39 dry cell battery diagram
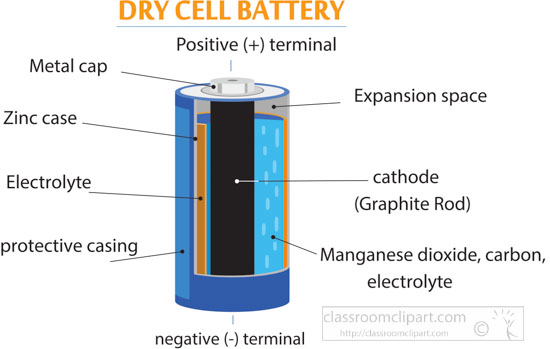
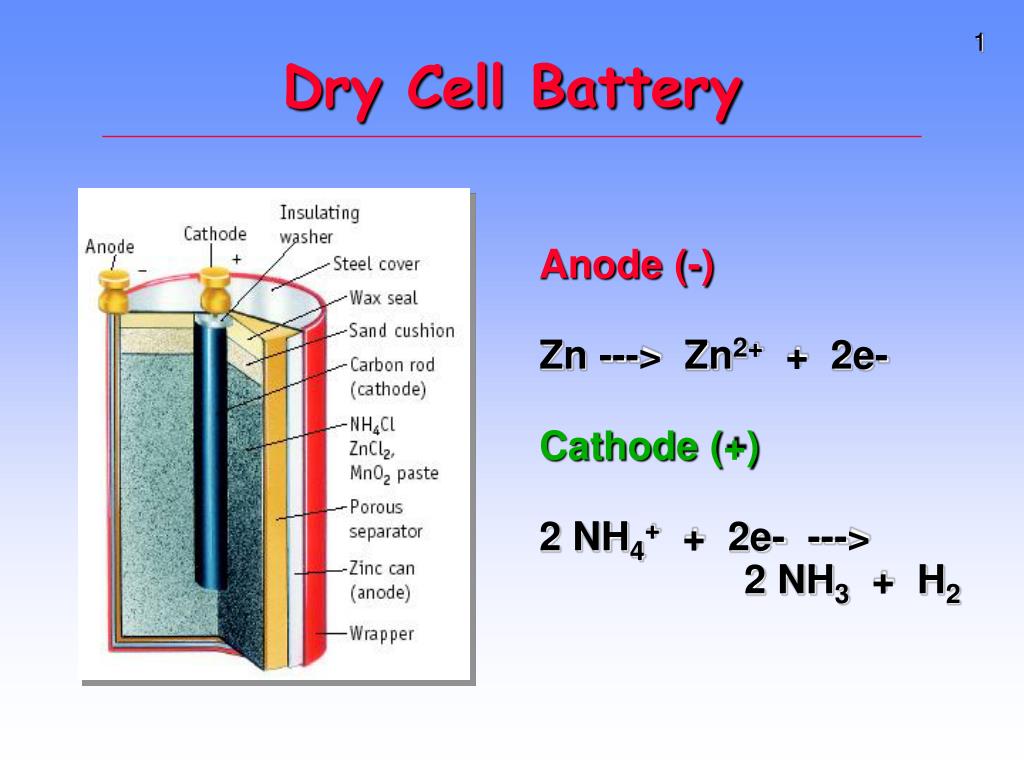
The zinc-carbon dry cell (or battery), shown in a cutaway diagram, is a modern version of the Leclanché cell. This 1.5 volt "Long Life" Dry Cell is an exact replacement for the original No. 6 in terms of A-Hr capacity and run time. Folks have loved it because it is renewable. Like the majority of our other No. 6 units, the Model 1900L is protected against accidental short circuits and battery mis-installations (which happens quite frequently).
