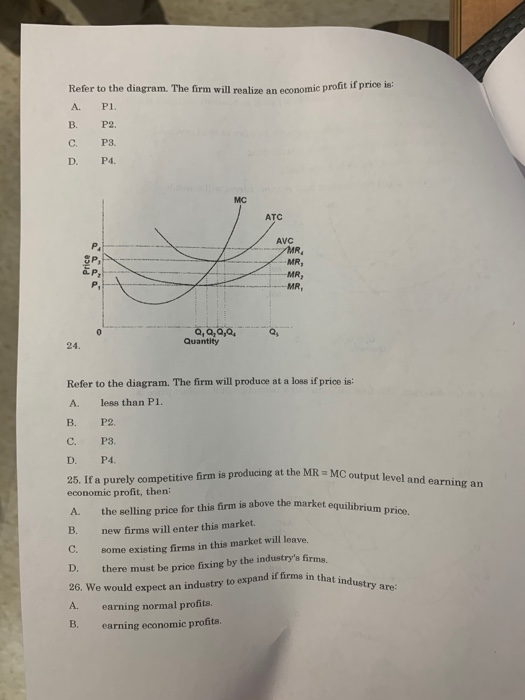
36 at p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce
If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A) lose P1P 2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B) lose P1P 2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. Practice Questions and Answers from Lesson I -6: The Market Strikes Back . 2 . quality of their apartments in order to increase rents. b. The income-supplement policy causes a rightward shift of the demand curve from
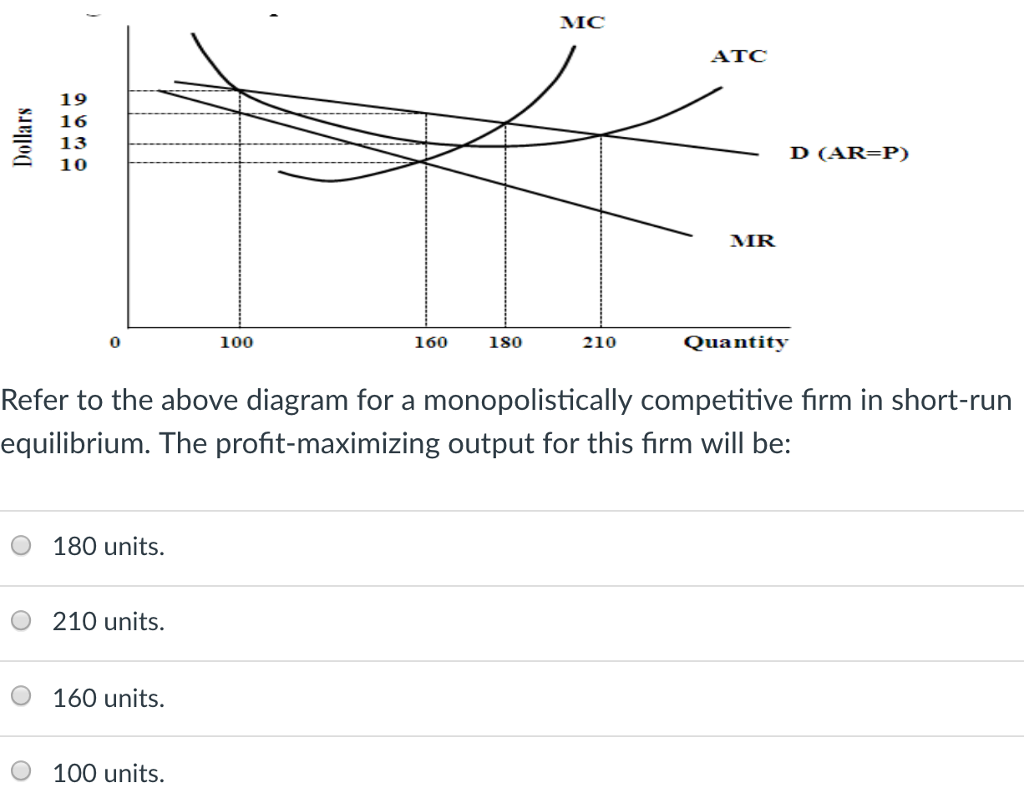
105. Refer to the above diagram. At P2, this firm will: A) produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. B) produce 44 units and earn only a normal profit. C) produce 66 units and earn only a normal profit. D) shut down in the short run. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 106. Refer to the above diagram. At P1, this firm will produce:

At p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce
At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. At 3 units of output, total ... If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm will produce: 1. 4 units at a loss of $109. 2. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 3. 8 units at a loss of $48.80. 4. zero units at a loss of $100. 2. Refer to the above data. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce: Therefore, if Firm 1 can move first, it does best to select "aggressive" in which case Firm 2 will select its best response "passive" earning Firm 1 a payoff of 33 and Firm 2 a payoff of 10. The Subgame perfect equilibrium: In period 2 Firm 2 will choose "passive" if Firm 1 chooses "aggressive" in period 1.
