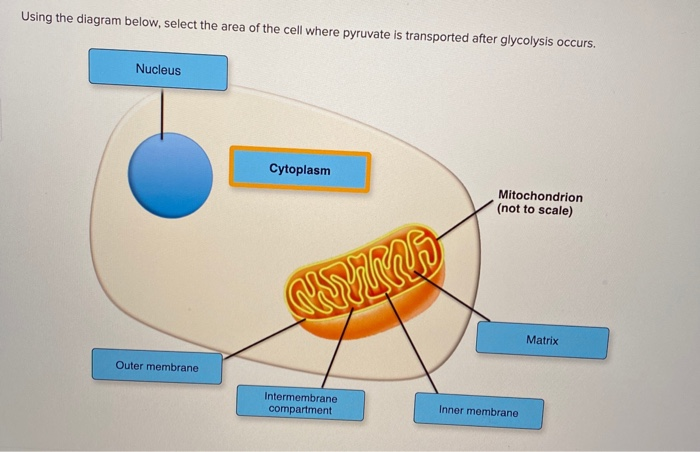
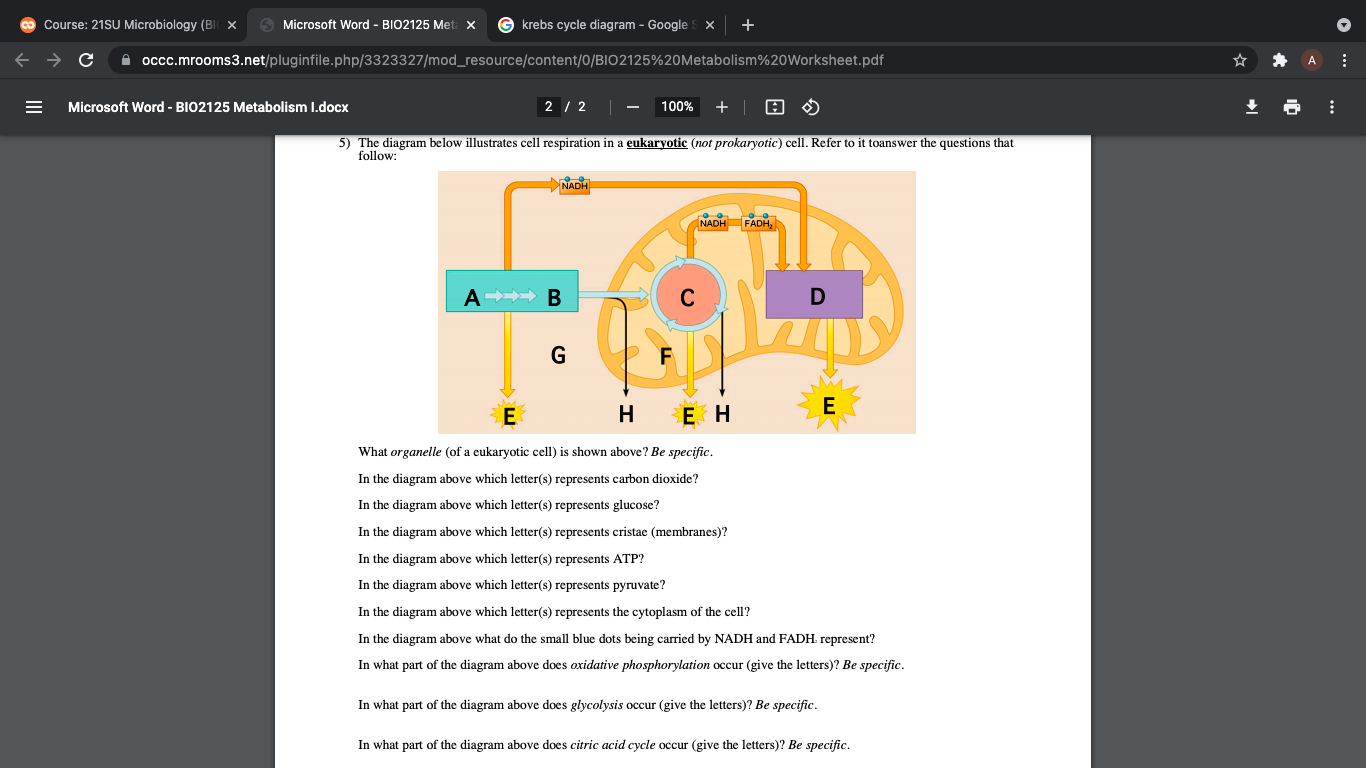
37 using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs.