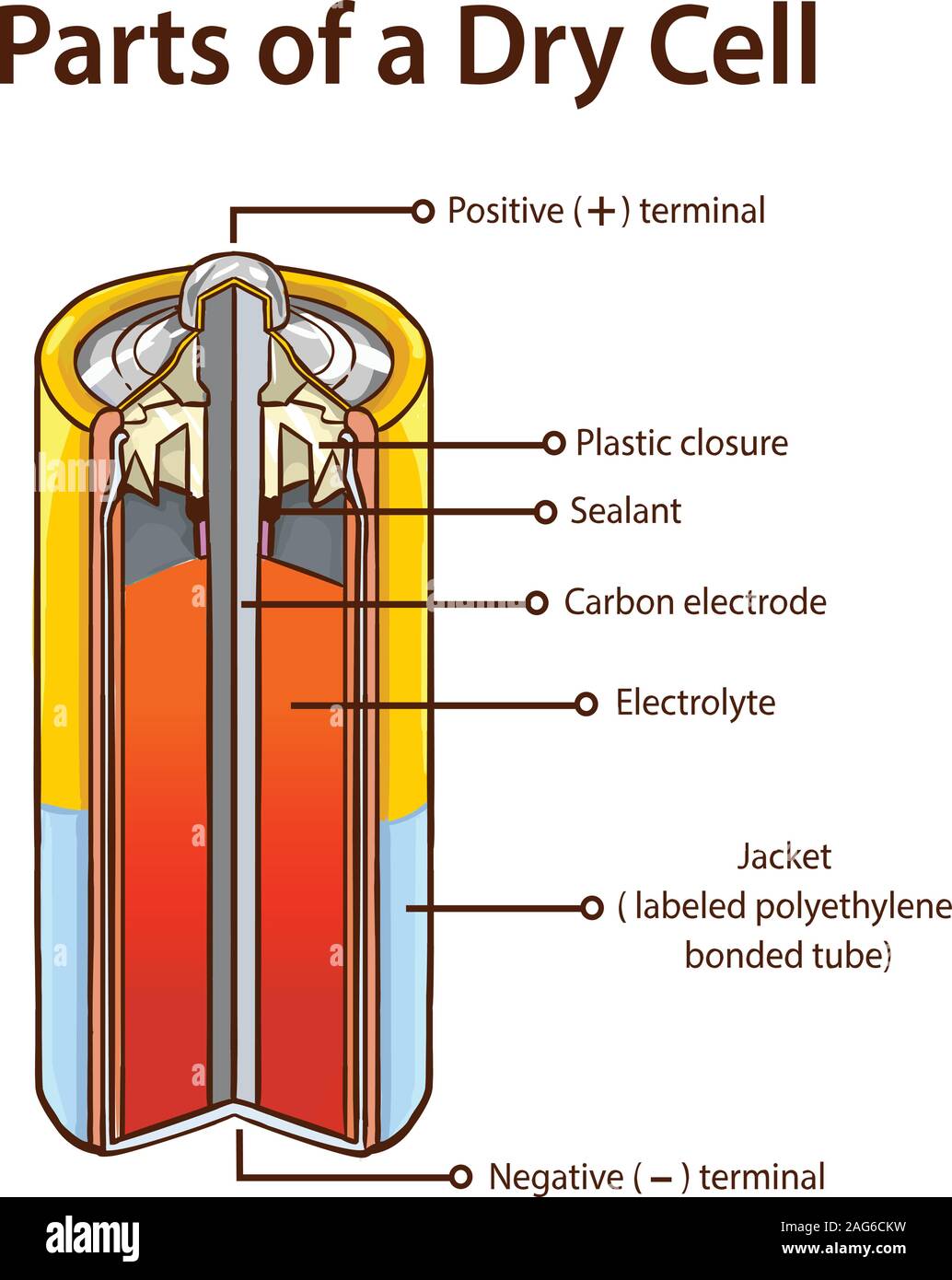
Dry Cell Battery Structure Diagram. Dry cell battery structure diagram including parts components electrical circuit anode cathode carbon electrode mixture jacket cup metal cover bottom separator sealant barrier film simple easy for science education. Image Editor Save Comp.