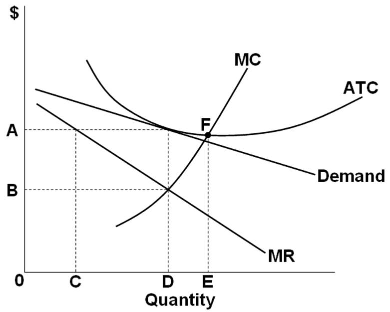
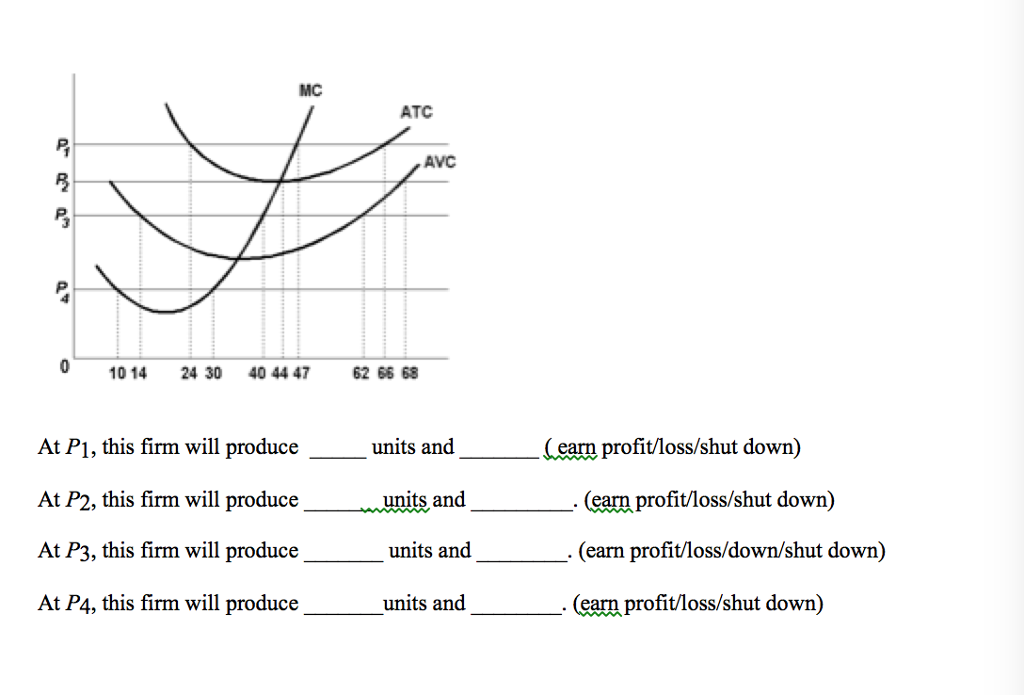
At p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. The accompanying graph (top of next page) summarizes the demand and costs for a firm that operates in a perfectly competitive market. a. What level of output should this firm produce in the short run? b. What price should this firm charge in the short run? c. What is the firm's total cost at this level of output? d. 6) Refer to Figure 12-9. At price P 1 , the firm would produce A) Q 1 units B) Q 3 units. C) Q 5 units. D) zero units. Answer: D. 7) Refer to Figure 12-9. At price P 1 , the firm would A) lose an amount equal to its fixed cost. B) lose an amount more than fixed cost. C) lose an amount less than fixed cost. 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will make economic profit Refer to the accompanying diagram. This firm will earn less than a normal profit if product price is Less than P3 Refer to the accompanying diagram. The firm will produce nothing in the short run if price is less than p1 At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will
66. Refer to the above diagrams. The demand for Firm A's product is perfectly elastic. True False 67. Refer to the above diagrams. The demand for Firm B's product is elastic at all prices in excess of $4. True False 68. Refer to the above diagrams. Firm B's average revenue curve coincides with its marginal revenue curve. True False 69. The firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least as much as the price indicated by the distance: a. F. b. E. c. N. d. P. e. G. ... In the accompanying diagram, this is optimal for prices in the range from 0 to P1. b. The firm operates in the short run despite sustaining 41. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If product price is $60, the firm will A) produce 3 units and incur a $40 loss. B) shut down. C) produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. D) produce 4 units and realize a $120 economic profit.
