40 free body diagram on a ramp
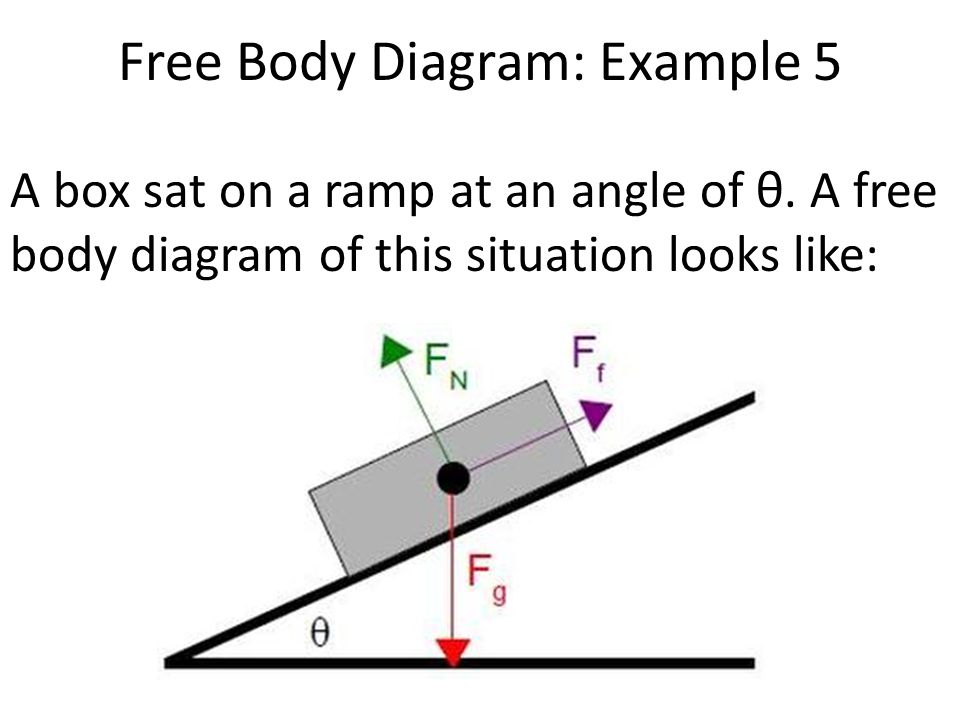
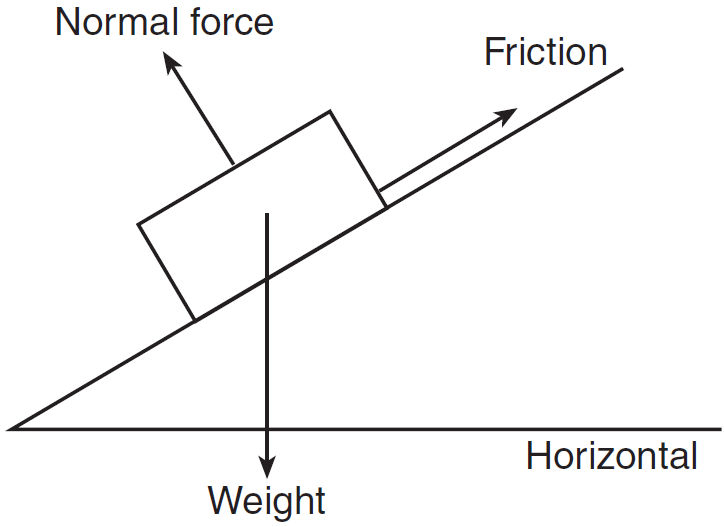
I am working on an innovation on the wheelchair for an innovation challenge at my school. One of the judges says I should include a free body diagram, but my major is biology so... not so great at physics. Think of just a person sitting in a chair, and then someone lifting them into a standing position. The innovation is going to help the patient stand with the nurses help by raising the seat of the chair (think like a barber chair, straight up and down) so that the patient can just scoot forwar... Free Body Diagrams. The first step is to draw a Free Body Diagram (also called a Force Diagram) ... Box on a Ramp. The box weighs 100 kg. The friction force is enough to keep it where it is. The reaction force R is at right angles to the ramp. The box is not accelerating, so the forces are in balance: ...
