40 transition states energy diagram
Transition state theory (TST), also called activated complex theory, is often introduced in general chemistry courses when discussing kinetics. A reaction energy diagram is used to follow the progress of the reaction from reactants through a transition state to products (see figure 1). The reaction energy diagram plots the Diagrams like this are described as energy profiles. In the diagram above, you can clearly see that you need an input of energy to get the reaction going. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic. If you had an endothermic reaction, a simple energy profile for a non …
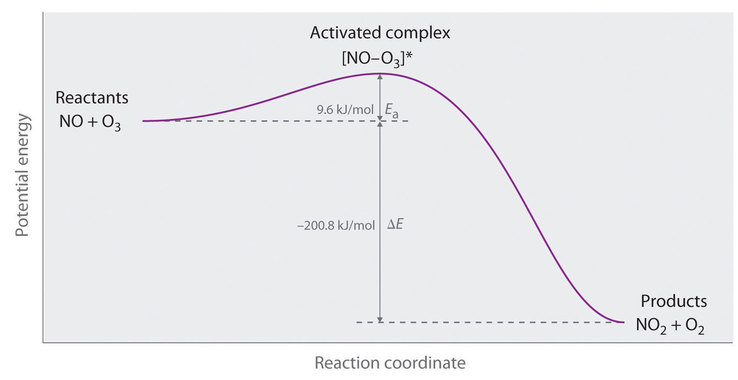
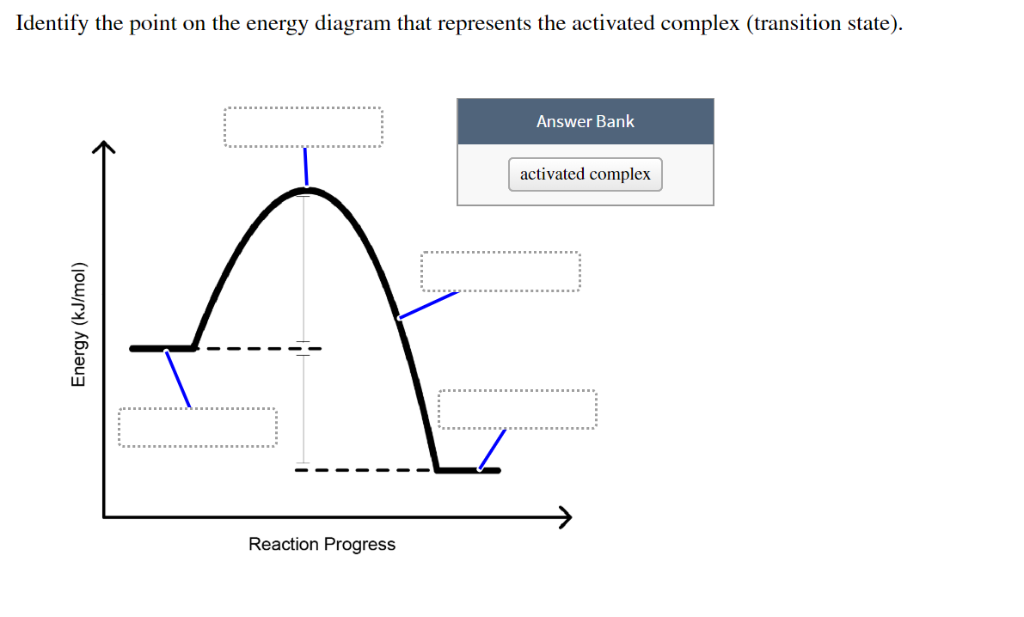
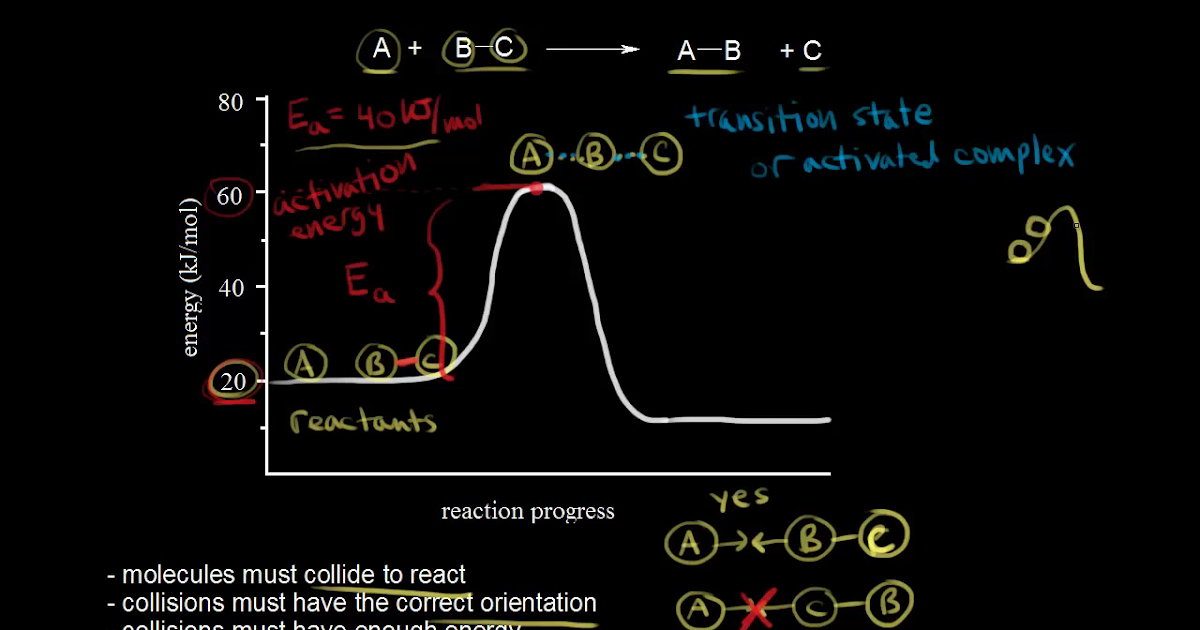
This particular intermediate configuration of atoms or molecules with the maximum value of potential energy is called activated complex and the state is defined as transition state. I m a g e w i l l b e U p l o a d e d S o o n Now the diagram above shows the transition state of a chemical reaction taking place.

Transition states energy diagram