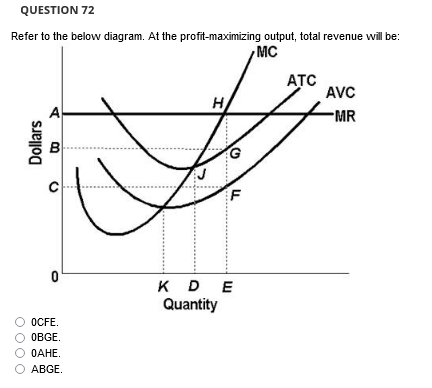
70. Refer to the above diagram. At P1, this firm will produce: A. 47 units and break even. B. 47 units and realize an economic profit. C. 66 units and earn only a normal profit. D. 24 units and earn only a normal profit. If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will A) produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40. B) produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00. C) shut down in the short run. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce 66 units and earn only a normal profit. 24 units and earn only a normal profit. 47 units and break even. 47 units and realize an economic profit. At P2 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will A. produce 44 units and realize an economic profit. B. produce 44 units and earn only a normal profit. C. produce 68 units and earn only a normal profit. D. shut down in the short run.
Firm 1 and firm 2 produce horizontally differentiated products. The demand for firm 1's product is given by the equation Q_1 = 100 - P_1 + \frac{P_2}{2}. The demand for firm 2's product is given by...
120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
To find the Stackelberg equilibrium in which Firm 1 is the leader, we start by writing the expression for Firm 1's total revenue: TR = (280 - 2Y - 2X)X In place of Y, we substitute in Firm 2's reaction function: Y = 60 - 0.5X TR = [280 - 2(60 - 0.5X) - 2X]X = (160 - X)X Firm 1's marginal revenue is therefore MR = 160 - 2X ...
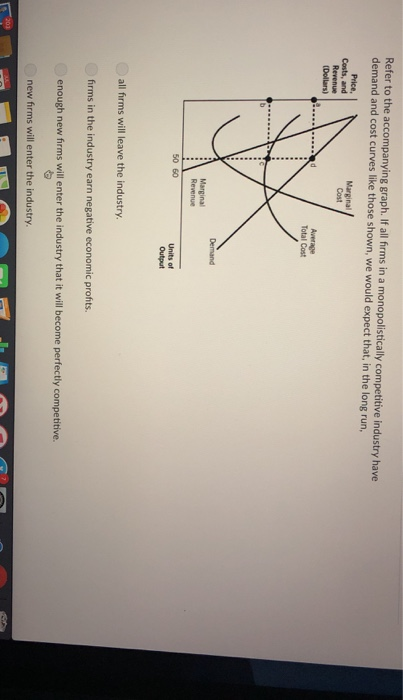
That's because that when firm produce the output level where MR=MC (output level Q), price is greater than average variable cost. The loss from continuing the business is lower than the loss from totally shutting down. 2. (3.6 page 406) According to a report in the Wall Street Journal, during the fourth quarter of 2003,
Award: 1.00 point At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce 14 units and realize an economic profit. produce 62 units and earn only a normal profit. produce 40 units and incur a loss. shut down in the short run.
25. Refer to the above diagram. The firm will produce at a loss if price is: A. less than P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4. 26. Refer to the above diagram. The firm's supply curve is the segment of the: A. MC curve above its intersection with the AVC curve. B. MC curve above its intersection with the ATC curve.