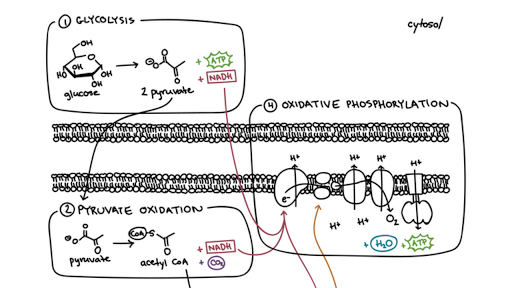
Figure of the 4 step citric acid cycle. Step 1: Glycolysis. A 6-carbon glucose molecule is split into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Pyruvate is needed in order to create acetyl CoA. Step 2: The transformation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. This is a very short step in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (19 ratings) Kreb cycle is the second step of aerob …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the Krebs cycle occurs. Previous question Next question.
The diagram below summarizes a series of chemical reactions that occur in cells. ... The folds greatly increase the membrane's surface area. This improves the ability of the mitochondrion to do which of the following? ... Photosynthesis occurs only in cells containing chlorophyll, but cellular respiration occurs in all cells.
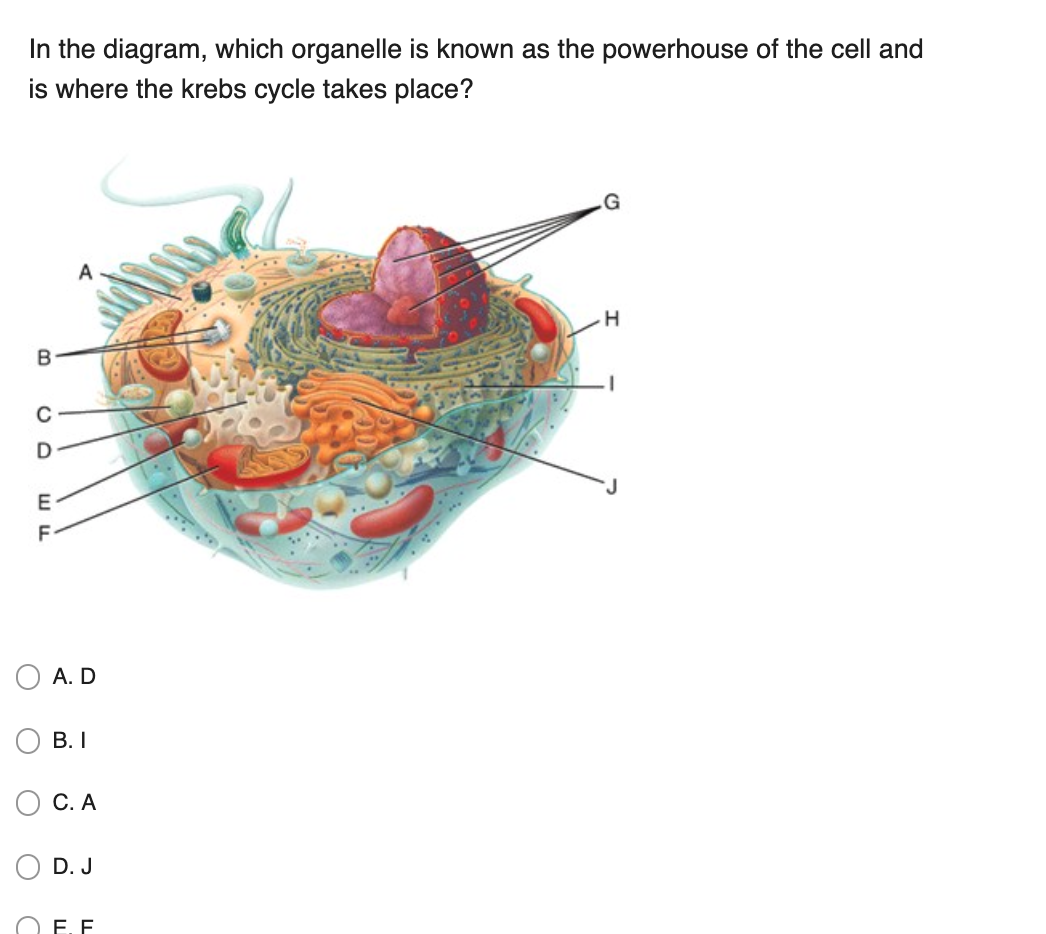
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs.
