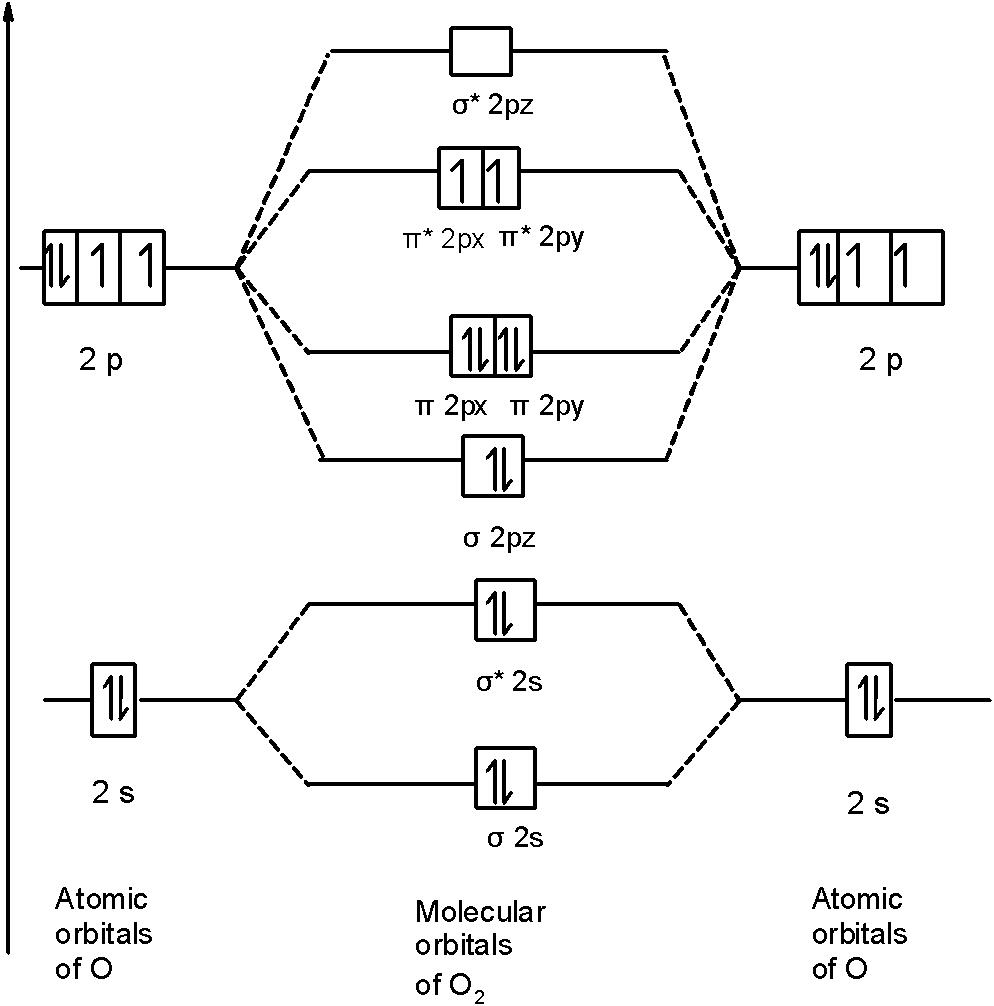
37 use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2.
Place the following in order of increasing X-Se-X bond angle, where X represents the outer atoms in each molecule. ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ ... O2^2⁺ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2 2⁺ ...
The bond order varies from one molecule to another. Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. Let us first know what is meant by bond order. Bond order. The bond order may be defined as half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals (Nonbonding) and the number of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital. Formula ...