Dry cell battery diagram
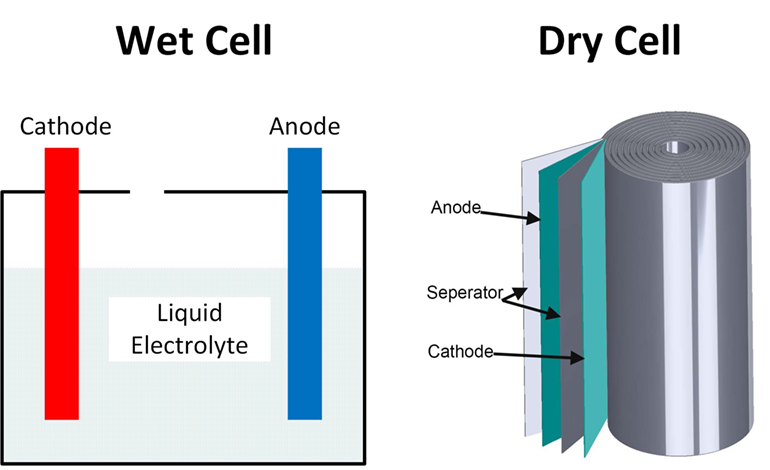
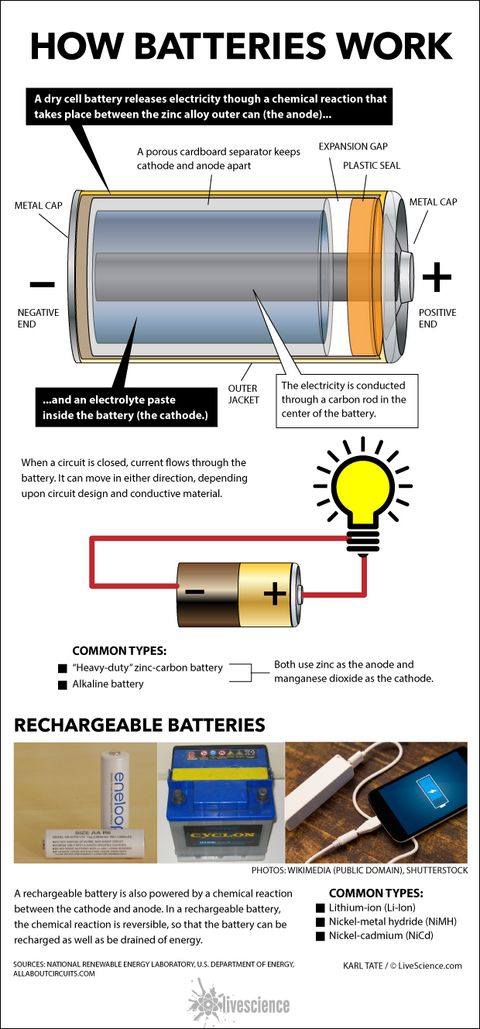
Lead-acid batteries did not achieve the safety and portability of the dry cell until the development of the gel battery. A common dry cell is the zinc-carbon battery, sometimes called the dry Leclanché cell, with a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, the same as the alkaline battery (since both use the same zinc-manganese dioxide combination). Nov 2, 2016 - A dry cell battery is a type of chemical battery that uses an electrolyte, which is in the immobilized state. The electrolyte in this cell ... The diagram shows a cross section of a flashlight battery, a zinc-carbon dry cell. Visit this site to learn more about zinc-carbon batteries. Alkaline batteries ( Figure 2 ) were developed in the 1950s partly to address some of the performance issues with zinc-carbon dry cells.
Dry cell battery diagram. 1. Use circuit symbols to construct schematic diagrams for the following circuits: a. A single cell, light bulb and switch are placed together in a circuit such that the switch can be opened and closed to turn the light bulb on. See Answer. b. A three-pack of D-cells is placed in a circuit to power a flashlight bulb. The cell and battery both store the chemical energy and then transforms the stored chemical energy into an electrical energy. One of the major difference between the cell and the battery is that the cell is the single unit, whereas the battery is the group of cells. Some other differences between them are explained below in the comparison chart. A dry cell is a type of electric battery, commonly used for portable electrical devices.It was developed in 1886 by the German scientist Carl Gassner, after development of wet zinc-carbon batteries by Georges Leclanché in 1866. The modern version was developed by Japanese Sakizō Yai in 1887.. A dry cell uses a paste electrolyte, with only enough moisture to allow current to flow. The overall voltage of the battery is therefore the sum of the voltages of the individual cells. Figure 11.5. 1: Three Kinds of Primary (Nonrechargeable) Batteries. (a) A Leclanché dry cell is actually a "wet cell," in which the electrolyte is an acidic water-based paste containing MnO 2, NH 4 Cl, ZnCl 2, graphite, and starch.
