39 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
PDF UNF PMASON - unf.edu is the same as that of a purely competitive indiLstry is its average variable cost curve does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist. Use the following to answer questions 15-16: $19 100 MC ATC MR 160 180 210 Quantity 15, Refer to the above diagram for 8 monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's ... Solved 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely ... View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O total revenue curve. total profit curve. total cost curve O total cost curve. O marginal revenue curve.
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: a. may be either greater or less than $5 b. will also be $5 c. will be less than $5 d. will be greater than $5. b. will also be $5. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 39. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. B. total revenue curve . 40. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics ... - Learn CBSE Sep 29, 2019 · Answer: The marginal cost curve of a perfectly competitive firm is the firm’s short- run supply curve at the point where price is equal to or greater than average variable cost. To determine its quantity supplied the firm equates the price of its product with its marginal cost. Price and Output Determination under Monopoly (6 Answers) Since there is just one solitary seller in a pure monopoly market, there is no difference between the market demand curve and the demand curve for the firm’s product. The output of a pure monopoly firm is the downward-sloping market demand curve that would be faced by an entire competitive industry.
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. Perfect competition - Wikipedia As it is well known, requirements for firm's cost-curve under perfect competition is for the slope to move upwards after a certain amount is produced. This amount is small enough to leave a sufficiently large number of firms in the field (for any given total outputs in the industry) for the conditions of perfect competition to be preserved. Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - 46151 - Facebook 46. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. B) total revenue curve. C) marginal revenue curve. D) total profit curve. Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 418 MI: 174 47. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. 41. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: A. an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and upward ...
Chapter 10 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet The lowest point on a purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve corresponds to: the minimum point on its AVC curve. ... Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total cost curve. Refer to the diagram. The firm will realize an economic profit if price is. P4-The firm represented by the diagram would maximize its profit where: Chapter 12 - Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Quizlet A. is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: A. may be either greater or less than $35. (PDF) MARKET STRUCTURE - ResearchGate As a purely competitive firm is a price taker, it can maximise its economic profit (or minimize its loss) only by adjusting its output. In the short run, the firm has a fixed factor of production. PDF exam: 060205RR - Product Markets - JustAnswer 4. Curve (3) in the diagram above is a purely competitive firm's A. total cost curve. B. marginal revenue curve. C. total economic profit curve. D. total revenue curve. € 5. Which of the following is a characteristic of a pure monopoly economic system? A. Price taker B. Many sellers C. Free entry D. Blocked entry € 6. If production is ...
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Pure Competition 4. Purely competitive firms are not Dynamically Efficient. ... if acompetitive firm has a higher ATC curve than its competitiors then they will earn losses and go out of business E. Purely Competitive Firms are NOT Dynamcially Efficient So far in the long run analysis of pure competition, we assumed that entry/exit of firms is merely a reaction ... ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97. PDF Practice PC in Short Run - Mount Saint Mary College C. purely competitive market. D. oligopolistic market. 14. Refer to the above data. If the firm's minimum average variable cost is $10, the firm's profit-maximizing level of output would be: A. 2. B. 3. C. 4. D. 5. 15. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d.
Macroeconomics Quiz 100.pdf - 40. Award: 1.00 point Curve ... Award: 1.00 point Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total cost curve. total revenue curve. marginal revenue curve. total profit curve.
PDF AP Unit 6 4. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is less elastic than that of a purely competitive producer. True False 5. The larger the number of firms and the less the degree of product differentiation, the greater will be the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive seller's demand curve. True False 6.
Curve 1 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... Type: G Topic: 3 E: 418 MI: 174 47. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: A) an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and upward shift in curve (1). B) a decrease in the steepness of curve (3), a downward shift in curve (2), and an upward shift in curve (1). C) an downward shift in curve (4) and an upward ...
DOCX Loudoun County Public Schools / Overview Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 16. ... In the short run the individual competitive firm's supply curve is that segment of the: A. average variable cost curve lying below the marginal cost curve.B. marginal cost ...
Ch10quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram. At P 4, this firm will: A. shut down in the short run. B. ... Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is: A.
Chapter 10 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Which point in the accompanying graph is definitely not on the competitive firm's short-run supply curve? A. A B. B C. C D. D. A. Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift ... Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve.
Microeconomics Lecture #12 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. The average total cost (ATC), marginal cost (MC), and marginal revenue (MR) curves are already labeled.
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips The nondiscriminating monopolist's demand curve: A. is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. B. is perfectly elastic. C. coincides with its marginal revenue curve. D. is perfectly inelastic. 10-3 ... Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: A. a market in which there are an extremely large number of other firms ...
ECON 150: Microeconomics - Brigham Young University-Idaho Key Points for Pure Competition in the Long Run. 1. Short run economic profits (losses) leads to firms entering (exit) the industry. 2. Ease of entry will cause long run economic profits to be zero. 3. In the long run, purely competitive firms will be both productive and allocatively efficient. 4. Economic surplus is maximized in pure competition.
ECON202 CH10 Heath Flashcards - Quizlet Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's marginal revenue curve Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as
micpure Using the diagram above, in order to maximize profits, this firm would produce _____ which would result in _____. ... A purely competitive firm, as shown above, will face what kind of change in profits over the long run, assuming industry demand is constant? A. Profits will increase. ... The short-run supply curve for a competitive firm is the ...
revmncmp less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. B. less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. ... production for the firm shown in the diagram above is: A.
Market Structure Questions and Answers | Study.com A competitive firm currently produces and sells 7,500 units of output at a price of $2.50 per unit. The firm's average fixed cost is $0.75 and its average total cost is $2.80. In the short run, sho...
Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q 4. B. q 3. C. q 2. D. q 1. 7. ... is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. B. is perfectly elastic. C. coincides with its marginal revenue curve. D.
intro to micro chapter 10 quiz Flashcards | Quizlet the accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will a) produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40 b) produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00 c) shut down in the short run d) produce 6 units at a loss of $23.80
Price and Output Determination under Monopoly (6 Answers) Since there is just one solitary seller in a pure monopoly market, there is no difference between the market demand curve and the demand curve for the firm’s product. The output of a pure monopoly firm is the downward-sloping market demand curve that would be faced by an entire competitive industry.
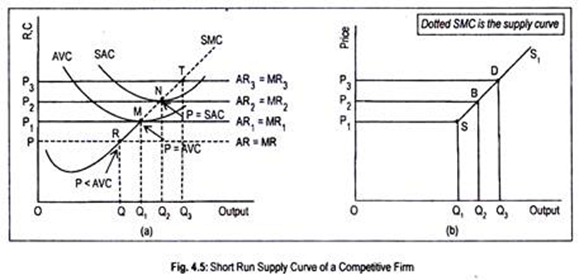
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics ... - Learn CBSE Sep 29, 2019 · Answer: The marginal cost curve of a perfectly competitive firm is the firm’s short- run supply curve at the point where price is equal to or greater than average variable cost. To determine its quantity supplied the firm equates the price of its product with its marginal cost.
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 39. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. B. total revenue curve . 40. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.
0 Response to "39 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment