36 force diagram roller coaster loop
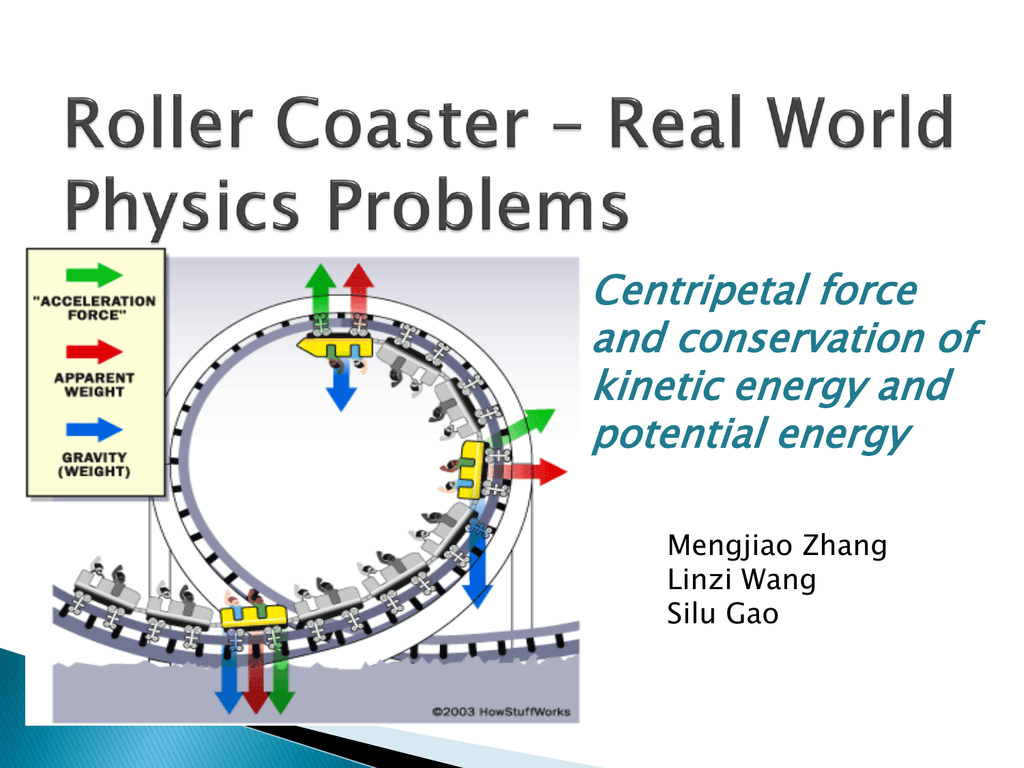
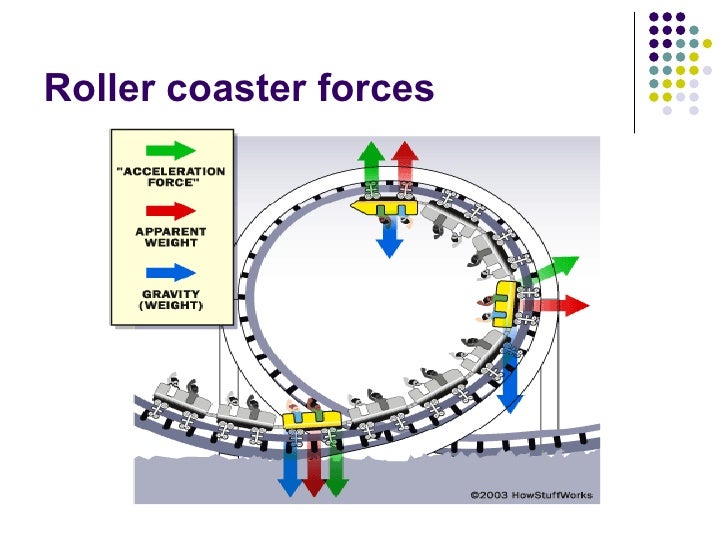
body diagram is the same in the two situations at the top of the loop. . Note that the normal force at the bottom is larger than it is at the top. This difference is enhanced by the fact that the speed of the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop is larger than the speed at the top. The loop-the-loop in a roller coaster acts exactly the same way as a merry-go-round. As you approach the loop, your inertial velocity is straight ahead of you. But the track keeps the coaster car, and therefore your body, from traveling along this straight path. The force of your acceleration pushes you from the coaster-car floor, and your ...
Second, we made an assumption that the coaster loop sits on the surface of the Earth because, as shown in the diagram, the distance between the center of the Earth and the car when it is at the ...

