39 roller coaster free body diagram
Roller Coasters and Amusement Park Physics The motion of objects along curved sections of roller coaster tracks (loops, turns, bumps and hills, etc.) can be analyzed using a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations. The Physics Classroom demonstrates how using numerous examples. Solved 1. The two diagrams below depict the free-body ... The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the above principles of vector resolution to determine the net force of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible effect of friction and air resistance.
If the track is to be designed so that the ... - Holooly.com Free-Body Diagram:The free-body diagram of the passenger at positions B and C are shown in Figs. a and b, respectively. Equations of Motion: Here, [latex] { a ... If the track is to be designed so that the passengers of the roller coaster do not experience a normal force equal to zero or more than 4 times their weight, determine the limiting ...
Roller coaster free body diagram
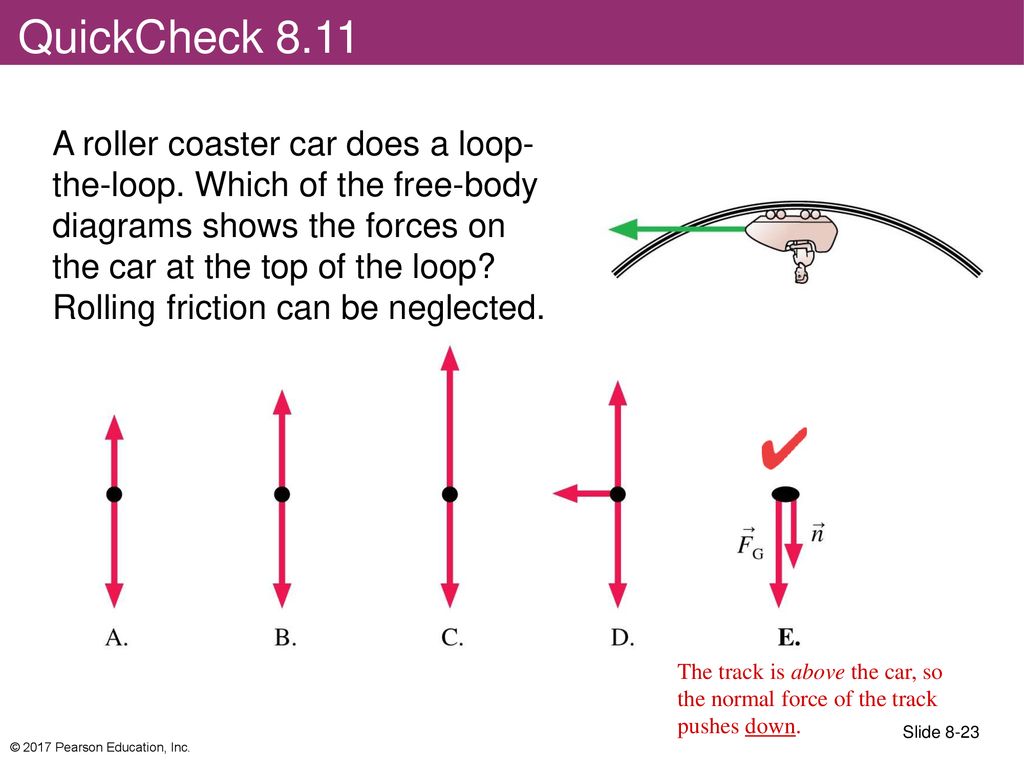
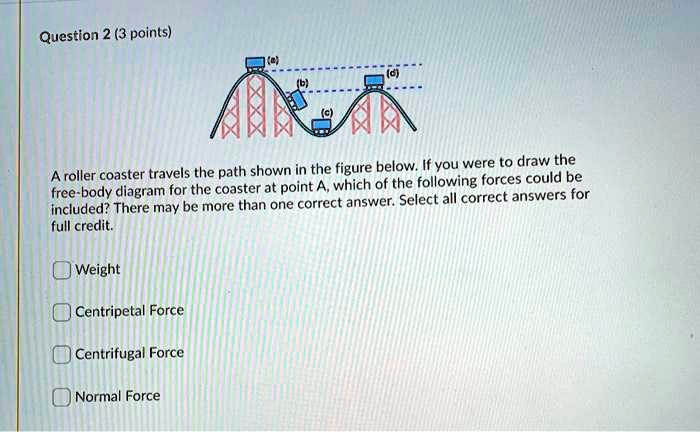
PDF For Scientists and Engineers The free-body diagrams below show the coin from behind, moving away from you. Which is the correct diagram? QuickCheck 8.6 Slide 8-67 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. A coin sits on a turntable as the table steadily rotates ccw. What force or forces act in the plane of the turntable? QuickCheck 8.7 Slide 8-68 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. rollercoaster - Physics & Astronomy Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 1000 kg roller coaster car. Steps 1 and 2 involve the construction of a free body diagram and the identification of known and unknown quantities. This is shown in below. Given Info: m = 1000 kg Given Info: m = 1000 kg a top = 15.0 m/s 2, down a bottom = 20.0 m/s 2, up Find: a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at ... a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at