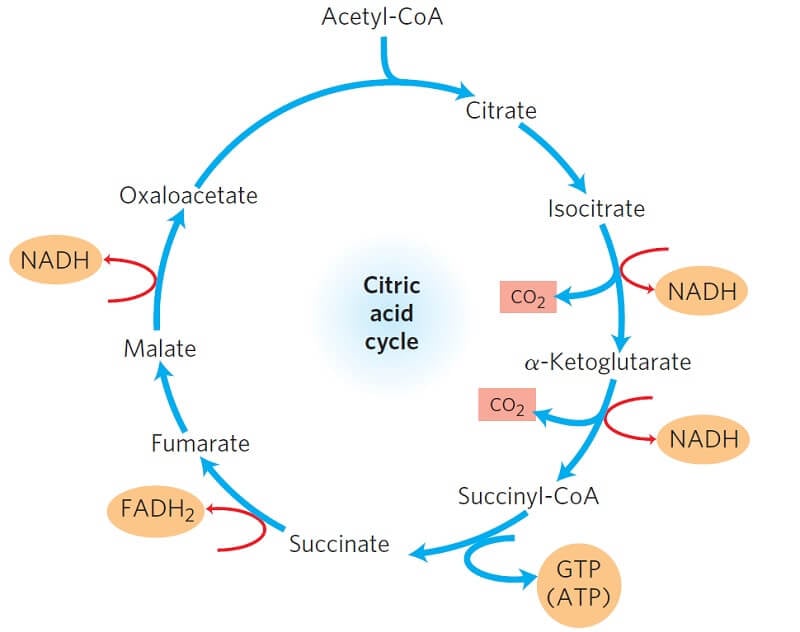
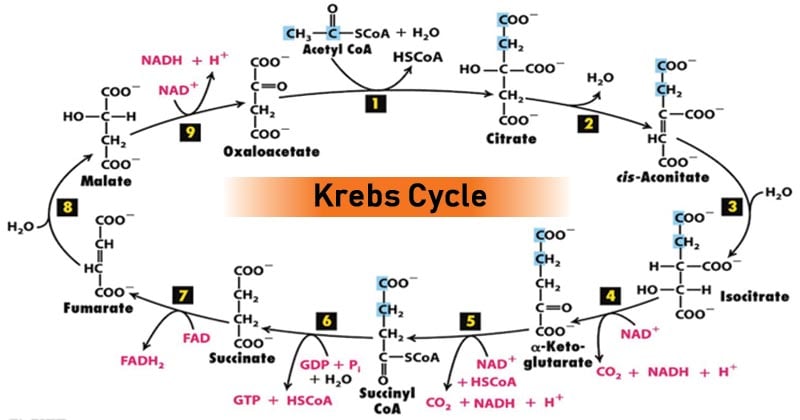
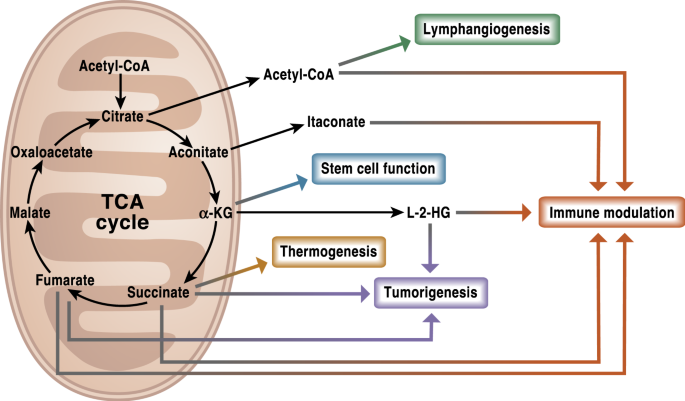
The acetyl group enters a cyclic sequence of reactions known collectively as the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid [TCA] cycle). The cyclical design of this complex series of reactions, which bring about the oxidation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide and water, was first proposed by Hans Krebs in 1937.