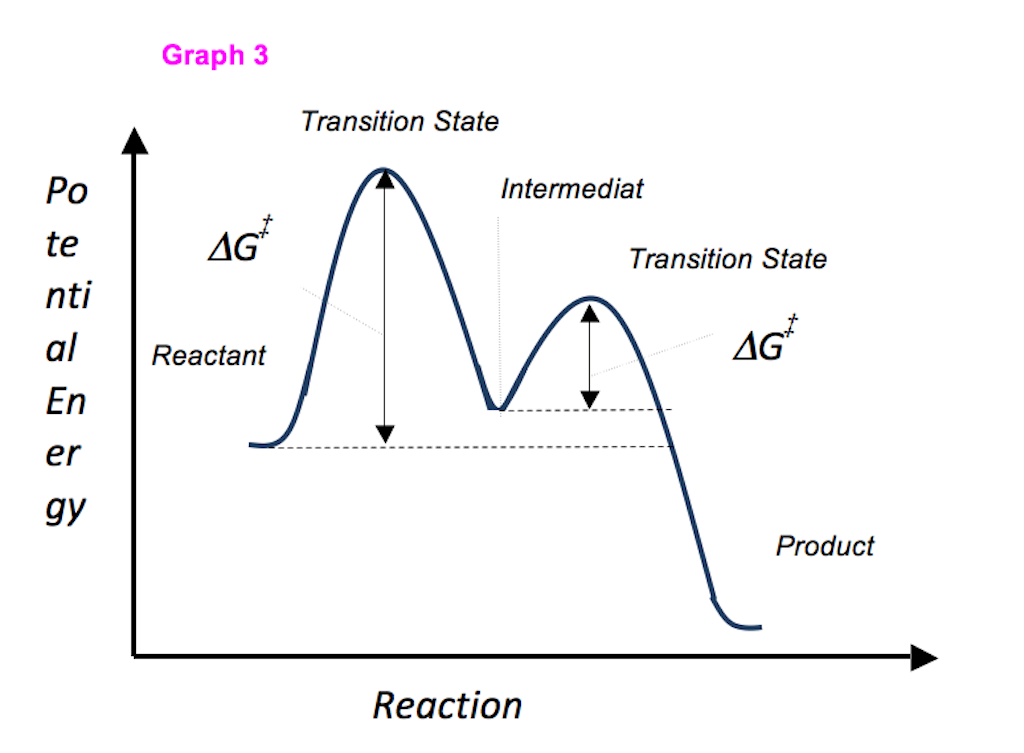
A reaction starting from reactants that change into products must pass through an unstable state at the highest energy level; this is called a transition state.A certain amount of energy is required to overcome the energy barrier, and this energy, called activation energy, is represented by ΔG ‡.The magnitude of ΔG ‡ determines the rate of a chemical reaction. Quantized energy levels result from the wave behavior of particles, which gives a relationship between a particle's energy and its wavelength.For a confined particle such as an electron in an atom, the wave functions that have well defined energies have the form of a standing wave. States having well-defined energies are called stationary states because they are the states … Transition state and energy diagram of an reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. Due to their extremely short lifetime, transition states cannot be measured directly. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. Their lifetime does not last any longer than one molecular vibration, which is approximately 10 -12 s.