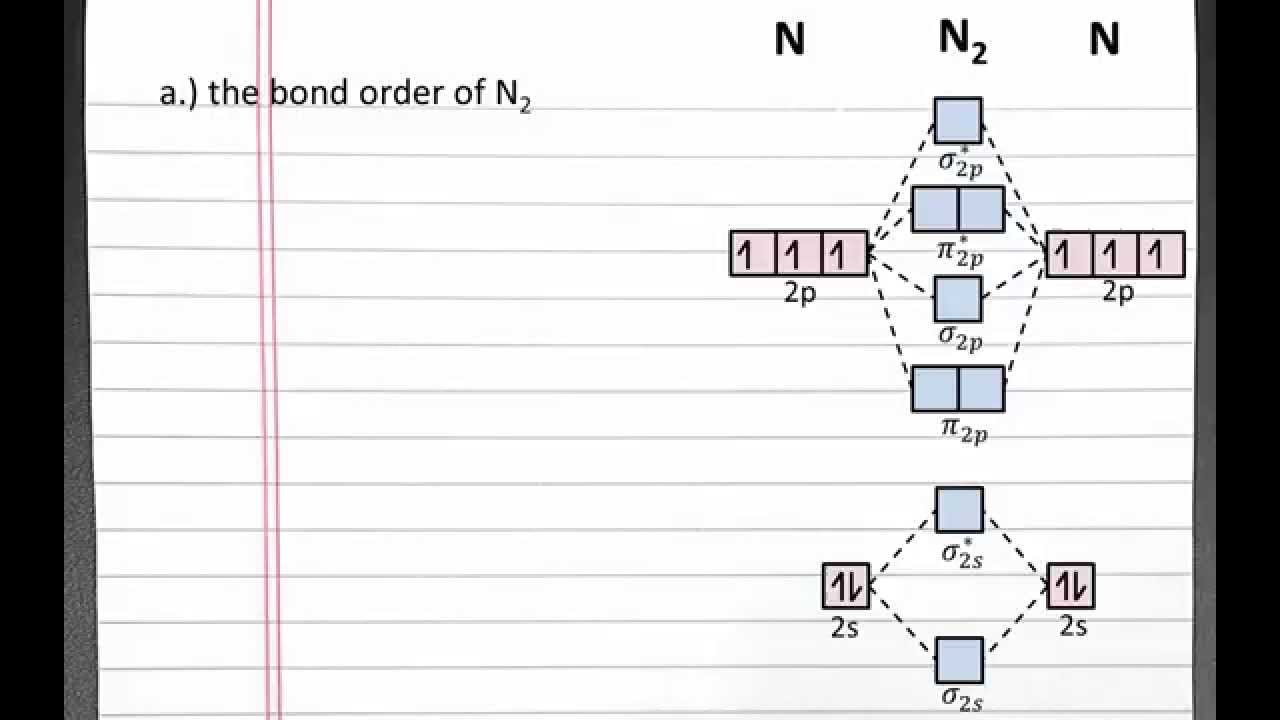
Transcribed image text: Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: • What is the bond order for N? [Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] netic? _ [ Select] • What is the bond order for N? (Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] • What is the bond order for Not?

Use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2.
Use the drawing of MO energy diagram for CO to predict the bond order. (Use the energy ordering of O2) The two sigma bonds form between a hybrid sp orbital on Be and a p orbital on Br.
Problem 7.92: Use the MO diagram in Figure 7.18b to describe the bonding in O 2 +, O 2, and O 2-. Which of the three should be stable? What is the bond order of each? Which contain unpaired electrons? First, here is the image: This diagram actually applies to this problem and to the next.
Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
Use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2..
(a) Use the MO diagram from Figure 2.18 from the textbook: The electron configuration for O 2 - is 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 3. This leaves 1 unpaired electron and gives a bond order of 1.5. (b) Use the same MO diagram as in (a), giving an electron configuration for O 2 + of: 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 1.