Answer (1 of 2): The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria of all eukaryotic cells that have mitochondria (i.e. not red blood cells). The Krebs cycle is also referred to as the citric acid cycle and more properly as the tricarboxylic acid cycle. I would refer you to this figure: Citric acid cyc...
Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) 1. It is a linear pathway. 1. It is a cyclic pathway. 2. It occurs in the cell cytoplasm. 2. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. 3. It occurs in both aerobic as well as in anaerobic respiration. 3. It occurs in aerobic respiration only. 4.
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs..
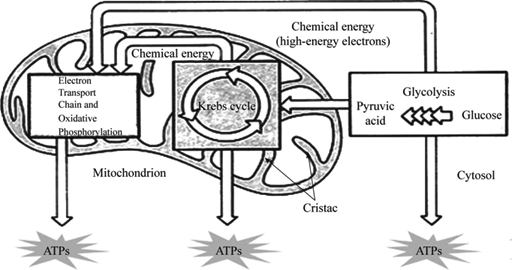
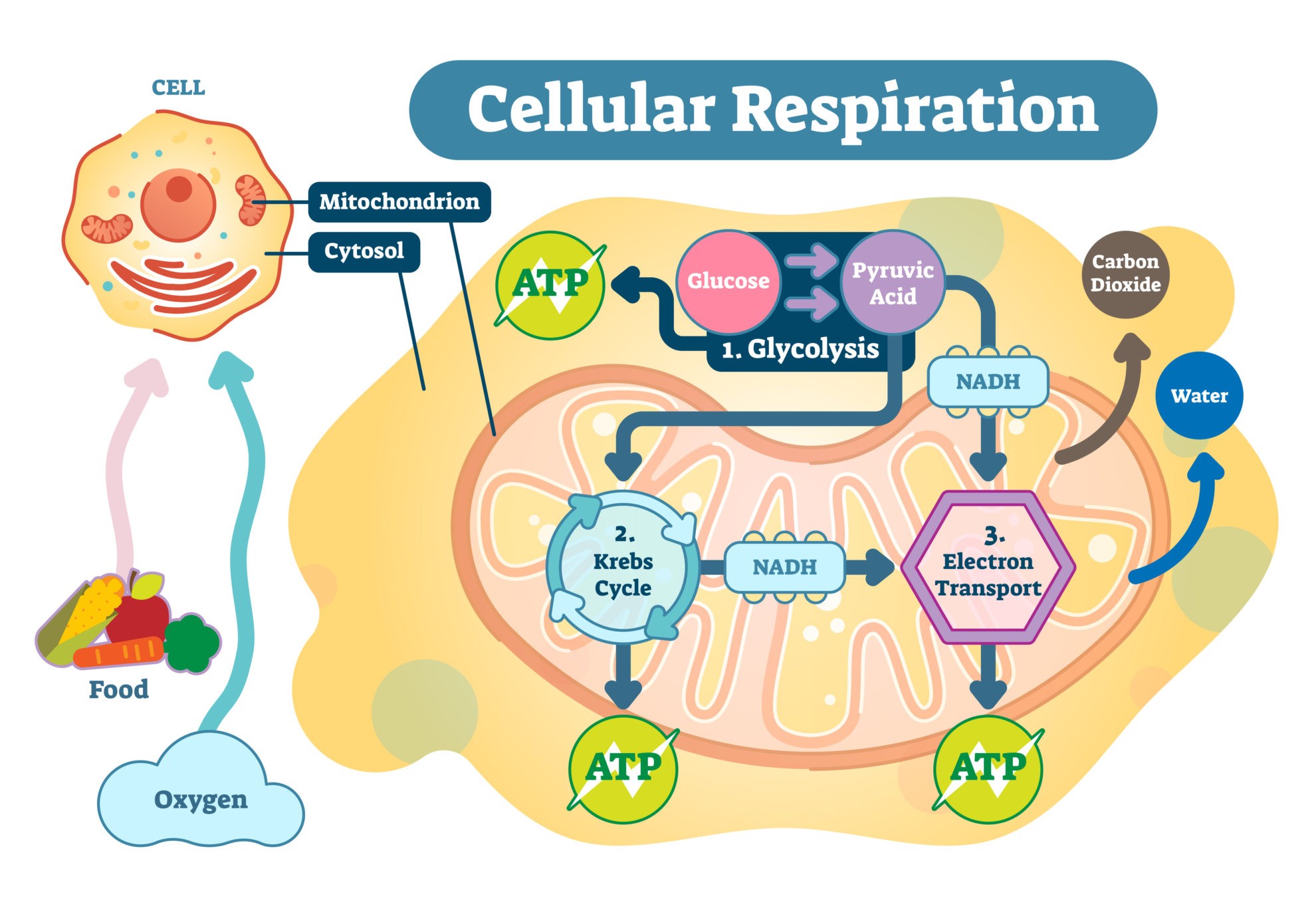
Overview Cellular respiration is the process of using oxygen in the mitochondria to chemically break down organic molecules such as glucose. This releases the energy stored in the bonds of glucose. In this process, molecules of water and carbon dioxide are released as waste products. This series of reactions produces 36 molecules of ATP! You can draw…
Krebs Cycle (TCA or Citric Acid Cycle): It is the common pathway for complete oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids as they are metabolised to acetyl coenzyme A or other intermediates of the cycle.The Acetyl CoA produced enters the Tricarboxylic acid cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucose is fully oxidised in this process. The acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate (4C) to form citrate (6C).
A. The knee only allows flexion whereas the hip allows flexion and extension. B. The knee allows more rotation than the hip. C. The knee is used to walk forwards whereas the hip is used for running around corners. D. The knee allows movement in one plane whereas the hip allows movement in three planes. D.