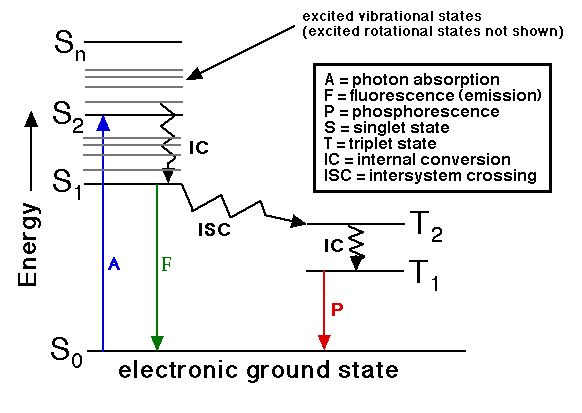
Transition states energy diagram. The active intermediate is shown in transition state at the top of the energy barrier. A class of reactions that also goes through a transition state is the S N2 reaction. A. The Transition State ... The entire energy diagram for the ABC system is shown in 3-D in Figure PRS.3B-3. Fig. 6-1. Energy level diagram of some of the excited states of the 12C nucleus. The angular momentum (J), parity (P), and isospin (T) quantum numbers of the states are indicated on the left using the notation J P. P and n respectively at the top of the diagram indicate the separation energies for a proton and a neutron. UCI Chem 51A Organic Chemistry (Fall 2009)Lec 19. Organic Chemistry -- Energy Diagrams, Transition States, and Reaction RatesView