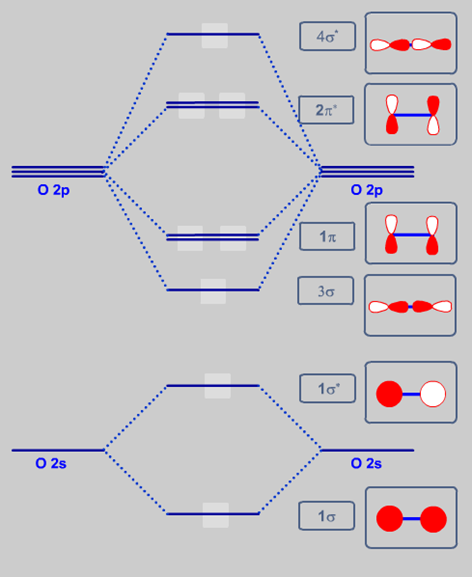
Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons.
Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
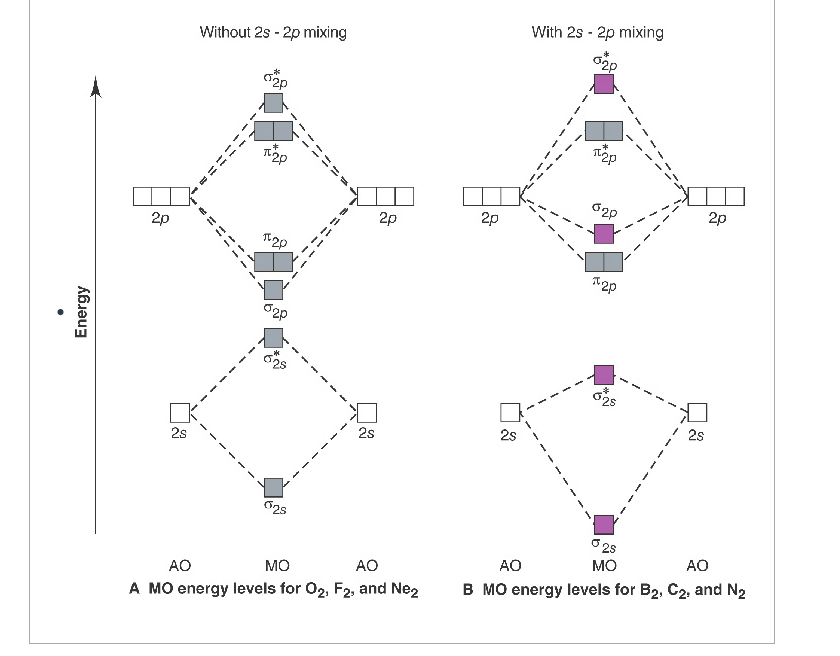
Without 2s-2p mixing With 2s-2p mixing CK :O r 25 20 2s AO MO AO AO MO AO A MO energy levels for O Fa. and Ne B MO energy levels for Ba Cz and Ng 0.5 This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading
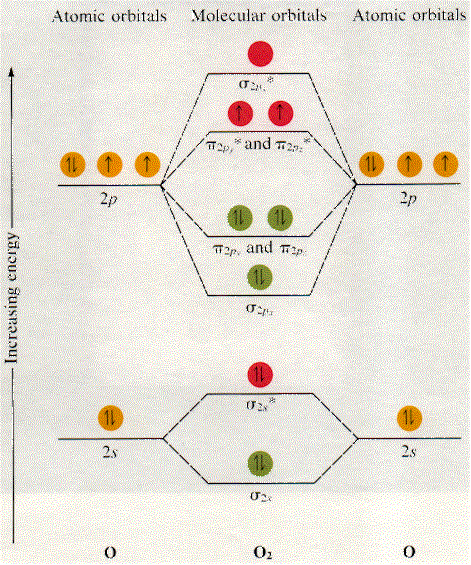
As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [ N b − N a ] / 2 = [ 1 0 − 6 ] / 2 = 2 .