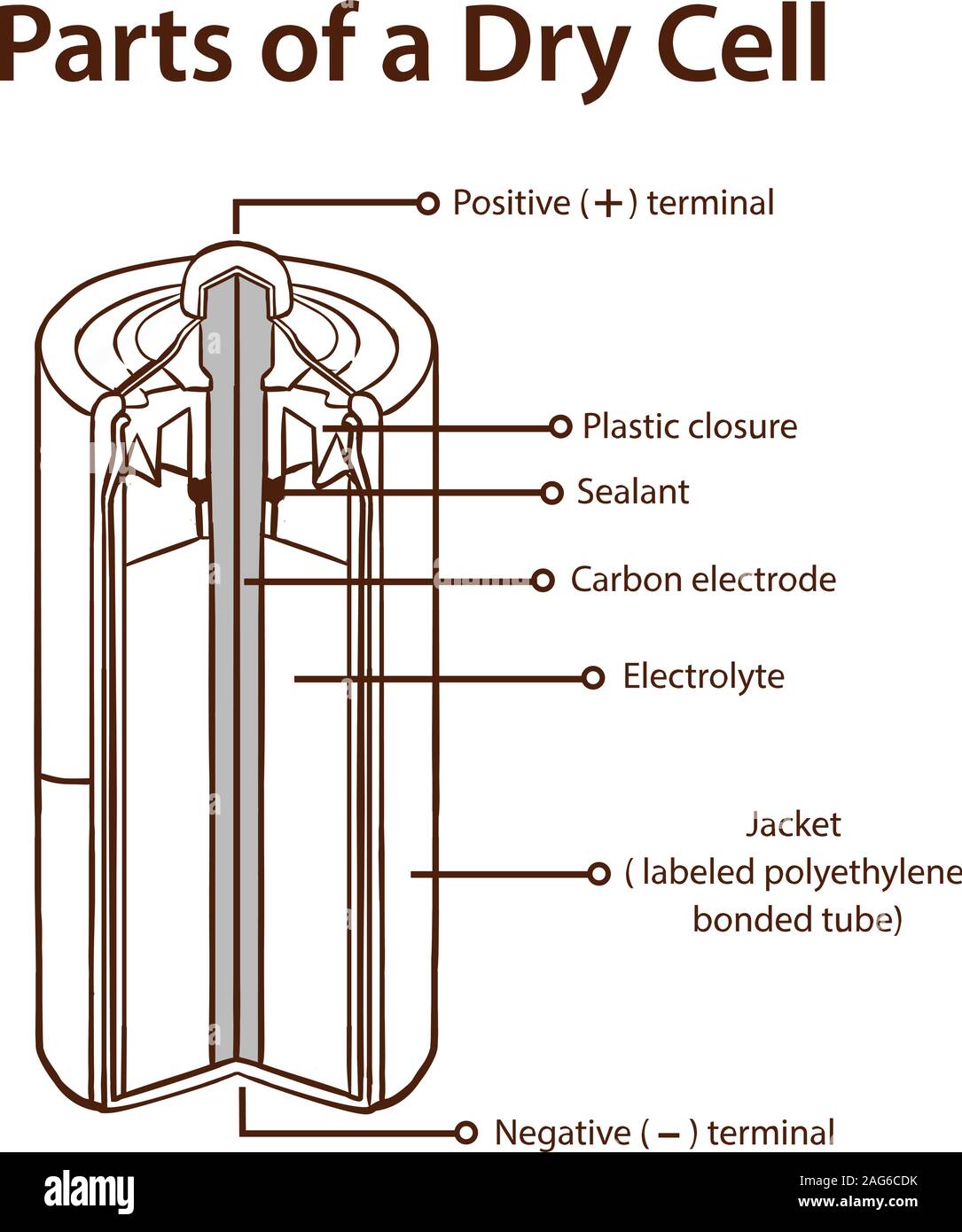
A dry cell is one type of electric battery, which is generally used for the home and portable electronic devices. A battery is a device that consists of one or more electrochemical cells, which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. A dry cell is one of the electrochemical cells, developed by the "German scientists Carl Gassner ... Draw Neat and Labelled Diagram of Dry Cell. Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (General) 12th Board Exam. Question Papers 231. Textbook Solutions 13984. MCQ Online Tests 73. Important Solutions 3704. Question Bank Solutions 14303. Concept Notes & Videos 737. Time Tables 24. Syllabus. A battery is a device that creates electrical energy by means of chemical reactions.There are two types of batteries: wet cell and dry cell. A wet cell battery operates by means of a liquid electrolyte solution, while in a dry cell battery the solution is in the form of a paste. Some wet cells can be recharged, while others are only good for a shorter period of time. - A dry cell is basically a type of an electrochemical cell or a battery which is mostly used for the house equipment and portable electronic devices. The electrolytes present in it are in the form of a paste to form low moisture immobilized electrolytes, which restricts it from flowing and the moisture is low but enough to allow the current to ...
A dry cell battery is a type of chemical battery that uses an electrolyte, which is in the immobilized state. The electrolyte in this cell battery contains very little moisture to allow the passage of current through it. This ScienceStruck post provides the history, definition, composition, uses, and recycling process of the dry cell battery. Dry Cell Battery Working Principle and Uses A dry cell is