
24. Curve G approaches curve F because - marginal cost is above average variable costs. - fixed cost falls as capacity rises. - total cost falls as more and more is produced. - average fixed cost falls as output rises.
If because of an externality the economically efficient output is q2. 29 curve g approaches curve f because a marginal cost is above average variable costs. In that case the diagram shows the effect of a negative externality in the production of a good. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 58 a sunk costs.
14.07.2015 · Because of the success of neighboring anatomy–guided segmentation approaches in segmenting challenging cases pertaining to lung abnormalities, much work is currently in progress in this area, and more developed updates of neighboring anatomy–guided segmentation approaches are currently evolving (25,54). Despite the fact that these ...
The rotating lines in the right hand part of the animation are a very simple case of a phasor diagram (named, I suppose, because it is a vector representation of phase). With respect to the x and y axes, radial vectors or phasors representing the current and the voltage across the resistance rotate with angular velocity ω.
The notation f(x) is the standard way to show that it's a function (by convention called f if we're only listing one) and its output changes based on one variable (in this case, x). Change x, and the output for f(x) changes. So far, so good. Now, let's look at parametric functions, and how they cheat. Let's take the following two functions:
Lacks reliability because difference in the slope of a demand curve can produce a larger change in the independent variable. For example, the slope between two points A and D is -0.44 but the slope between the points that lie in between these two points is large, B and C is -0.66.
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The curve BC in is the plot of vapor pressure versus temperature as described in the previous module of this chapter. This “liquid-vapor” curve separates the liquid and gaseous regions of the phase diagram and provides the boiling point for water at any pressure. For example, at 1 atm, the boiling point is 100 °C.
Refer to the diagram to the right. Curve G approaches curve F because. average fixed costs falls as output rises. ... Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 11-4. Curve G approaches curve F because A) fixed cost falls as capacity rises. B) average fixed cost falls as output rises. C) marginal cost is above average variable costs. D) total cost falls as more and more is produced.










/dotdash-INV-final-How-the-Ideal-Tax-Rate-Is-Determined-The-Laffer-Curve-2021-01-9873ad4f5a464341aa6731540b763d76.jpg)












0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram to the right. curve g approaches curve f because"
Post a Comment