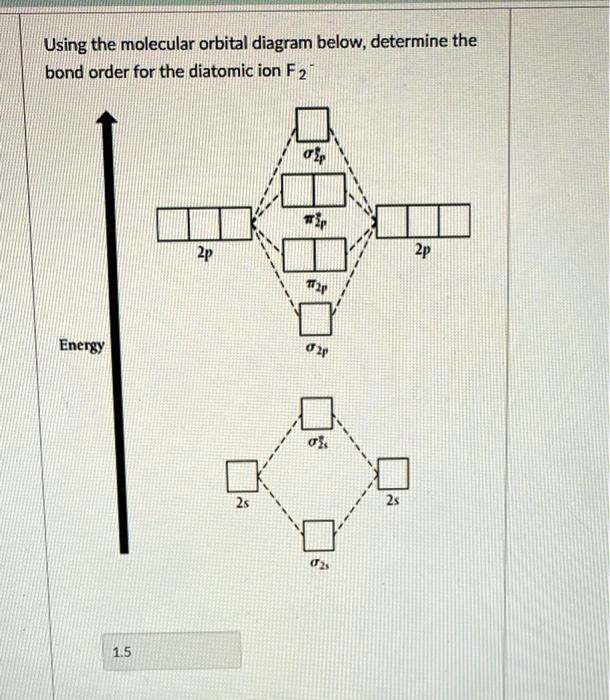
Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: What is the bond order for F2? 1 Is F2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for F2-? Is F2- paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for F2+? Is F2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Which of the three has the longest bond? Which of the three has the ...
Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
4a1 is the σ* 2pz antibonding MO. To obtain the bond order, look at the molecular orbitals formed and decide whether they are bonding or antibonding. BO = 1 2 (bonding e− − antibonding e−) = 1 2 [(2 + 2 + 2 + 2) − (2 + 1)] = 2.5. And this should make sense because NO+ is isoelectronic with CO, which has a bond order of 3.
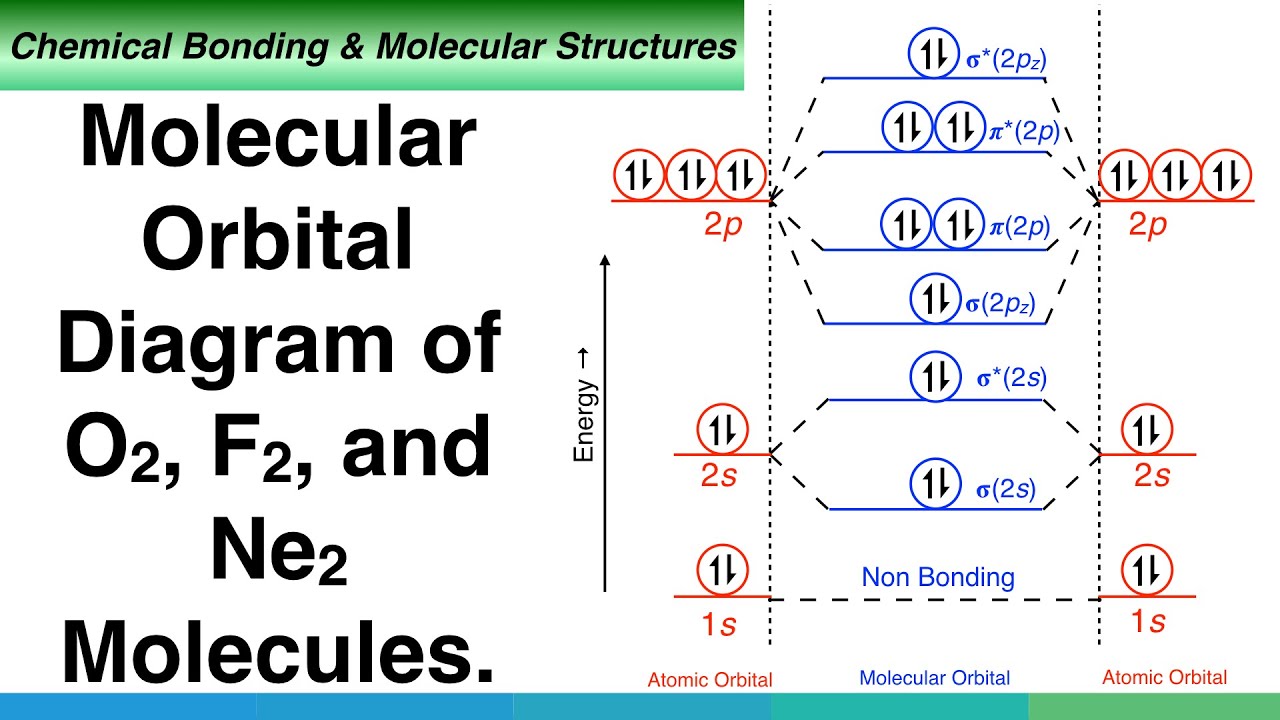
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
To find the bond order of O2+ we can use the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory. In this method we have to count the number of molecules in the Bonding Molecular Orbital and the Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbital. In the 1s shell there are 2 electrons in both BMO and ABMO . Also in the 2s shell there are two electrons in both the BMO and ABMO.
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
The bond order in sulfur dioxide, for example, is 1.5 the average of an S-O single bond in one Lewis structure and an S=O double bond in the other. In molecular orbital theory, we calculate bond orders by assuming that two electrons in a bonding molecular orbital contribute one net bond and that two electrons in an antibonding molecular orbital ...
On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.
To find the bond order of O2+ we can use the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory. In this method we have to count the number of molecules in the Bonding Molecular Orbital and the Anti-Bonding Molecular Orbital. In the 1s shell there are 2 electrons in both BMO and ABMO . Also in the 2s shell there are two electrons in both the BMO and ABMO.