Force diagram roller coaster loop
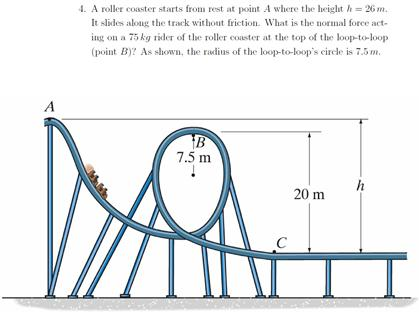
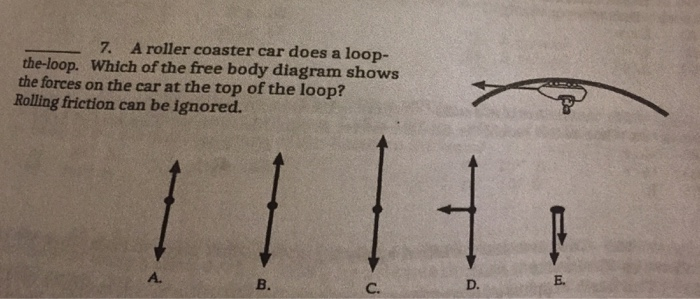
Roller Coaster Loop Problem. A roller-coaster car initially at position a position on the track a height h above the ground begins a downward run on a long, steeply sloping track and then goes into a circular loop of radius R whose bottom is a distance d above the ground. Ignore friction. This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the normal force at the bottom and at the top of the hill given the speed and radius of the circular hi... Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N +(- mg) ...
Force diagram roller coaster loop. 9 Jan 2020 — Energy In this problem, energy is conserved as gravity is a conservative force. Normal force does no work as it will be acting perpendicular ... Which statement identifies the net centripetal force on a roller coaster car while it is at the top of a vertical, circular loop? ... In which free-body diagram are the forces correct on a roller coaster car when it is upside down at the top of the . The roller coaster loop problem in this paper is more realistic than many textbook problems, but is still an idealization of real roller coasters, which are never completely friction-less. The center of mass in the train moves with a smaller radius than the radius of the track and the position in the train influences the forces on the rider. Sophia, whose mass is 52 kg, experienced a net force of 1800 N at the bottom of a roller coaster loop during her school's physics field trip to the local amusement park. Determine Sophia's acceleration at this location. Also determine the Fnormal acting on her at this point in time.
Force Diagram Roller Coaster Loop 26.12.2018 4 Comments Roller coaster loops assume a tear-dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as As depicted in the free body diagram, the magnitude of Fnorm is always. Energy conservation and forces on a train in a vertical roller coaster loop. . Think about a roller coaster going around a loop. Because of the force of gravity, the speed of the coaster in the circular path is not constant. The coasters car accelerated on the downward path and decelerates on the upward part. The speed is a minimum at the top of the loop and a maximum at the bottom of the loop. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. First of all, to get through the loop, a coaster must be moving at a certain velocity. That way, it can get through the loop in the first place. How the loop works is a matter of centripetal force, or circular force. Your inertia is going outwards, but your seat exerts positive G forces as it pulls you through the loop.
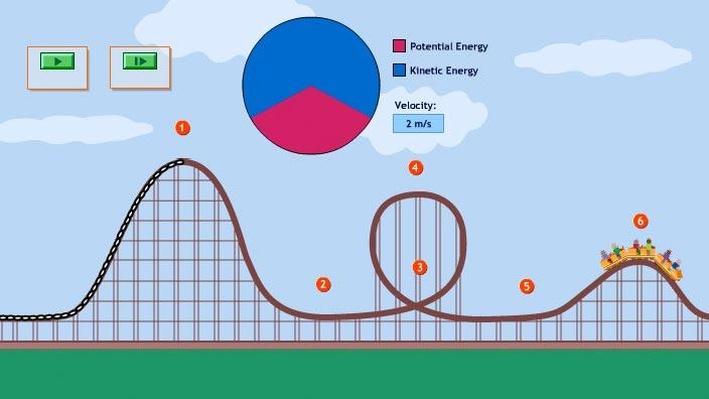
Potential and Kinetic Energy: Roller Coasters Teacher Version This lab illustrates the type of energy conversions that are experienced on a roller coaster, and as a method of enhancing the students' understanding of that concept, they will create their own roller coasters to test out their ideas. California Science Content Standards: • 1 ... What forces supply the centripetal force in a vertical roller coaster loop? What's the minimum velocity to make it around the loop? Examine the picture of the forces acting on a roller coaster. Please write a paragraph response about the forces that are labeled in the diagram and how they are related to the functionality, physics, and experience of the ride. ... When you are on a roller coaster and you go on big loop. Gravity is pushing down on you. This will involve a two-step process: first the net force (magnitude and direction) must be determined; then the net force must be used with the free body diagram to determine the normal force. This two-step process is shown below for the top and the bottom of the loop. Bottom of Loop F net = m * a F net = (864 kg) * (26.3 m/s 2, up)
Draw a quantitative force diagram for the child. 5. Exiting the loop at valley "e" the 2000 kg rollercoaster exerts a downward normal force on the track of 90,000 N. The track radius is 130 meters. Draw a quantitative force diagram for the rollercoaster train. 6. At the top of hill "f" the rollercoaster crests the 5-meter radius curve ...