the complete course: http:/... Aug 15, 2020 · It is indicated on a Jablonski diagram as a straight line going down on the energy axis between electronic states. Fluorescence is a slow process on the order of 10 -9 to 10 -7 seconds; therefore, it is not a very likely path for an electron to dissipate energy especially at electronic energy states higher than the first excited state.
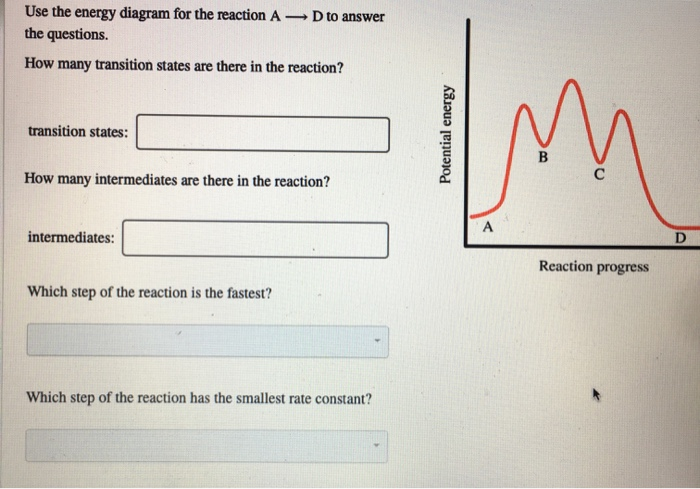
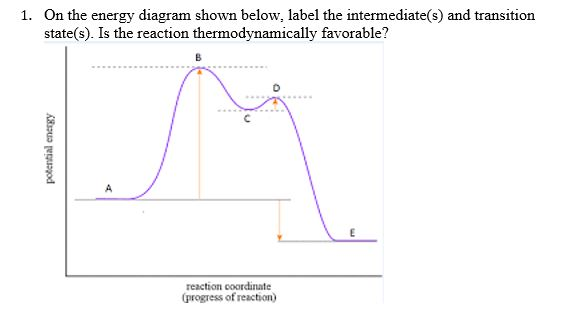
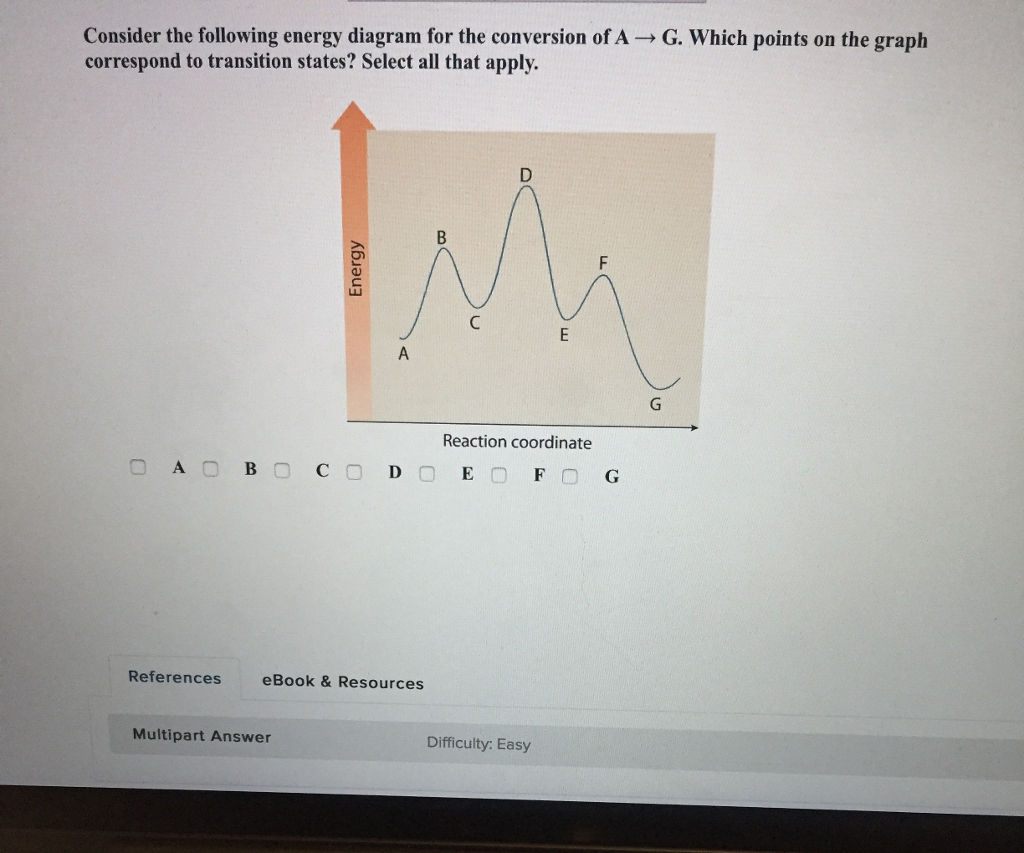
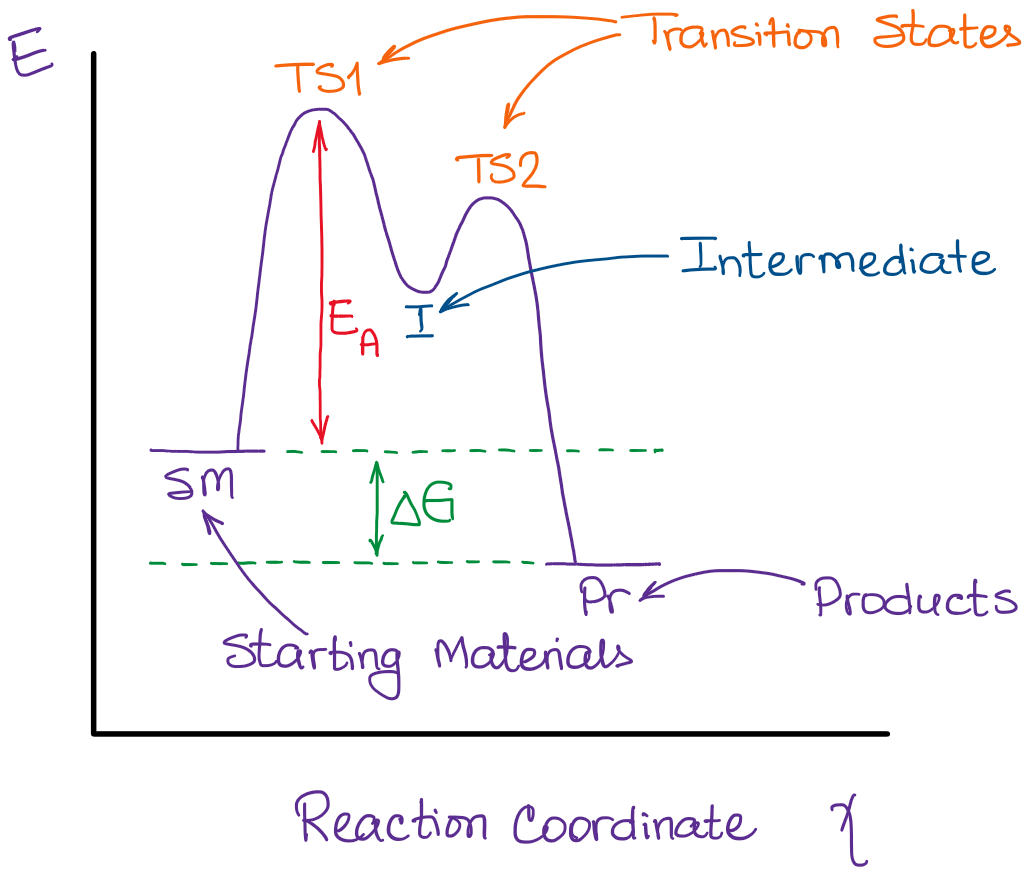
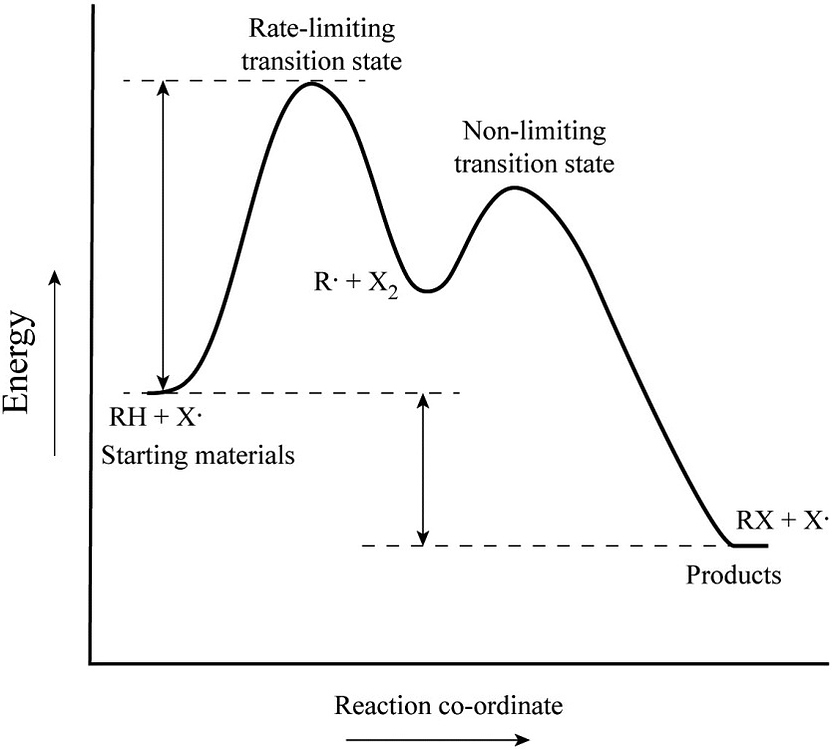
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (55 ratings) Transcribed image text: How many intermediates and transition states are in the mechanism represented by the following free energy diagram? The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea). The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The energy diagram for this reaction will look like this: So, we “hop” into the air, and we land with new products in hand and no stops in the “mid-air” for an intermediate. How does a reaction with an intermediate look like then? Example of a Reaction with Two Transition States and One Intermediate. Well, since we’re already talking about the substitution and elimination reactions ... The state transition diagram also illustrates the states and transitions of the communication protocol between the recipe phase and the equipment phase. The phase logic must adhere to the rules depicted in the state transition diagram. Only valid state transitions as depicted in Figure 8.6 may be utilized.
