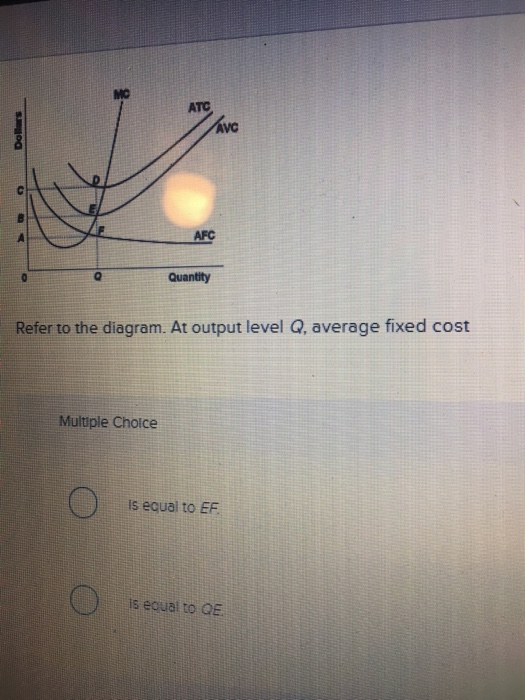
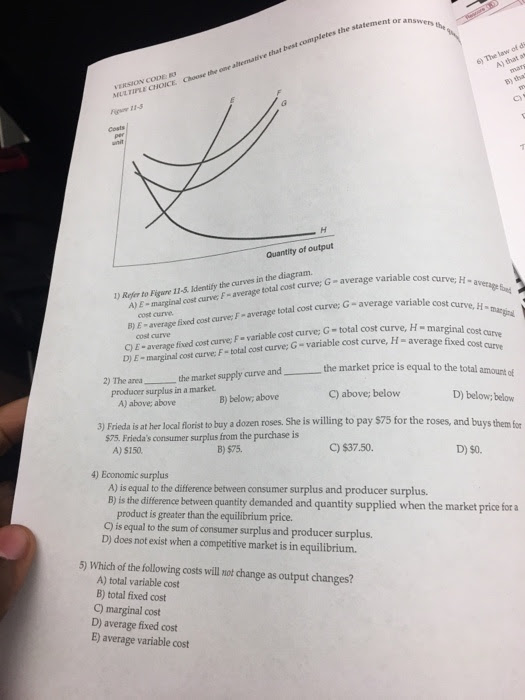
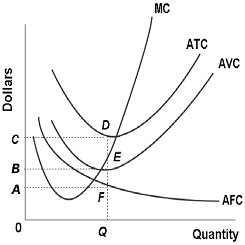
39 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is
Fixed cost and variable cost, combined, equal total cost. Revenue is the amount of money that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services (as opposed to monies from security sales such as equity shares or debt issuances). The five ways formula is to increase leads, conversation rates, average dollar sale, average number of sales and ... The law of diminishing marginal returns states that additional inputs will eventually lead to a negative impact on outputs. For it to be valid, some assumptions need to be made: All the technology involved is constant. Changing the technological tools used in production would change the marginal and average cost and value of a product.
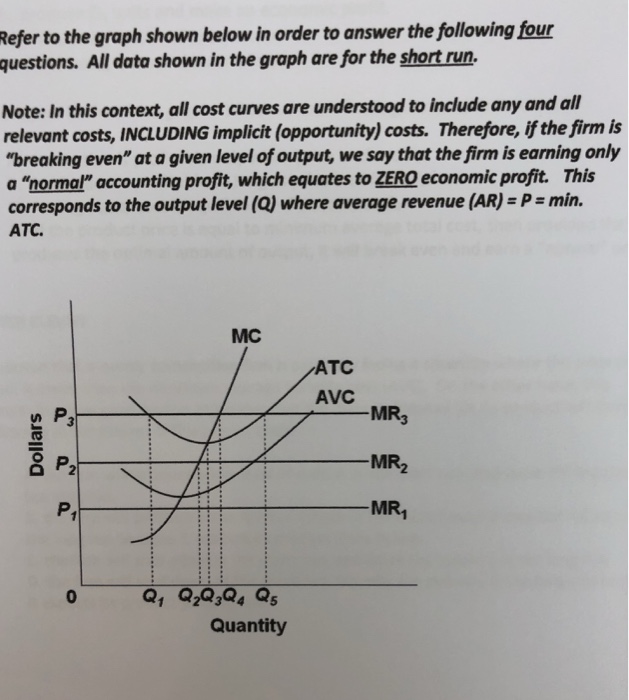
At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost: not 10 Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm.

Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is
The output of the NAND gate is always at logic high/"1″ and only goes to logic low/"0″ when all the inputs to the NAND gate are at logic 1. In other words, we can say that the output of the NAND gate always continues true if at least one of its inputs remains false or logic low. Scenario 1: Barbara is a producer in a monopoly industry. Her demand curve, total revenue curve, marginal revenue curve and total cost curve are given as follows: Q = 160 - 4 P TR = 40 Q - 0.25^ (Q^2) MR = 40 - 0.5 Q TC = 4 Q MC = 4 Refer to Scenario 1. The price of her product will be ________. A. 71. Cost which can be directly identified with and allocated to cost units or centre. a. Indirect costs. b. Direct costs. c. Product cost. d. None of the above. 72. Overheads or on cost is the total of . a. All direct expenses. b. All indirect expenses. c. Direct Expenses + Factory OH. d. None of the above. 73. Prime cost is the total of . a ...
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A. the law of diminishing returns. B. the average fixed cost at each level of output. C. marginal cost at ... Change in costs is the level of output that determines an increase or decrease in cost because when the output is high, it will lead to high costs, and vice versa, lower outputs mean lower costs. One simple reason for this is the presence of variable costs that are linked directly to the production volume and which decreases or increases ... The total cost of a business is composed of fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs and variable costs affect the marginal cost of production only if variable costs exist. The marginal cost of ... A firm experiencing economic losses will still continue to produce output in the short run as long as: A) Revenues are greater than total fixed cost. B) Price is above average variable cost. C) MR = MC. D) All of the above. Refer to the above diagram. At P 2, this firm will: A. produce 44 units and realize an economic profit.
To determine the total variable cost the company will spend to produce 100 units of product, the following formula is used: Total output quantity x variable cost of each output unit = total variable cost. For this example, this formula is as follows: 100 x 37 = 3,700. This means that the total variable cost required to produce 100 units is $3,700. The average cost is calculated by dividing total cost by the number of units a firm has produced. The short-run average cost (SRAC) of a firm refers to per unit cost of output at different levels of production. To calculate SRAC, short-run total cost is divided by the output. SRAC = SRTC/Q = TFC + TVC/Q. Where, TFC/Q =Average Fixed Cost (AFC) and. Let us now see how to implement the following Boolean function by using basic logic gates. F = (A + B) . (A + B) In the given function, we have a complement term, B. So, to represent the compliment input, we are using the NOT gates at the input side. And to represent the sum term, we use OR gates. Data visualization provides a good, organized pictorial representation of the data which makes it easier to understand, observe, analyze. In this tutorial, we will discuss how to visualize data using Python. Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