The roller coaster's trajectory bends downwards because there are downward-acting forces, pointing towards the center of the loop. If it's not going fast enough, the car will fall off the track, and move on a slightly different downward-bending trajectory because of gravity.
The figure shows the roller-coaster free-body diagram at the bottom of the loop. ! Since the net force is toward the center (upward at this point), n> F G . This is why you "feel heavy" at the bottom of the valley on a roller coaster. ! The normal force at the bottom is larger than mg. Slide874$ CHAPTER8_LECTURE8.1$ 12
diagrams on your roller coaster picture that show the different forces. You may want to choose 2 of the various locations: the ball/car at rest on the starting point, the ball/car going down a hill, a ball/car in the loop, the ball/car going the home stretch (before it stops).
We might ask how fast the coaster can go until the rider just (barely) looses contact with the seat. That means the normal force between seat and rider is zero. That occurs for. n = mg - m v 2 / r = 0. m v 2 / r = mg. v 2 / r = g. v 2 = g r. We have described this with a diagram showing a guest on the top of a hill of a roller coaster.
Physics. Physics questions and answers. Review I Constants I Periodic Table You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop. Part A Determine the direction of the acceleration at the bottom of the loap. upward Odownward Previous Answers Submit Correct Part B Construct a force diagram for this position. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot.
The free-body diagrams for these two positions are shown in the diagrams at the right. The magnitude of the force acting on the roller coaster car (or passenger) can be calculated using the formula FGRAV=m.g, where the acceleration due to gravity is represented by g (where g=9.8 m/s 2 ).
Sketch a free-body diagram for just the water, if the speed is less than the critical speed. a = g "down" is down. mg m. b. g. N=0. If same . v. o, same path! Roller coaster. On a roller coaster, when the coaster is traveling fast at the bottom of a circular loop, you feel much heavier than usual. Why? Draw a free-body diagram and apply ...
This will involve a two-step process: first the net force (magnitude and direction) must be determined; then the net force must be used with the free body diagram to determine the normal force. This two-step process is shown below for the top and the bottom of the loop. Bottom of Loop Fnet= m * a Fnet= (1000 kg) * (20 m/s2, up) Fnet= 20 000 N, up
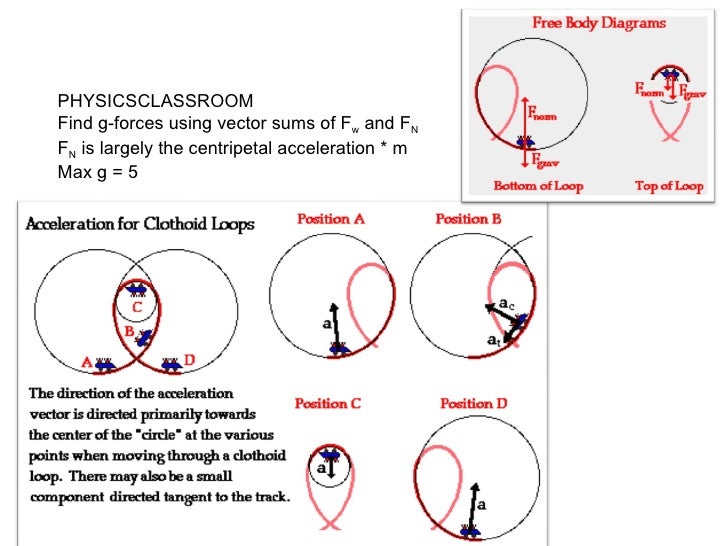
The diagram below depicts the free-body diagrams for a rider at four locations along the loop. The diagram also shows that the vector sum of the two forces (i.e., the net force) points mostly towards the center of the loop for each of the locations.
When an object (such as a roller coaster car) travels at constant speed along a circle, the magnitude of the centripetal force on the car is constant. The normal force (directed toward the center of the circle) is given by the sum of the centripetal force and the radial component of the weight. Both these forces vary along the loop.
How does a roller coaster loop work? When an object moves in a circle, which is effectively what a roller coaster does when it travels through a loop, the moving object is forced inward toward what's called the center of rotation. It's this push toward the center—centripetal force—that keeps an object moving along a curved path.
Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N +(- mg) ...
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the normal force at the bottom and at the top of the hill given the speed and radius of the circular hi...
Roller Coaster Loop Problem. A roller-coaster car initially at position a position on the track a height h above the ground begins a downward run on a long, steeply sloping track and then goes into a circular loop of radius R whose bottom is a distance d above the ground. Ignore friction.

The Georgetown loop is nestled high in the rocky mountains 45 miles west of Denver off interstate 70.














0 Response to "36 force diagram roller coaster loop"
Post a Comment