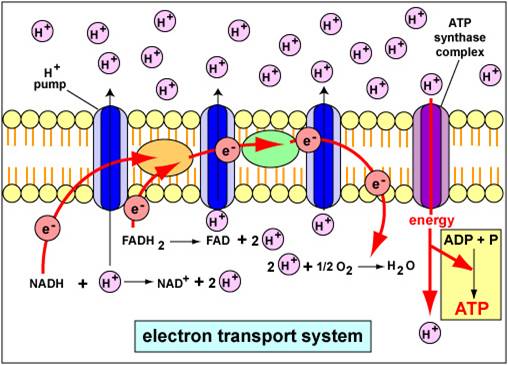
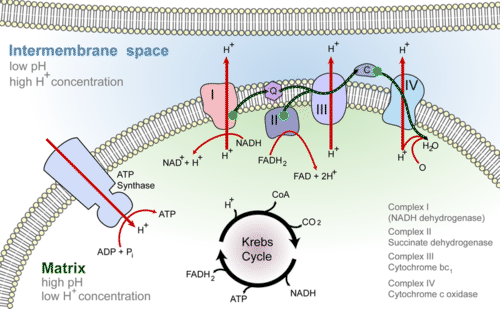
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
Krebs cycle. In the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid is changed into carbon dioxide. High-energy electrons are accepted by NAD- and FAD. This results in the formation of NADH and FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are used in another process to make ATP. A model of the Krebs cycle is shown below. 1. Fill in the details missing from the concept map below. s ...
Cell Communication and Cell Cycle (Cell Signaling) Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can activate an action potential in a postsynaptic neuron (Figures 1 and 2). A researcher is investigating the effect of a particular neurotoxin that causes the amount of acetylcholine released from presynaptic neurons to increase.
6. Below is an outline diagram of the Krebs cycle. A two carbon acetyl group enters the cycle by combining with a molecule of oxaloacetate. A molecule of citrate is formed which is decarboxylated and dehydrogenated to regenerate the oxaloacetate. citrate (6C) CoA intermediate (4C) intermediate (5C) P Q S R T V oxaloacetate (4C) fatty acids ...
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where pyruvate is transported after glycolysis occurs. Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondrion (not to scale) Matrix Outer membrane Intermembrane compartment Inner membrane ; Question: Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where pyruvate is transported after glycolysis occurs. Nucleus ...