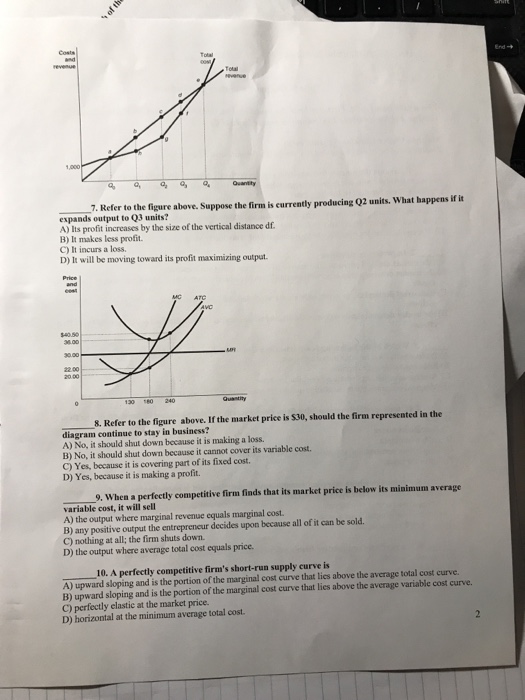
Marginal revenue can be defined as the revenue generated from sale of the last unit of output, on the other hand, marginal cost can be described as the cost incurred in the production of one additional unit of output. Both TR and TC functions involve a common variable, which is output level (Q). The average total cost curve is above the marginal cost curve. C) Diminishing returns occur with greater output. D) There are diseconomies of scale. In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market. Use both diagrams to answer the indicated questions. Figure 8.1 . 18 ... Marginal cost is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in quantity. Let us say that Business A is producing 100 units at a cost of $100. The business then produces at additional 100 units at a cost of $90. So the marginal cost would be the change in total cost, which is $90. The variable cost to make all of the cakes is $72. If Pierre's recipe makes 6 dozen cakes (72 cakes), the variable cost per unit would be $1. Variable cost/total quantity of output = x variable cost per unit of output. Variable cost per unit = = $72/72 = $1.
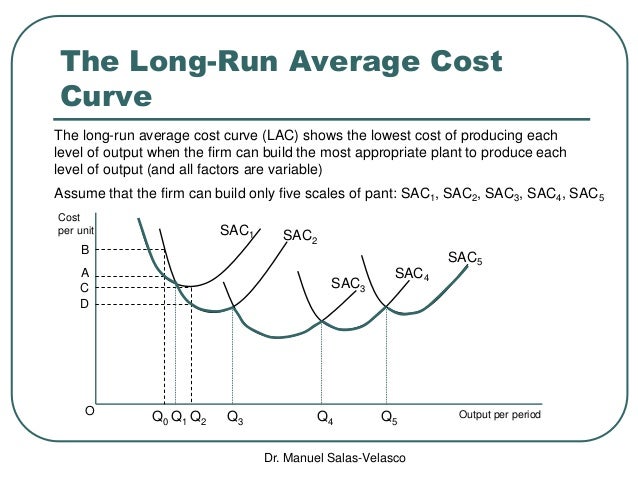
the given level of cost, output level Q 3 is unattainable. And, neither output level Q 0 nor level Q 1 would be chosen, since higher levels of output can be produced with the fixed cost outlay. The highest possible output with the given level of cost is produced by using L …
Refer to the above diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S t is a supply curve comprising all costs of production, including external costs. Assume that the number of people affected by these external costs is large. Without government interference, this market will result in: A. an overallocation of resources to this product. B. an optimal allocation of society's resources. C. a ...
Net income formula. Net income is your company's total profits after deducting all business expenses. Some people refer to net income as net earnings, net profit, or simply your "bottom line" (nicknamed from its location at the bottom of the income statement).It's the amount of money you have left to pay shareholders, invest in new projects or equipment, pay off debts, or save for ...
At output level Q, the total variable cost is OBEQ. It is because OQ is the quantity that the firm is producing at... See full answer below.1 answer · Top answer: The correct answer is A) OBEQ At output level Q, the total variable cost is OBEQ. It is because OQ is the quantity that the firm is producing at...