the top of the loop. (1 point) b. Write the expression for the net force in the y-direction at the top of the loop, in terms of w, FN, m, v, and r. (1 point) c. Write the equation that will tell you the velocity at which the coaster will fall when it reaches the top of the loop. (1 point) d.
Roller coaster free body diagram. PDF E90: The Roller Coaster Project - Swarthmore Home E90: The Roller Coaster Project Travis Rothbloom Advised by Erik Cheever Swarthmore College Engineering Department December 8, 2010 trothbl1@gmail.com Abstract A process for designing three-dimensional coaster track by in-putting gravitational forces and roll angle was created by using free-body-diagram-derived equations of equilibrium in ... roller coaster sample problems.pdf - Free Body Diagrams on a ... free body diagrams on a loop‐the‐loop roller coaster draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the bo3om and top of a loopand write the equa9ons for the net force. mgfnet fn fnet=ma = mac the net force in the loop must be centripetal force fnet= fn + (– mg) fn> mg mg fnetfn fnet=ma = mac the net force in the loopmust be centripetal force fnet= … AP Physics C: Mechanics - Unit 2 Progress Check MCQ ... A roller coaster has a circular loop of radius r. The minimum speed of a coaster car at the top of the loop needed to make it through the loop without losing contact is vmin. ... Box B has a weight of 2N and is at rest on top of box A. Which of the following free-body diagrams is correct for the two boxes? E. F floor-on-A = 7 N F B-on-A = 2 ... Vertical circular motion - Boston University Physics At rest, the free-body diagram is simple, with an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. These are the only two forces in the system even when circular motion is going on. The force of gravity has a constant magnitude and direction. The normal force, however, changes both magnitude and direction.
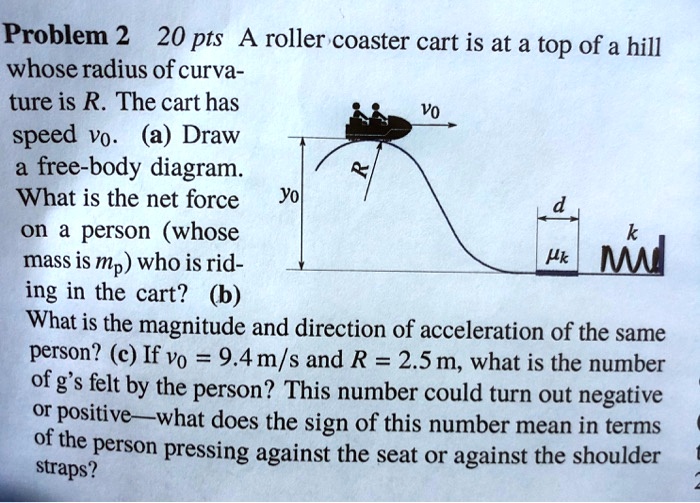
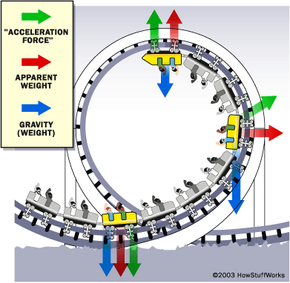