R5Improve their ability to draw free body diagrams. R5Be able to identify errors in diagrams and correct them. R5Recognize free body diagrams as representations of forces, and connect them with real-world objects and phenomena. Motivation R5Free body diagrams are a key problem-solving strategy for physics and engineering students.

Free body diagram on a ramp
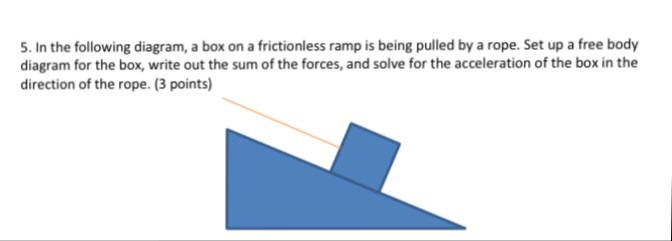
You are lowering two boxes, with a small box on top of a larger one. You are letting them slide down a ramp by pulling on a rope parallel to the surface of the ramp. Both blocks move with constant velocity of 15 m/s. The co-efficient of kinetic friction between the lower box and the ramp is 0.35 and the coefficient between the boxes are 0.64. As I see the problem right now, I am confident I can answer this, assuming that I have all the forces correct. The main issue is that I actually dont k... free body diagram box on ramp. 42 box on ramp free body diagram. I'm going to draw my free body diagram off to the side and0863. the tr… Written By Stefanie Hartmann Wednesday, February 2, 2022 Add Comment Edit. 2008+mack+gu813+fuse+box+diagram. 42 2008 mack gu813 fuse box diagram. FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
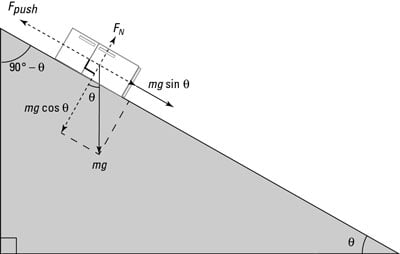
Free body diagram on a ramp. A free body diagram is defined as an illustration that depicts all the forces acting on a body, along with vectors that are applied by it on the immediate environs. Apart from the acting forces and subsequent work done, the moment magnitudes are also considered to be a part of such diagrammatic representations. A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it. In physics and engineering , a free body diagram ( FBD ; also called a force diagram ) [1] is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces , moments , and ... I’m working on elevator problems right now, and the example shows that net force equals normal force minus weight. Where is the force causing the elevator to move? To solve this problem you should start by drawing a free-body diagram. Part D Determine the object of interest for this situation. For this. Question: Provide Chadwick now needs to push the piano up a ramp and into a moving van. (Figure 2) The piano slides up the ramp without friction. Is Chadwick strong enough to push the piano up the ramp ...
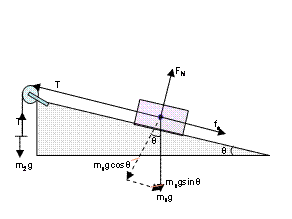
Free-body diagram: F N acting perpendicular to the ramp (upward) F g acting down F T acting up along the ramp F K acting down along the ramp For the 6.0-kg mass: Free-body diagram: F g acting down F T acting up (b) The acceleration of the 4.0-kg mass along the ramp is 3.3 m/s2. (c) The tension in the cable is 39 N. (d) 2a = 3.37 m/s I'm having trouble figuring out how this free body diagram would look. The question involves a block at rest on a ramp, which is in turn at rest on a table. All objects are made of the same material, with the same coefficients of friction. Below is what I've got so far, but it doesn't seem correct. A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton's first law or acceleration according to Newton's second law. ... A force of 1600 N acts parallel to a ramp to push a 300-kg piano into a moving van. The ramp is inclined at In this video I explain how to identify the forces acting on a mass that is moving down a ramp. I also explain how to draw these forces on a free body diagra...