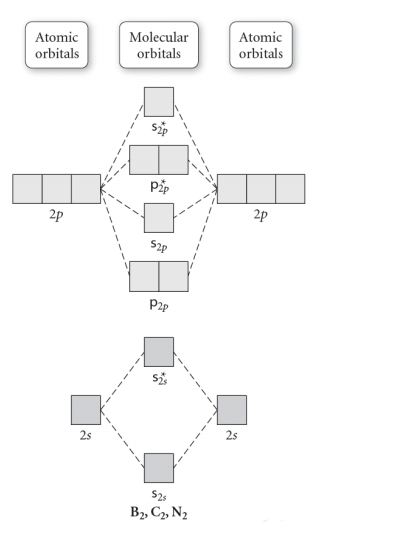
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B - Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order . + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Problem Details. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown below to determine which of the following diatomic species has the highest bond order. a. F 22⁻ b. F 22⁺ c. O 22⁺ d. F 2 e. Ne 22⁺. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems.
19. Draw an MO diagram for OF+ (use the energy ordering of O 2 and F 2). [4 points] a. Calculate the bond order. [2 points] 𝐎 = 𝐢 𝐠 𝐄𝐥 − 𝐢 𝐢 𝐠 𝐄𝐥 𝐎= 𝟖− = b. Is the molecule predicted to be stable or unstable?
Molecular orbitals (MO) are constructed from atomic orbitals. In O 2 and F 2, there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials: the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals'. Information from the MO diagram justify O2's stability and show that it's bonding order is 2.
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
Answer (1 of 2): The higher the bond order, the stronger the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the bond length. so, we know how to calculate the bond order….actually let me just show it (B.O)=1/2[(no of electron in anti bonding MO)-(no.of electrons in bonding MO)] for, O2 : BO=1/2[10-...
In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]` The two formulas for bond order tell us the same information.
In the molecular orbital theory, bond length, bond strength, bond order, and magnetic properties of different molecules plays an important role. Bond order is just several electrons that are present between two atoms. One can calculate the bond order of any molecule by creating a molecular orbital diagram like calculate the bond order in h−2.. To create the molecular diagram, you can start ...