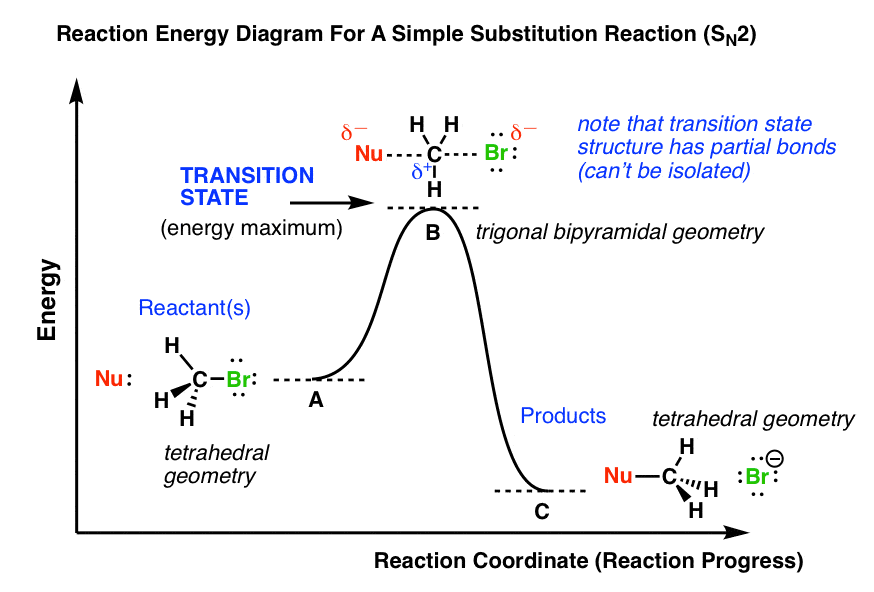
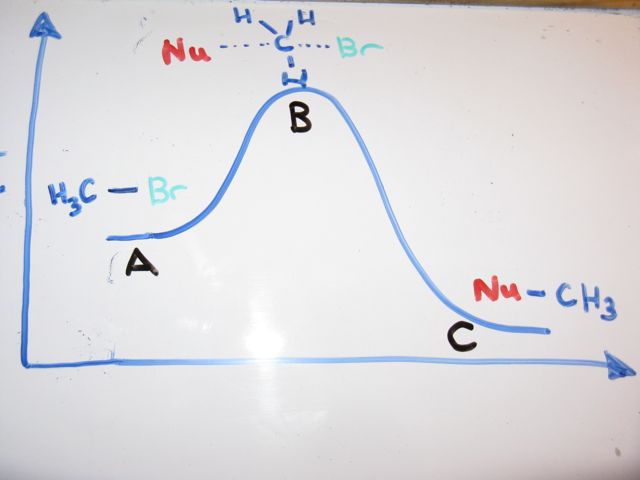
The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - , indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic and the products are more stable. Orgel diagrams are useful for showing the energy levels of both high spin octahedral and tetrahedral transition metal ions. They ONLY show the spin-allowed transitions. For complexes with D ground terms only one electronic transition is expected and the transition energy corresponds directly to Δ. At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (TS), which is the point at which the bonds are in the process of breaking and forming. The transition state is an ‘ activated complex’ : a transient and dynamic state that, unlike more stable species, does not have any definable lifetime. Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from ...
On the far left of the diagram are the reactant species and on the far right are the product species. Transition State The transition state is the high energy point between two minima along the reaction coordinate. Each step in a mechanism will have a transition state.
Concern about disputes with governments and other authorities likely reflects uncertainty about regulation and government incentives for energy transition and decarbonisation investments. Where investments cross borders, disputes may take the form of investment treaty proceedings against states that undermine the value of related investments ...
The state transition diagram is abstract in that it uses states labeled {S0, S1, S2, S3} and outputs labeled {red, yellow, green}. To build a real circuit, the states and outputs must be assigned binary encodings. Ben chooses the simple encodings given in Tables 3.2 and 3.3. Each state and output is encoded with two bits: S 1:0, L A1:0, and L B1:0.

Home sweet home - J.S. Gordon (John Sloan Gordon) O.S.A., R.C.A.- (1886 - 1940) - 1904 - 1907 oil painting on canvas of a Lone rider
Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction. - A maximum on an energy diagram. • Activation Energy, ∆G‡: The difference in Gibbs free energy between reactants and a transition state. - If ∆G‡ is large, few collisions occur with sufficient
Both of the triplet state transitions are diagrammed on the right-hand side of the Jablonski energy profile illustrated in Figure 1. The low probability of intersystem crossing arises from the fact that molecules must first undergo spin conversion to produce unpaired electrons, an unfavorable process.
The Bohr model for an electron transition in hydrogen between quantized energy levels with different quantum numbers n yields a photon by emission with quantum energy: This is often expressed in terms of the inverse wavelength or "wave number" as follows: The reason for the variation of R is that for hydrogen the mass of the orbiting electron is not negligible compared …
between the reactant energy and the transition state at the peak of the diagram. The activation energy for the reverse reaction, E a(rev), is the difference between the product energy and transition state at the peak of the diagram. ΔH r is the difference between the potential energy of the reactant and the potential energy of the product. a.