The diagram below represents what occurs when plant cell is placed into an unknown solution. A plant cell and its changes after being added to solution. The cell goes from normal to shriveled. A plant cell and its changes after being added to solution. The cell goes from normal to shriveled.
Select all the molecules that can be used as electron acceptors at the end of the electron transport chain during anaerobic respiration in different organisms. ... In the diagram below, click on the area of the cell where the electron transport chain is found. ... The Krebs cycle occurs in the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion.
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the Krebs cycle occurs. 4. 5. 6. ... Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce the molecules that shuttle electrons to the electron transport chain. 12. ... click on the area of the cell where glycolysis occurs. Cytoplasm 16. In glycolysis, ...
The Krebs cycle occurs in the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion. T/F. NADH & FADH2. The electrons that are transferred through the electron transport system are brought there by. ... In the diagram below, click on the area of the cell where the electron transport chain is found.
Organisms that may make use of anaerobic respiration include animals bacteria yeast all of the above Select the answer that correctly identifies the processes in aerobic cellular respiration as they occur. Glycolysis, electron transport chain, fermentation Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain. Krebs cycle, glycolysis, electron ...
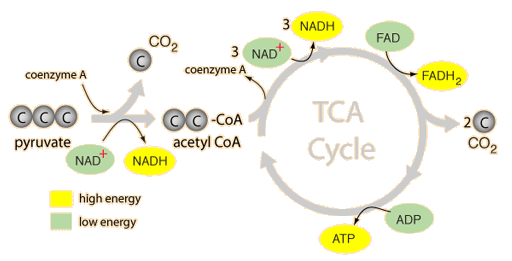
Krebs Cycle (Stage 2) To start the Krebs Cycle, pyruvate is pulled into the cell's mitochondria and converted to Acetyl-CoA. The Acetyl-CoA molecule is then converted (through several steps and two complete turns of the Kreb's Cycle) into 4 CO 2 molecules, 6 NADH molecules, 2 ATP molecules and 2 FADH 2 molecules.
Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol, but the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain occur inside the mitochondria. Electron carriers such as NADH produced during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle pass their electrons to the electron transport chain, which results in synthesis of a lot of ATP. Figure 6.
The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts (where would it occur in a prokaryote?). Carbon dioxide is captured by the chemical ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). RuBP is a 5-C chemical. Six molecules of carbon dioxide enter the Calvin Cycle, eventually producing one molecule of glucose.
Total energy production per glucose of ONLY the Krebs cycle (before electron transport chain) Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 8 NADH, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Describe the Pre-Krebs Cycle. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆.
Krebs cycle acetyl group joins a C4 molecule and forms citrate (C6) NAD+ reduced to NADH three times in cycle FAD reduced to FADH one time in cycle acetyl group oxidized to C02 substrate level ATP synthesis occurs to produce ATP inputs 2 (2C) acetyl groups 6 2 FAD 2 ADP +2 P Citric acid cycle outputs 4 C02 6 NADH 2 FADH2 ATP acetyl COA NADH
Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria; Glycolysis pathway (Embden-Meyerhof pathway) "Glycolysis" - breaking sugar. This process is anaerobic (without oxygen) and occurs in the cytosol of cells. During this stage, the six-carbon glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of three-carbon pyruvate.