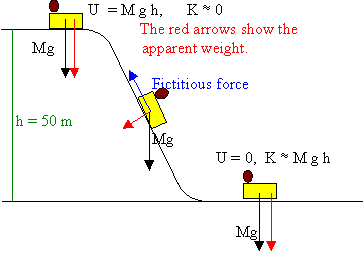
A Tale of Friction - Lesson - TeachEngineering Free-body diagrams are widely used in physics to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon objects in given situations. For this problem, a body's weight and surface friction are the forces acting on a spherical body rolling on an incline. ... roller coaster: An amusement park ride that consists on an elevated ... PDF 5-8 Vertical Circular Motion - WebAssign EXAMPLE 5.8B - Apparent weight on a roller coaster You are riding on a roller coaster that is going around a vertical circular loop. What is the expression for the normal force on you at the bottom of the circle? SOLUTION Once again, we apply the general method, starting with a diagram and a free-body diagram in Figure 5.21. Beam Calculations Made Easy - From Free Body to Stress ... Beams are everywhere and come with the challenge of many different loadings and supports. There are 5 steps to calculating the stress on a beam: Determine the loads. Determine the support conditions. Draw a shear-moment diagram or look up in a table. Calculate the section properties. Calculate the stress and apply design factor. Forces & Free Body Diagrams - SPH4U Laws of Motion Forces and Free Body Diagrams Hook This video describes different forces that are encountered during a roller coaster ride. Potential and kinetic energy are mentioned here. This is a good place to mention frames of reference, which will be looked at with greater detail later in the course.
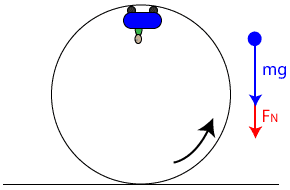
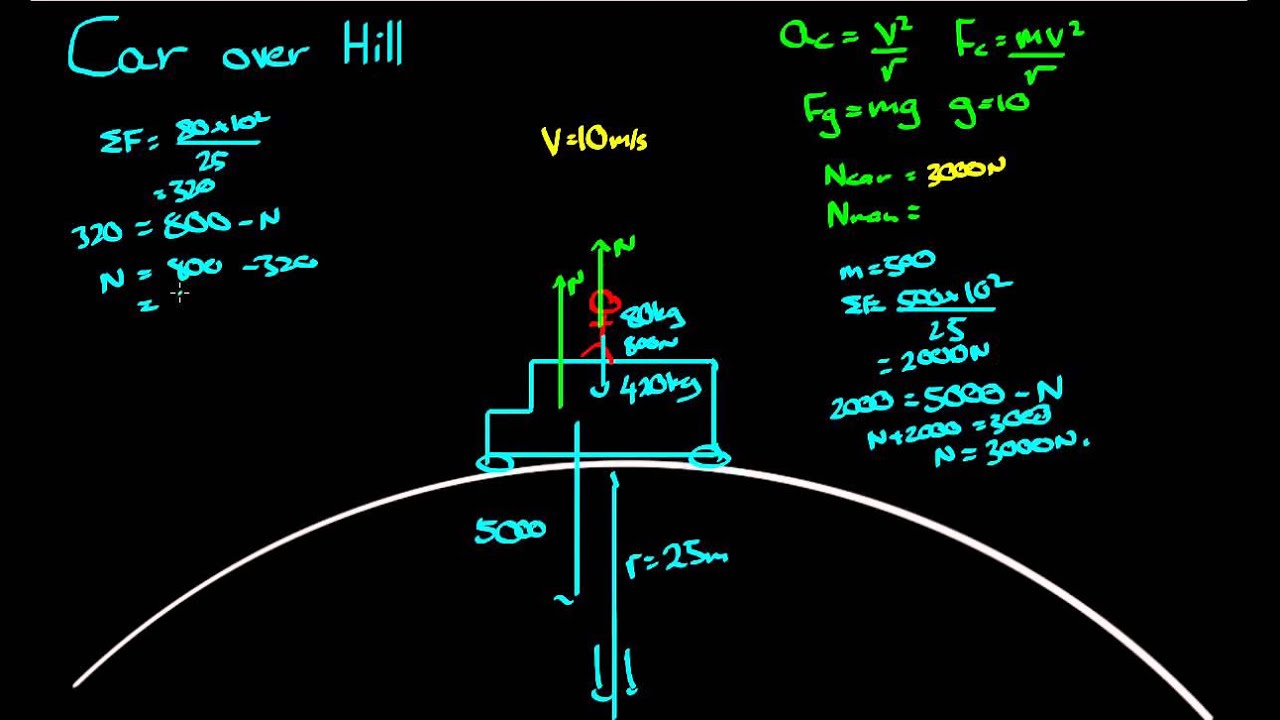
Inclined Planes - Physics Classroom The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate. PDF Chapter 8 Lecture physics - MiamiOH.edu The figure shows the roller-coaster free-body diagram at the bottom of the loop. ! Since the net force is toward the center (upward at this point), n> F G . This is why you "feel heavy" at the bottom of the valley on a roller coaster. ! The normal force at the bottom is larger than mg. Slide874$ CHAPTER8_LECTURE8.1$ 12 Solved Required information Problem 13.070 - Chegg.com A roller coaster starts from rest at A rolls down the track to B describes a circular loop of 12-m diameter, and travels up and down past point E. Assume that there is no energy loss due to friction. Given: h= 20 m. D=6m 25 m Problem 13.070.a - Roller coaster free body diagram Draw the free-body diagram of the roller coaster at the points B, D ... Roller coaster free body diagrams - Physics Forums Mar 08, 2008 · 7,171. 509. souljaxd said: i researched about free body diagrams and roller coasters. all i have now for the straight away is , f-gravity, f-normal, f - applied, and f- friction. Other than when the coaster ( and passengers) are being pulled up the incline by a chain mechanism or other means, there is no applied force; otherwise you have ...
Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net F N
Answered: 14-5. Determine the required height h… | bartleby 14-5. Determine the required height h of the roller coaster so that when it is essentially at rest at the crest of the hill A it will reach a speed of 100 km/h when it comes to the bottom B. Also, what should be the minimum radius of curvature p for the track at B so that the passengers do not experience a normal force greater than 4mg = (39 ...
Free body diagram, normal force, static friction | Physics ... a) F g arrow pointing straight down, F normal arrow pointing perpendicular to the cart, F friction arrow on right or left side of cart and F pull arrow on the other. b) F normal = (363kg) (9.81m/s 2 )cos (23degrees)=3277.95N c) coefficient of static friction=tan (23degrees)=0.42 maximum value of static friction=0.42 (3277.95N)=1376.74N
Roller Coaster - Texas State University One of the main analytical tools that we will learn to use is the Free Body Diagram. Using this vector analysis technique will enable students to resolve the various forces that are acting on the roller coaster at any given point in time and determine the level of excitement.