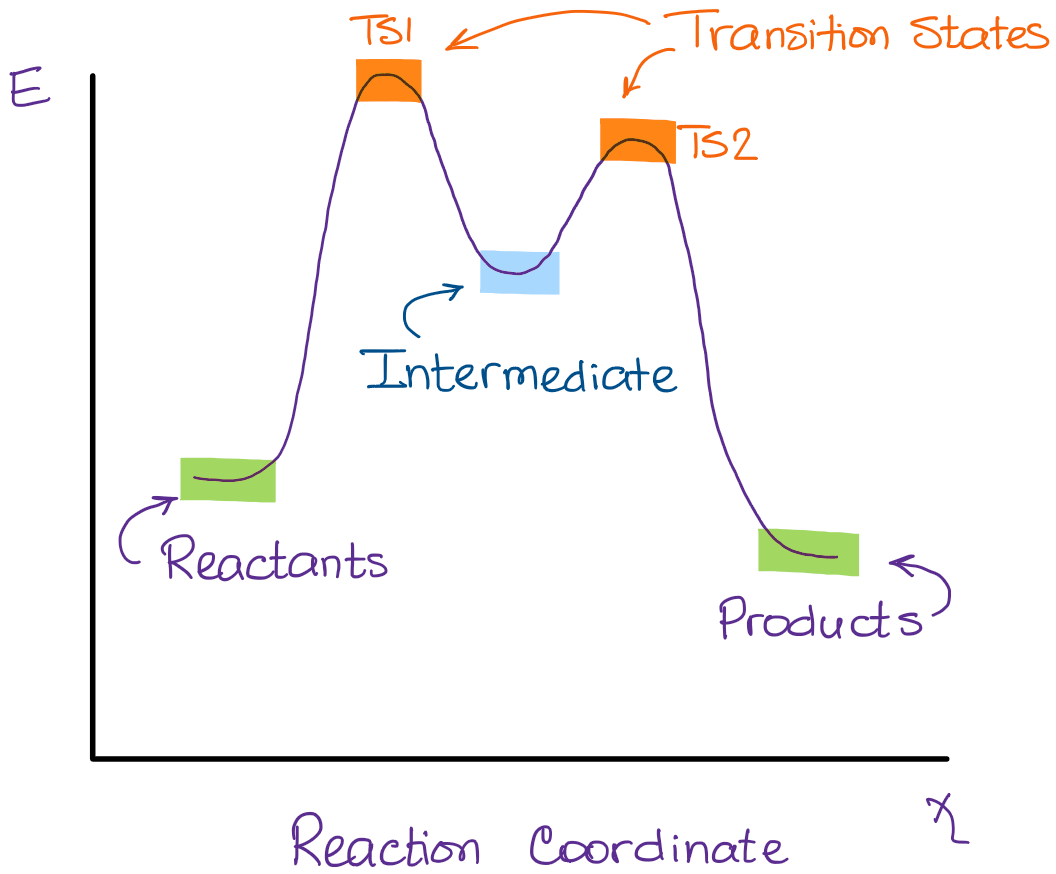
The saddle point represents the highest energy point lying on the reaction coordinate connecting the reactant and product; this is known as the transition state. A reaction coordinate diagram may also have one or more transient intermediates which are shown by high energy wells connected via a transition state peak.
a transition state. KEYWORDS: Reaction, Energy , Rate, Cation INTRODUCTION The easiest way to understand the difference between a transition state and an intermediate is to use what is commonly called a reaction (energy) diagram, like the one below. methylpropane with iodide, we know that the rate carbocation.
use a Reaction Energy Diagram to discuss transition states, Ea, intermediates & rate determining step; draw the transition state of a reaction ; You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal …
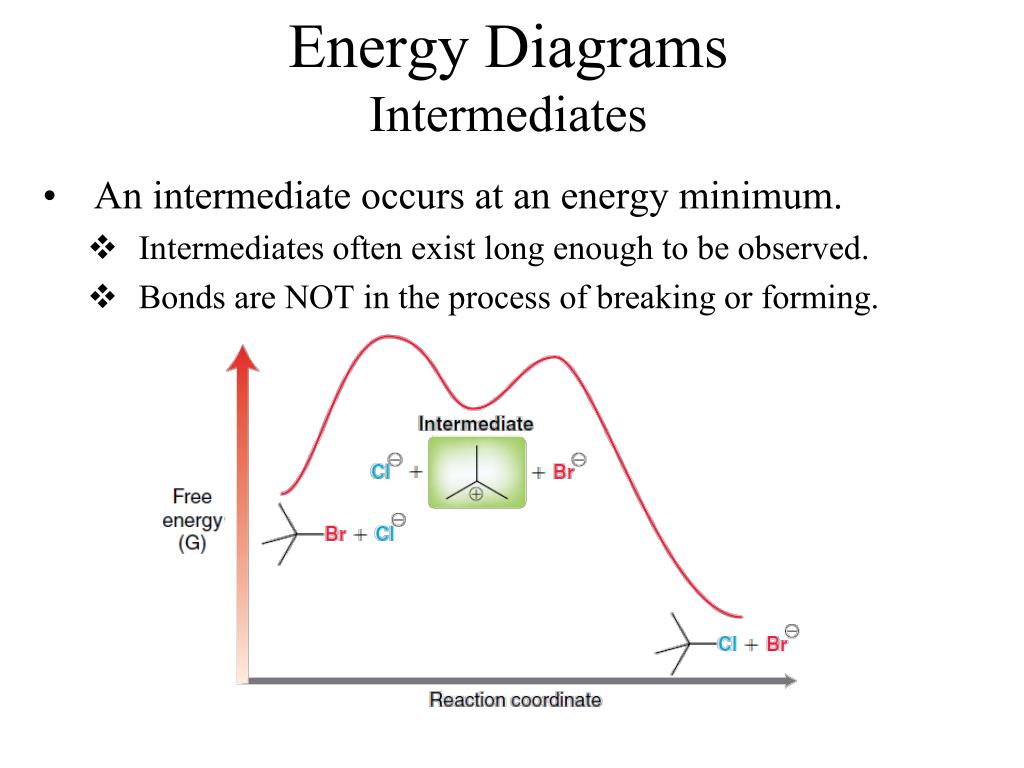
Energy Diagrams # Transition States! • An intermediate occurs at an energy minimum.! Intermediates often exist long enough to be observed.! Bonds are NOT in the process of breaking or forming. ! Energy Diagrams # Intermediates! 6! For each of the diagrams below, will the transition state
Transition State in Energy Diagram Transition State in Energy Diagram Definition An energy diagram refers to the plot which shows the reactants' relative potential energies, its transition states, as well as the products progression of the reaction with time. It is a plot between potential energy and reaction progress or time.
1. The Basic Equation. According to transition state theory, the rates of reactions are given by the following equation: where k is the rate constant for a given reaction, k is Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature, h is Planck's constant, and DG* is the free energy difference between the transition state and the reactants, i ...
A transition state is a chemical species which has only fleeting existence and represents an energy maxima on reaction coordination diagram . While an intermediate lies in depression on potential energy curve . Therefore actual lifetime of an intermediate depends on the depth of the depression.
In this video, I go over how to properly label and explain a reaction mechanism diagram which is also referred to as an energy diagram or energy graph. I'll ...
the beginning state. The energy of the TS≠ must be closer to the beginning state. There's just no other way to draw the diagram. We call this TS≠ "early" since the structure of the transition state has not evolved far from its starting point. Case 2: the ending state is higher than the beginning state - In this case