the simplest form of electricity-producing source. A number of cells combined cells together forms a battery. The lead-acid or nickel-cadmium battery is the advanced version of dry cell. This cell was first invented by French engineer Georges Leclanche in the year 1866. The dry cell battery is one of the most commonly used types, including AA, 9-volt, and watch batteries. Dry cell batteries are different from wet cells because their electrolytes are contained in a low-moisture paste, while a wet cell has electrolytes contained in a liquid, hence the difference in names.
Secondary cell/battery. Primary Cells. Primary cells produce electricity by the virtue of chemical reaction. In primary cells,the reaction occurs only in one direction, and cannot be reversed. As a result these cells become deadover a period of time. Primary cells cannot be recharged/reused. Typical primary cells are, Daniell cell, Dry cell ...
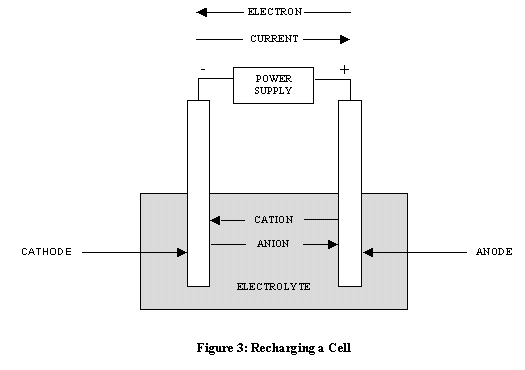
We use circuit symbols to draw diagrams of electrical circuits, with straight lines to show the wires. The diagram shows some common circuit symbols. Think of what we usually call a single battery ...
Draw neat and labelled diagram of dry cell. Medium. View solution > Explain construction and working of Dry Cell. Medium. View solution > Label the parts represented by (A), (B) and (C). Medium. View solution > In dry cell, cathode is: Easy. View solution > View more. CLASSES AND TRENDING CHAPTER.
Anatomy of a Battery. Take a look at any battery, and you'll notice that it has two terminals. One terminal is marked (+), or positive, while the other is marked (-), or negative. In normal flashlight batteries, like AA, C or D cell, the terminals are located on the ends. On a 9-volt or car battery, however, the terminals are situated next to ...