At P 1 in the accompanying diagram this firm will produce A 47 units and break from AA 1
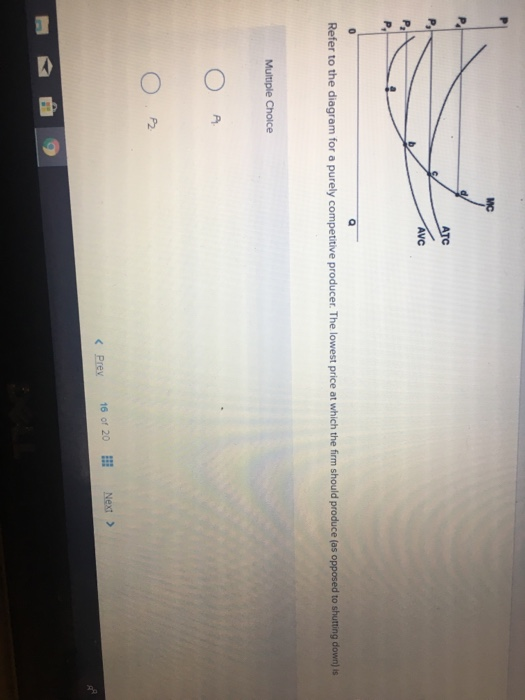
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: A. Above P1. B. Above P3. C. Above P4. D. Between P2 and P3. 21. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3: A.
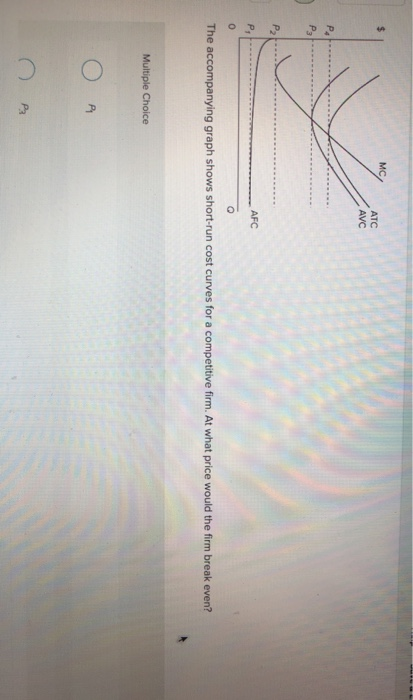
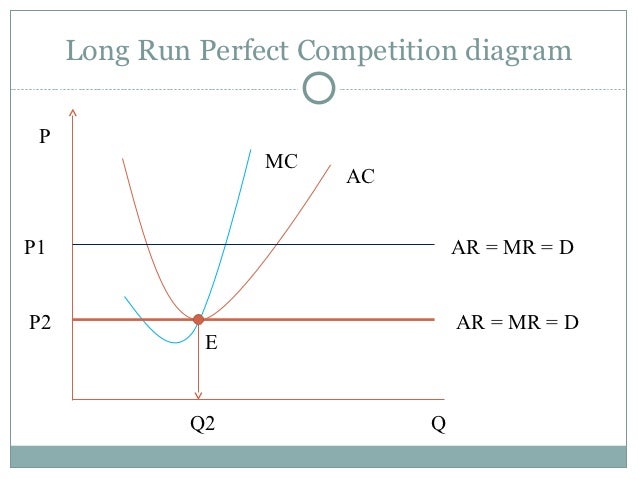
The shut down price is the minimum price a business needs to justify remaining in the market in the short run. A business needs to make at least normal profit in the long run to justify remaining in an industry but in the short run a firm will continue to produce as long as total revenue covers total variable costs or price per unit > or equal to average variable cost (AR = AVC).
A2 Micro Business Economics Diagrams Advice on drawing diagrams in the exam • The right size for a diagram is ½ of a side of A4 - don't make them too small - if needed, move onto a new side of paper rather than squeezing a diagram in at the bottom of a page
Therefore, if Firm 1 can move first, it does best to select "aggressive" in which case Firm 2 will select its best response "passive" earning Firm 1 a payoff of 33 and Firm 2 a payoff of 10. The Subgame perfect equilibrium: In period 2 Firm 2 will choose "passive" if Firm 1 chooses "aggressive" in period 1.
If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm will produce: 1. 4 units at a loss of $109. 2. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 3. 8 units at a loss of $48.80. 4. zero units at a loss of $100. 2. Refer to the above data. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce:
At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. At 3 units of output, total ...

















0 Response to "36 at p1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce"
Post a Comment