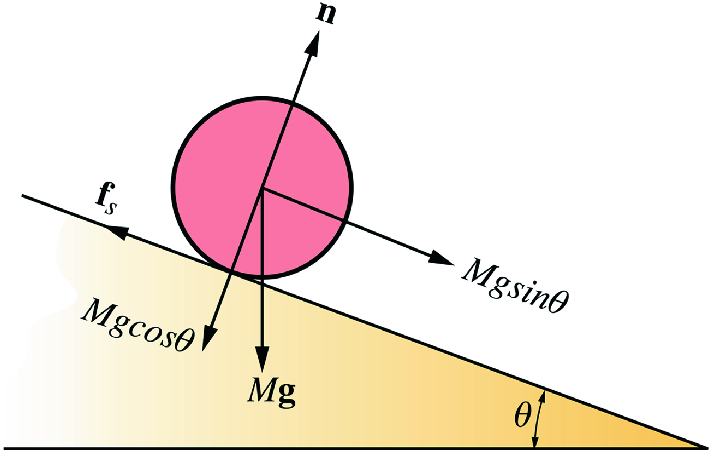
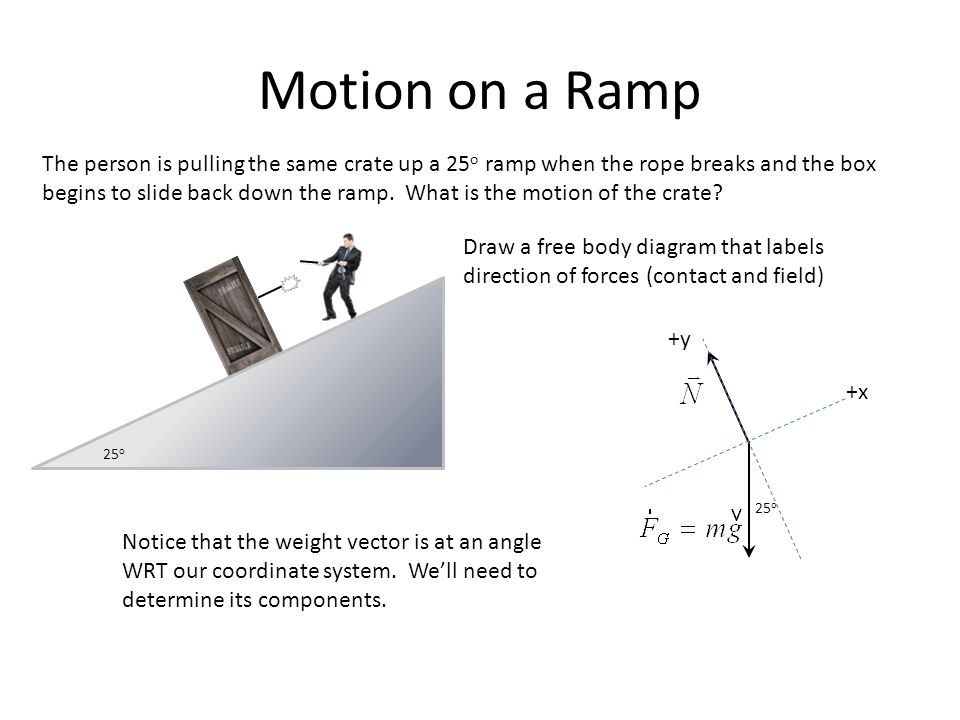
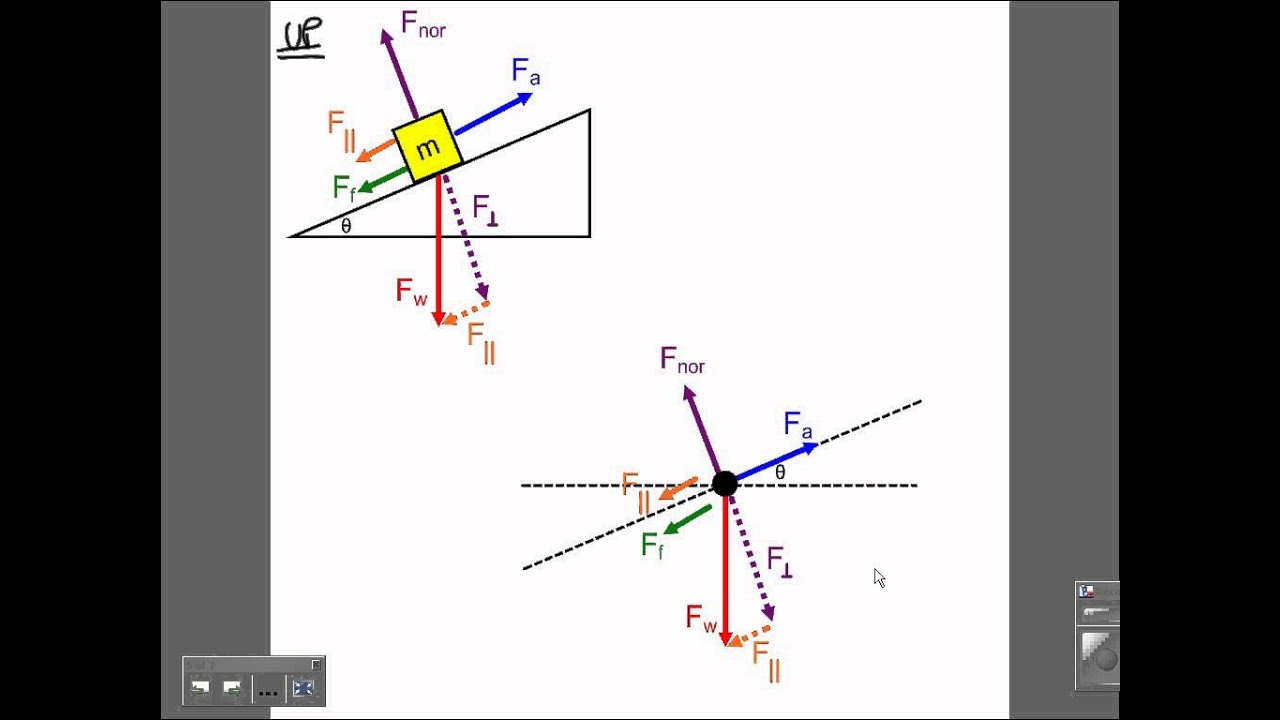
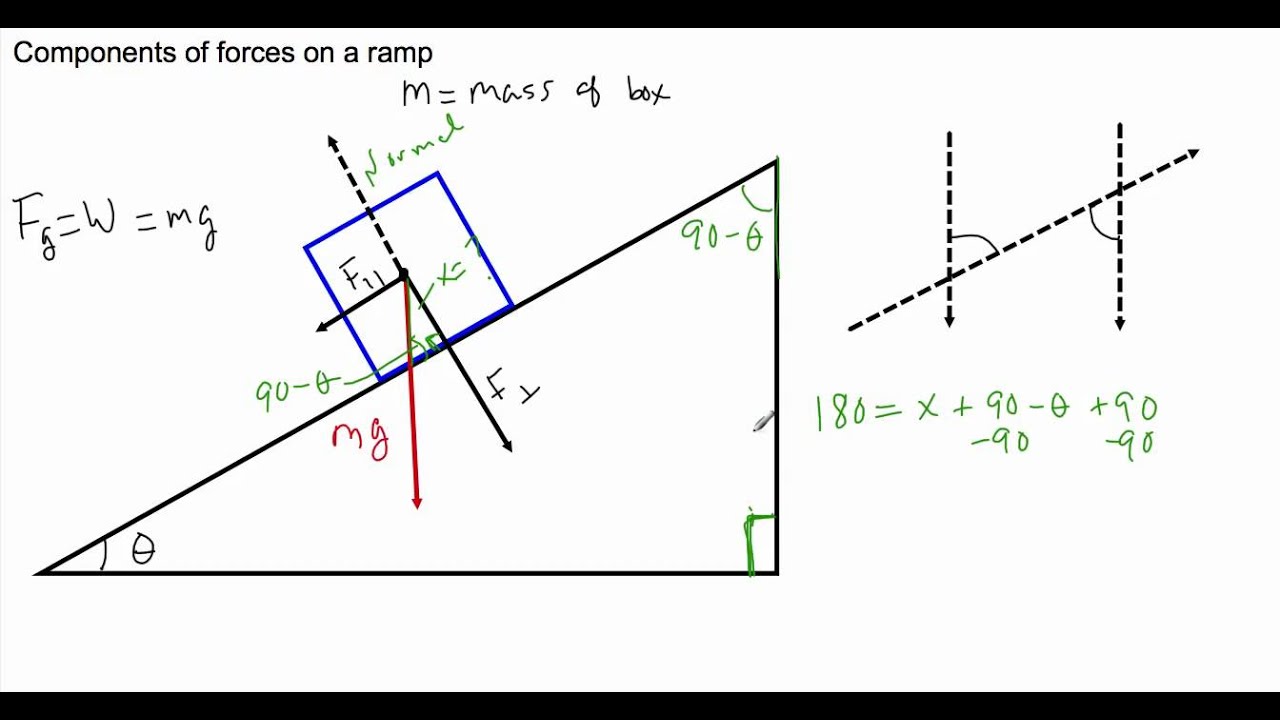
In this case we have a block moving up a ramp, so for our convenience, we will use tilted coordinate axes, with the x axis in the direction of motion (uphill). After drawing the coordinate axes on the free-body diagram of the block, we proceed to find the components of the individual forces acting on the block: A small box is on a ramp tilted at an angle θ above the horizontal. The box may be subject to the following forces: frictional (f ) ,gravitational (mg), pulling or pushing (F P) and normal (I).In the following free-body diagrams for the box, the lengths of the vectors are proportional to the magnitudes of the forces. In other words, what's the force required at a seem or between two flat surfaces to make a device waterproof? Also, im assuming that as you dive deeper under water, the force of the water seeping into the phone increases, but is there some sort of function/equation to predict that increase? I understand that waterproof seals are a simple concept, but my intention is to understand all the forces at play in a mathematical way. Free Body Diagrams Name Student Activity Class ©2011 Texas Instruments Incorporated education.ti.com2 Move to page 2.3. 3. Change the angle of the ramp by grabbing the point at the end of the ramp. Grab the point by clicking and holding until the hand closes. Drag the point up to 90° and observe the effect on the