Start studying Battery Diagram (wet cell). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
This type of battery offers high performance, featuring high voltage and reliability, and a maximum amount of energy per volume that can be as high as ten times that of manganese dry batteries. Its electrolyte contains no water, allowing for use at low temperature.
Sofia, Bulgaria - 11 August 2019: Multiple used Philips AA alkaline batteries are seen. dry cell battery vector diagram. MASSA ...
The Dry Cell: A dry cell is a very convenient source of electric current. The dry cell, as its name suggests, contains dry or semi-solid ingredients. Let us take a look inside a dry cell [Fig. 14.3(a and b)]. The dry cell contains a paste of ammonium chloride inside a zinc container.
The lower diagram depicts a serial arrangement. The four batteries in series will together produce the current of one cell, but the voltage they supply will be four times that of a single cell. Voltage is a measure of energy per unit charge and is measured in volts. In a battery, voltage determines how strongly electrons are pushed through a ...
Electrochemical CellsAn electrical battery is a combination of one or more electrochemical cells, used to convert stored chemical energy into electrical ener...
The reactants in these batteries are consumed after a certain period of time, rendering them dead. A primary battery cannot be used once the chemicals inside it are exhausted. An example of a primary battery is the dry cell - the household battery that commonly used to power TV remotes, clocks, and other devices.
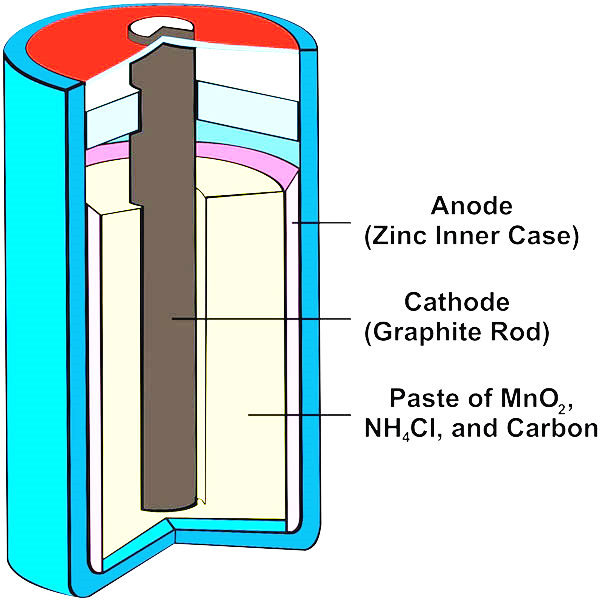
The venerable carbon-zinc cell or Lechlanche' cell was invented in 1866 and was the most common small battery throughout most of the 20th century until largely supplanted by alkaline cells.The oxidation at the zinc electrode (the anode) is straightforward and similar to that in other cells like the Daniell cell.The other reactions involve the MnO 2 which is contained near the carbon center rod ...
A common dry-cell battery is the zinc-carbon battery, which uses a cell that is sometimes called the Leclanché cell. The cell is made up of an outer zinc container, which acts as the anode. The cathode is a central carbon rod, surrounded by a mixture of carbon and manganese(IV) dioxide (MnO 2).
Alkaline Cells: Probably the most familiar of batteries is the alkaline cell. ... you get a battery with somewhere between 1.50 and 1.65 V. The diagram ...
The diagram shows a cross section of a flashlight battery, a zinc-carbon dry cell. Visit this site to learn more about zinc-carbon batteries. Alkaline batteries ( Figure 2 ) were developed in the 1950s partly to address some of the performance issues with zinc-carbon dry cells.
Nov 2, 2016 - A dry cell battery is a type of chemical battery that uses an electrolyte, which is in the immobilized state. The electrolyte in this cell ...
Lead-acid batteries did not achieve the safety and portability of the dry cell until the development of the gel battery. A common dry cell is the zinc-carbon battery, sometimes called the dry Leclanché cell, with a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, the same as the alkaline battery (since both use the same zinc-manganese dioxide combination).




























0 Response to "39 dry cell battery diagram"
Post a Comment