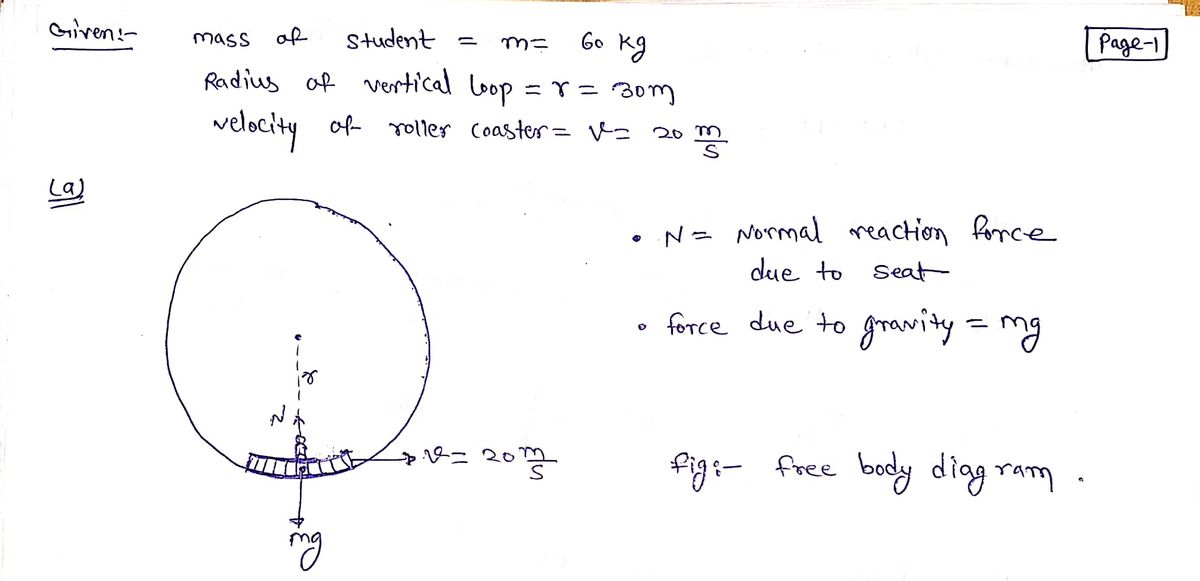
Answered: A 60 kg student rides on a roller… | bartleby A 60 kg student rides on a roller coaster that makes a vertical loop. a). Draw a free-body diagram for when the student is at the bottom of the loop. b). If the radius of the loop is 30 m, and the roller coaster is traveling at 20 m/s at the bottom of the loop, what is the net force acting on the student in the vertical direction? c).
Force Diagram Roller Coaster Loop - schematron.org In this paper, we look into the mathematical description of various possible loop shapes, as well as their riding properties. Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s.
PDF A Roller Coaster Project as Part of an Undergraduate ... the use of energy methods to determine roller coaster car velocity , and the use of free body diagrams to determine the normal force acting on a roller coaster car for 2-D track geometry. Example track used in this discussion included hills, valleys, linear sections at arbitrary angles, and circular loop s.
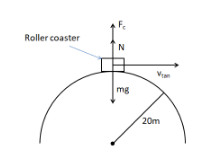
Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the top of the loop, where Normal Force and Force of Gravity are both pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn + Fg.
Let's Find The G's On A Coaster | Coaster Physics Looking at the free body diagram above (the FBD) the coaster drop is the black triangle. Z is the 65 degree angle of the drop from the horizontal meaning that W is 25 degrees (90 - 65). The blue arrow pointing directly downwards is the force of gravity while the other blue arrows are it's x and y components.
Experiment.docx - Experiment #2 - forces and free body ... methodology. This will depicts in real life as it is useful in visualizing all the forces acting on a single object. That is why this experiment already explain the concept of the forces and free-body diagram. Experiment #3 - Roller coaster-In labster experiment 4, this time I became in charge of the designs in roller coaster that makes everyone who rides it experiences the best ride ever.
a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at ... a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at the top of the loop. (1 point) b. Write the expression for the net force in the y-direction at the top of the loop, in terms of w, FN, m, v, and r. (1 point) c. Write the equation that will tell you the velocity at which the coaster will fall when it reaches the top of the loop. (1 point) d.
rollercoaster - Physics & Astronomy Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 1000 kg roller coaster car. Steps 1 and 2 involve the construction of a free body diagram and the identification of known and unknown quantities. This is shown in below. Given Info: m = 1000 kg Given Info: m = 1000 kg a top = 15.0 m/s 2, down a bottom = 20.0 m/s 2, up Find:
PDF For Scientists and Engineers The free-body diagrams below show the coin from behind, moving away from you. Which is the correct diagram? QuickCheck 8.6 Slide 8-67 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. A coin sits on a turntable as the table steadily rotates ccw. What force or forces act in the plane of the turntable? QuickCheck 8.7 Slide 8-68 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.