In the above diagram, the variable cost curve starts from zero. It means when output is zero, the variable cost is zero, but as production increases the variable cost increases. It keeps rising to the point that economies of scale cannot lower the per unit cost anymore hence the steep incline. D. Marginal Cost
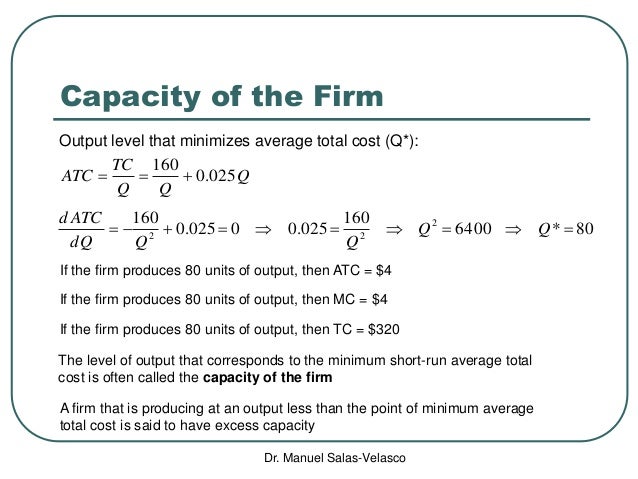
Long-run average total cost is a calculation that shows the average cost per unit of output for production over a lengthy period. A goal of both company management and investors is to determine ...
Total price: $ 26. free inquiry. Features Format. FREE bibliography page; FREE title page; FREE formatting (APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago/Turabian) 24x7 support; Part-by-part payment ; PowerPoint slides; Review your writer’s samples; Approx. 275 words / page; Font: 12 point Arial/Times New Roman; Double and single spacing; 10+ years in academic writing. 515 writers active. 97.12% orders ...
22.09.2021 · At zero level of output Total Cost of Production is equal to-(a) Total Fixed Cost (b) TotalVariableCost (c) Marginal Cost (d) Explicit Cost. 259. Total Fixed Cost Curve is indicated by a-(a) Positively sloped Curve (b) Vertical Straight Line Curve (c) Horizontal Straight Line Curve (d) Negatively sloped Curve. 260. Total cost curve shoots from a point on Y-axis means-(a) we are referring to ...
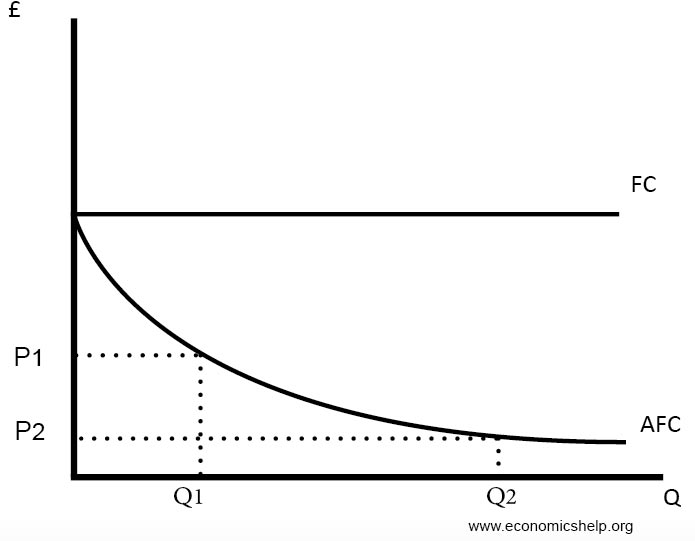
We now consider average variable cost (AVC) which is arrived at by dividing total variable cost by output, i.e., AVC= — TVC/Q . In Fig. 14.4, AVC is a typical average variable cost curve. Average variable cost first falls, reaches a minimum point (at output level Q 2) and subsequently increases.
Formula of Variable Cost. The formula to calculate variable cost is: Total Variable Cost = Total Quantity of Output * Variable Cost Per Unit of Output. To recognize variable costs, it is important ...
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total fixed cost is: 2 answers. QUESTION. Average total cost and marginal cost express info that is already contained in a firm's total cost. 3 answers. Subjects. Arts and Humanities. Languages. Math. Science. Social Science. Other. Features.
Refer below for MCQ Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs with solutions. ... If the output levels at which short-run marginal and average cost curves reach a minimum are listed in order from smallest to greatest, then the order would be ... Question. Short-run average variable cost is equal to (a) total variable cost divided by ...
The average variable cost (AVC) is the total variable cost per unit of output. This is found by dividing total variable cost (TVC) by total output (Q). Total variable cost (TVC) is all the costs ...