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
A free body diagram can help you determine the force of friction on the block by using Newton's second law. The work done by friction is equal to the force of friction times the distance the block travels up the ramp. The change in gravitational potential energy will also depend on the distance traveled up the ramp.
Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In (Figure) (a), a sled is pulled by force P at an angle of 30° 30 °. In part (b), we show a free-body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem-solving strategy. In part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x - and y ...
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
The key to understanding these situations is creating an accurate free body diagram after choosing convenient x- and y-axes. Problem-solving steps are consistent with those developed for Newton's 2nd Law.. Let's take the example of a box on a ramp inclined at an angle of Θ with respect to the horizontal.
Ramp Activity 1: Using free body diagrams for motion on an incline (Inquiry Based) Description There was simulation called "The Ramp", but our research showed that it had too many learning goals. The first tab of the sim is simplified and energy parts of the sim have been deleted as well.
A free-body diagram for a box on a ramp, in the special case of it being the maximum angle before the box starts to slide. The video includes an introduction...
Which of the following does a free body diagram help do in problem solving? I. help define the forces on the body II. help find the sum of the forces on the body III. help; Question: 1. Which of the following would represent the free body diagram of a block sliding down a ramp without friction? a. ramp gravity b. . gravity c. Frame gravity d.
Force Body Diagrams of object sliding down ramp. Ask Question Asked 6 years, 8 months ago. Active 6 years, 8 months ago. Viewed 1k times ... Browse other questions tagged newtonian-mechanics forces free-body-diagram or ask your own question. The Overflow Blog The Bash is over, but the season lives a little longer ...
#Solved Here's the question/diagram: https://gyazo.com/24579f62eaf7fe36df871ab2d0cbf496 Why does the force of gravity have an angle of 20 degrees here? Why dosen't the force of normal have an angle of 20 degrees? Like this: https://gyazo.com/50621a0875fea9bdf9ea15db85627084 ?
Forces: Free Body Diagram of Cart Rolling Down Ramp: The F1 force can be classified as the air resistance/drag/friction working against the cart as it is going down the ramp, the F2 force can be classified as gravity which is acting down upon the cart, and F3 can be classified as the opposing force of the ramp towards the car (Newton's 3rd Law).