SAKURAI / Introduction to M-Theory and SuperStrings / The Final Visualization In Twenty Six Dimensions
Transition state theory is also based on the assumption that atomic nuclei behave according to classical mechanics. It is assumed that unless atoms or molecules collide with enough energy to form the transition structure, then the reaction does not occur. However, according to quantum mechanics, for any barrier with a finite amount of energy ...
transition state product Exothermic Reaction Energy Reaction Coordinate reactant transition state product Endothermic Reaction Energy Reaction Coordinate Finally, the diagram gives information about the rate of a reaction. The higher the energy of the transition state (corresponding to an increase in activation energy Ea) the slower the
This is part 3 of a four part series in the Energy Diagram Module. Stay tuned for Part 4! Click on the following links to see earlier parts: Part 1. Part 2. Sometimes reactions are more complex than simply a transition state (Graph 3), which would represent a single step in the reaction mechanism.

Home sweet home - J.S. Gordon (John Sloan Gordon) O.S.A., R.C.A.- (1886 - 1940) - 1904 - 1907 oil painting on canvas of a Lone rider
Transition state An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction; a maximum on an energy diagram. FIGURE 5.1 An energy diagram for a one-step reaction between C and AJB. The dashed lines in the transition state indicate that the new CJA bond is partially formed and the A JB bond is partially broken. The energy of the
Transition state and energy diagram of an reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. Due to their extremely short lifetime, transition states cannot be measured directly. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. Their lifetime does not last any longer than one molecular vibration, which is approximately 10 -12 s.
Quantized energy levels result from the wave behavior of particles, which gives a relationship between a particle's energy and its wavelength.For a confined particle such as an electron in an atom, the wave functions that have well defined energies have the form of a standing wave. States having well-defined energies are called stationary states because they are the states …
A reaction starting from reactants that change into products must pass through an unstable state at the highest energy level; this is called a transition state.A certain amount of energy is required to overcome the energy barrier, and this energy, called activation energy, is represented by ΔG ‡.The magnitude of ΔG ‡ determines the rate of a chemical reaction.



















0 Response to "40 transition states energy diagram"
Post a Comment