The marginal cost may first decline, as in the diagram, if the additional cost per unit is high if the firm operates at too low a level of output, or it may start flat or rise immediately. At some point, the marginal cost rises as increases in the variable inputs such as labor put increasing pressure on the fixed assets such as the size of the building. In the long run, the firm would increase ...
Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Production and Costs Class 11 Economics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
To understand how to calculate total cost, you will need to know two terms: Fixed cost: A cost that is constant and already set in stone, such as the cost of leasing a warehouse or the cost of renting an apartment. Variable cost: The opposite of fixed cost: A cost that changes based on how many goods the company produces or how much of a service or additional services a person uses.
Marginal cost intersects average fixed cost at the latter's minimum point. Page 31. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is:.35 pages
Both the combinations Q and P produce the same level of total output. But the combination Q represents more of capital and labor than P. combinations Q must therefore be expensive and would not be chosen. The same argument can be made to rule out combination T or any other combination lying on a portion of the isoquant where the slope is positive.
Scenario 2: The production function for earthquake detectors (Q) is given as follows: Q = 4K 1/2 L 1/2, where K is the amount of capital employed and L is the amount of labor employed.The price of capital, P K, is $18 and the price of labor, P L, is $2 Refer to Scenario 2.Suppose that in order to produce Q=48 detectors 16 units of labor and 9 units of capital were being used.
The Sunshine Corporation finds that its costs are $40 when it produces no output. Its total variable costs (TVC) change with output as shown in the accompanying table. Use this information to answer the following question(s). Refer to the above information. The total cost of producing 3 units of output is:
0CDQ d. 0AFQ Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total fixed cost is: a. 0BEQ b. BCDE c. 0BEQ-0AFQ d. 0CDQ ...
Short- and Long-Run Cost Functions. To understand short and long run cost functions, it is important to understand the concept of cost. A cost is the value of inputs that are used to produce output. Total cost (TC) is the total cost of producing a given level of output and is divided into total fixed cost (TFC) and total variable cost (TVC).
A flexible budget recognizes the difference between fixed, semi-fixed and variable cost and is designed to change in relation to the change in level of activity. True. 29. Sales budget, normally, is the most important budget among all budgets. True. 30. Flexible budgets change with the level of activity. True. 31.
Cost Function Formula. The following is the typical cost function associated with producing goods. C (x) = FC + x * VC. Where C (x) is the total cost at x number of units. FC is the fixed cost. x is the total number of units. VC is the average variable cost per unit. This is considered the most standard cost function, but a cost function can be ...
Microeconomics Quiz 24.pdf - 70 Award 1.00 point Refer to the diagram At output level Q total variable cost is 0BEQ BCDE 0CDQ 0AFQ References Multiple | Course Hero
AVC = VC / Q. In the above formula, AVC refers to the average variable cost, VC refers to the total variable cost, and Q refers to the output. Additionally, for any firm, the short-term total costs (TC) can be classified as either fixed costs (FC) or variable costs (VC). This is represented by this formula:
71. Cost which can be directly identified with and allocated to cost units or centre. a. Indirect costs. b. Direct costs. c. Product cost. d. None of the above. 72. Overheads or on cost is the total of . a. All direct expenses. b. All indirect expenses. c. Direct Expenses + Factory OH. d. None of the above. 73. Prime cost is the total of . a ...
Scenario 1: Barbara is a producer in a monopoly industry. Her demand curve, total revenue curve, marginal revenue curve and total cost curve are given as follows: Q = 160 - 4 P TR = 40 Q - 0.25^ (Q^2) MR = 40 - 0.5 Q TC = 4 Q MC = 4 Refer to Scenario 1. The price of her product will be ________. A.
The output of the NAND gate is always at logic high/"1″ and only goes to logic low/"0″ when all the inputs to the NAND gate are at logic 1. In other words, we can say that the output of the NAND gate always continues true if at least one of its inputs remains false or logic low.














0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram. at output level q, total variable cost is"
Post a Comment