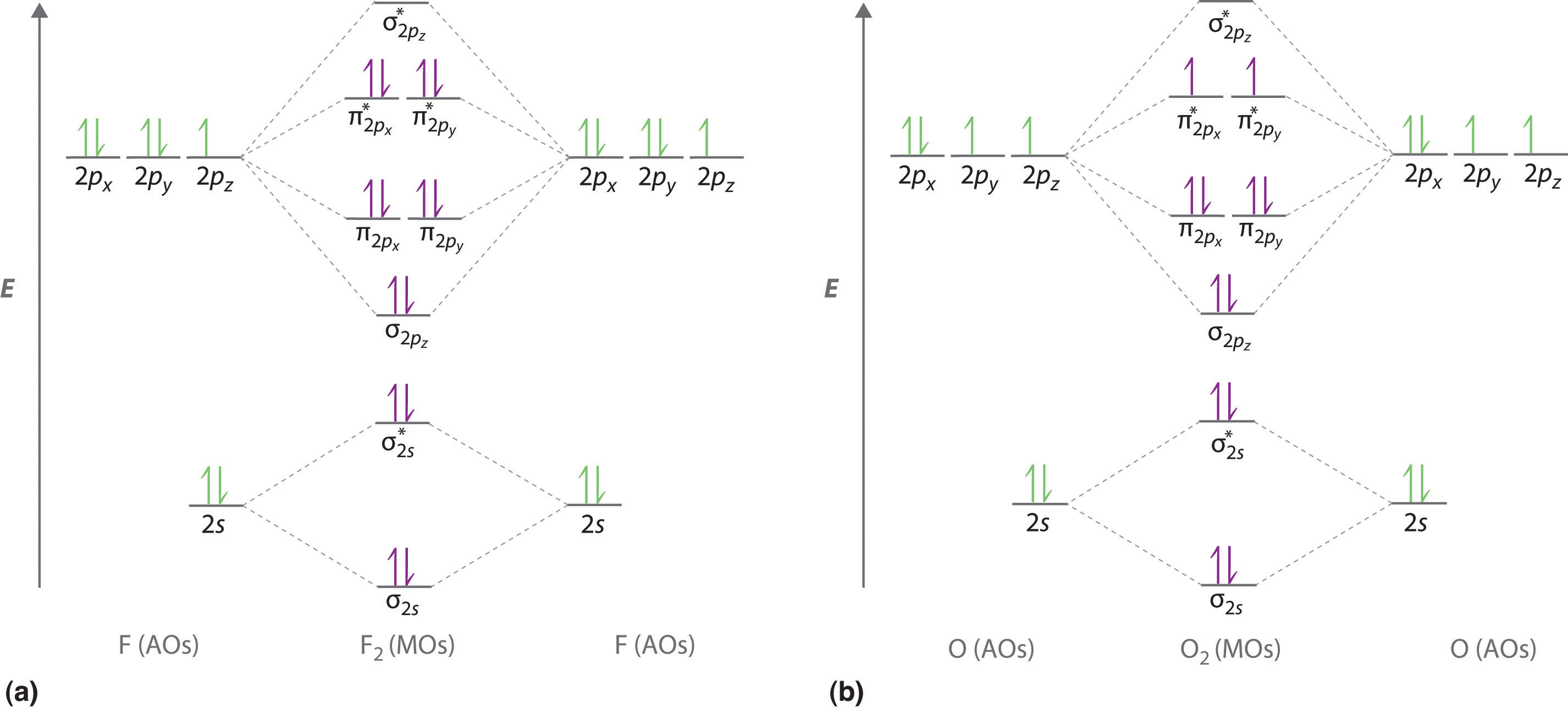

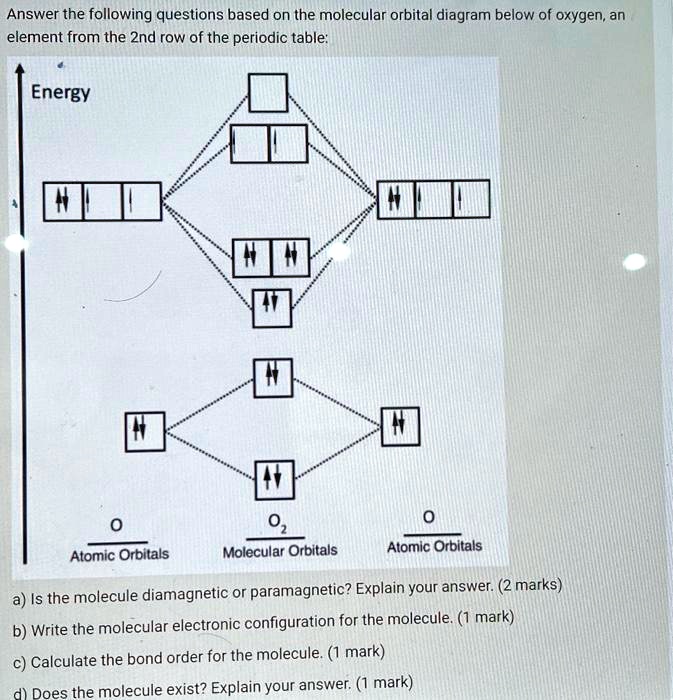










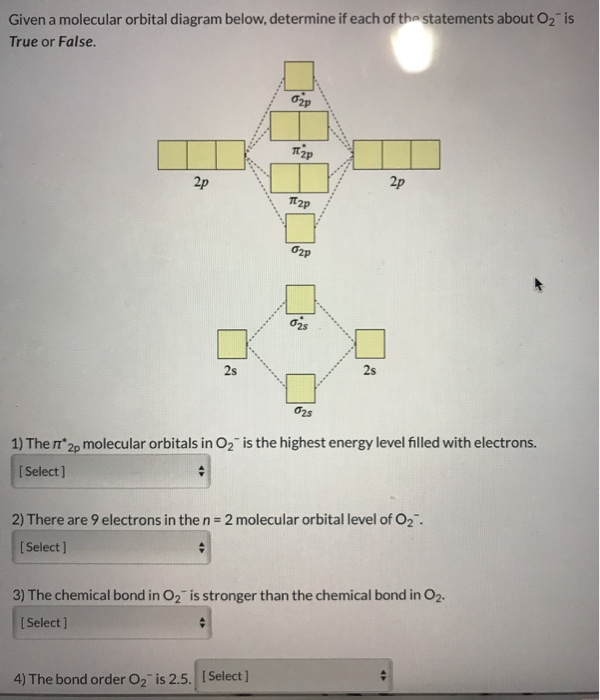



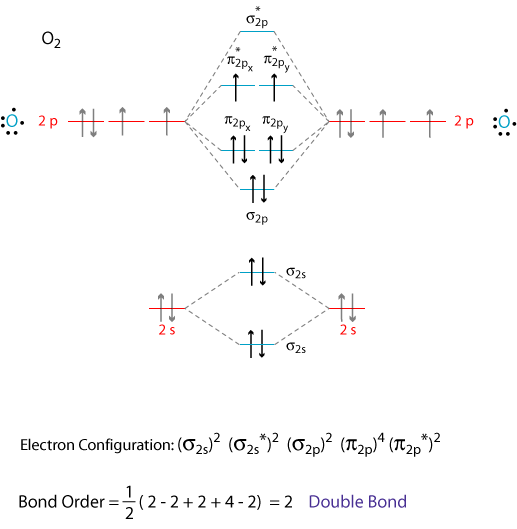
0 Response to "37 use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2."
Post a Comment