• Oxidation of intermediates in the Krebs cycle • Formation of a proton gradient by the electron transport chain Process Description (1 point each box; 3 points maximum) Catabolism of glucose in glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation • Prod uces NA D H for use in ETC • Produces acetyl-CoA for entry into Krebs cycle
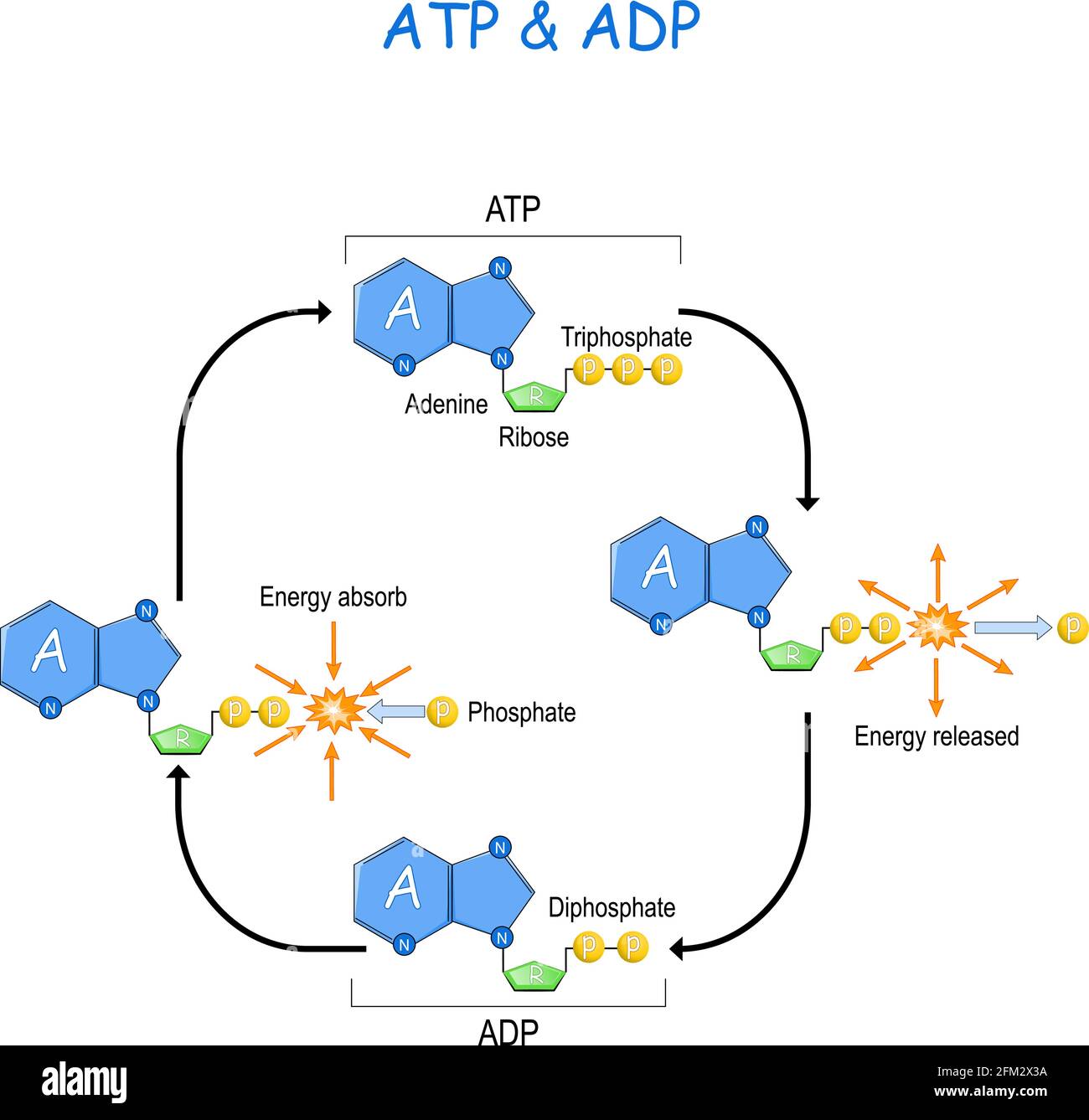
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphoryl (PO 3) group to a molecule. In biological systems, this reaction is vital for the cellular storage and transfer of free energy using energy carrier molecules. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), the most abundant energy carrier molecule, has two high-energy phosphate‑phosphate bonds that can be ...
The diagram below shows the energy conversions of the Krebs cycle, which is part of cellular respiration. The U-shaped arrows that show changes for NAD, FAD, and ADP molecules represent energy conversions. From each glucose molecule, two acetyl-CoA molecules are made for the Krebs cycle.
Krebs Cycle - Cellular Respiration. OVERVIEW. The Krebs cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or citric acid cycle, is the series of chemical reactions that generates energy through the oxidation of acetate. It was identified in 1937 by Hans Krebs, who was responsible for elucidating most of the pathway.
















0 Response to "37 using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs."
Post a Comment