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
I'm building a climbing training apparatus in my garage that both rests on the ground and hangs by a rope from a hook attached to a ceiling joist. I'm missing something from my free body diagram that's keeping me from setting up and solving my equilibrium equations. I have the full problem laid out, with included pictures and diagrams, at the StackExchange post [here](https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/674883/statics-question-free-body-diagram-help-for-garage-construction-project). I'...
When looking at the free body diagram of someone in a Gravitron theres Normal force, friction and then m\*g but why is there no centrifugal force, Is that force responsible for you feeling pinned to the wall? Or do i have the concepts wrong. Thanks! ​ Help a dumb student :(
Free Body Diagram - 941 Words | Cram. Show More. Check Writing Quality. Register to read the introduction…. Move the ramp to an angle of zero (horizontal) and draw a free body diagram of the cabinet here: On a horizontal plane, the normal force is _Perpendicular_______ to the weight. The cabinet has a mass of 100kg.
A sled slides down a snowy hill, experiencing friction from the snow. Draw the free body diagram for the sled
Question 1 A group of neighbourhood children play ice hockey. Unfortunately, the rink is on a slope. What forces are acting on the puck? Check your answers (C) Correct! Question 2 The Music Department wants to move a piano up a flight of stairs. The movers tie a rope to the piano, and pull it up a ramp placed over the stairs. The ramp is very smooth (no friction).
Block on ramp: Free-Body Diagram. Author: Nathaniel Cunningham. Free body diagram of a block on a ramp, without friction. Drag the point at the top of the ramp to change the ramp angle. Note how the green angles always track one another.
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
free body diagram box on ramp. 42 box on ramp free body diagram. I'm going to draw my free body diagram off to the side and0863. the tr… Written By Stefanie Hartmann Wednesday, February 2, 2022 Add Comment Edit. 2008+mack+gu813+fuse+box+diagram. 42 2008 mack gu813 fuse box diagram.
You are lowering two boxes, with a small box on top of a larger one. You are letting them slide down a ramp by pulling on a rope parallel to the surface of the ramp. Both blocks move with constant velocity of 15 m/s. The co-efficient of kinetic friction between the lower box and the ramp is 0.35 and the coefficient between the boxes are 0.64. As I see the problem right now, I am confident I can answer this, assuming that I have all the forces correct. The main issue is that I actually dont k...









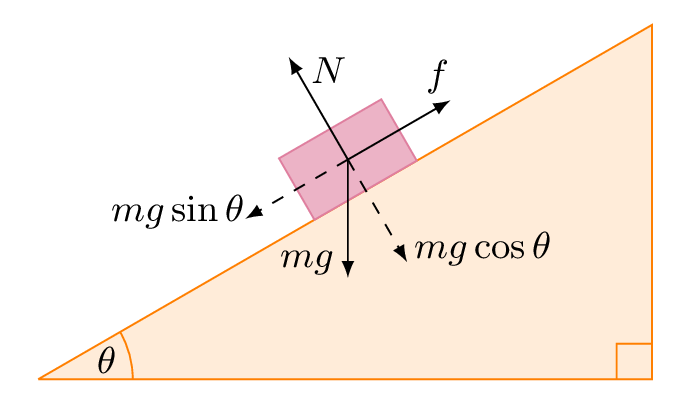
![Gr 11 Physics] Free Body diagram of a ramp : r/AskPhysics](https://external-preview.redd.it/jvOUyctCWu9d_r4DBRJCn0aI5uMZ-UlskKSAquuwkLM.jpg?width=640&crop=smart&auto=webp&s=4350c33cfaf04481cce0505a5e8e1954351d30d2)






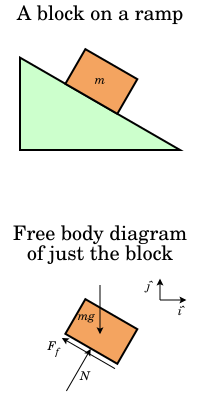




0 Response to "40 free body diagram on a ramp"
Post a Comment