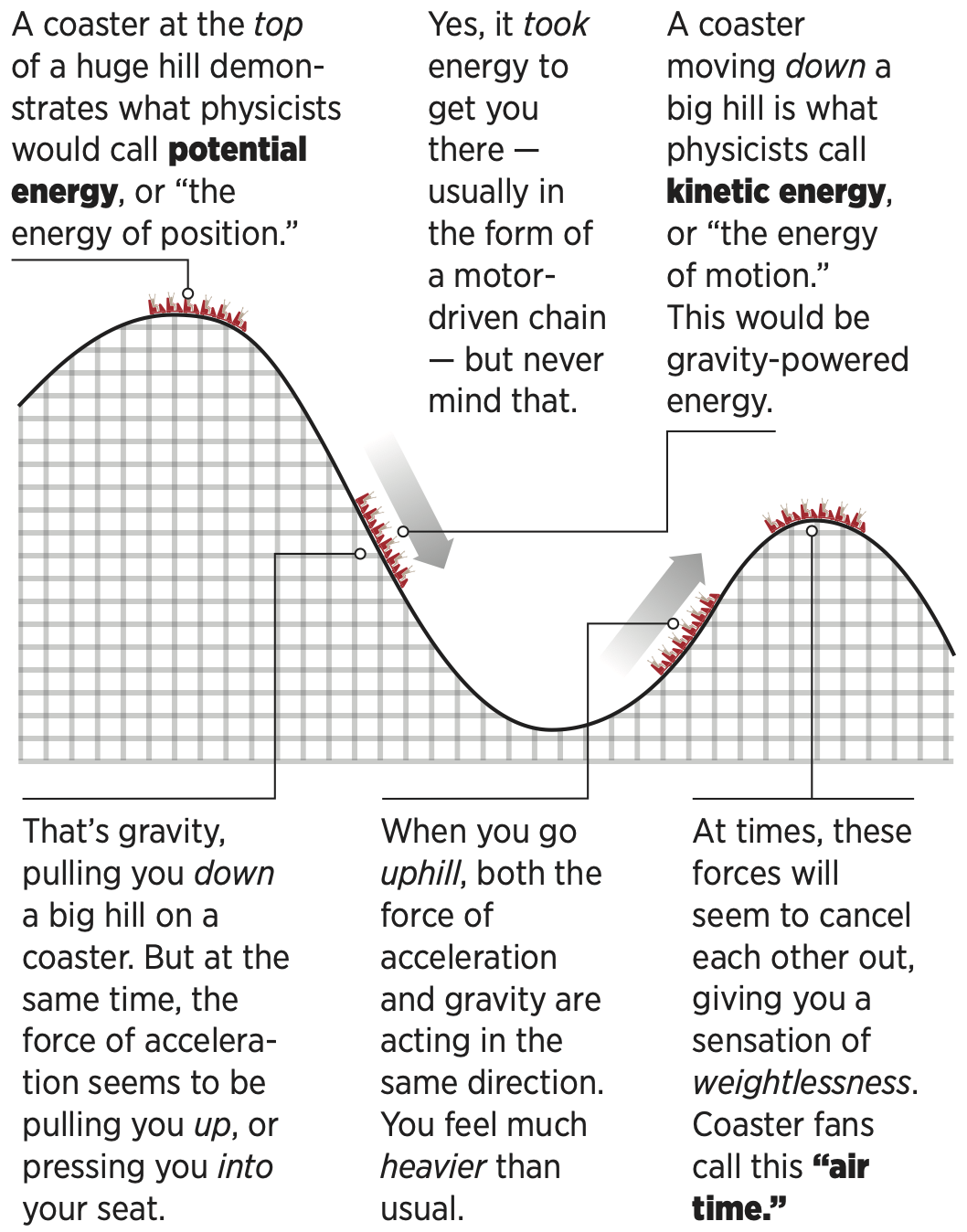
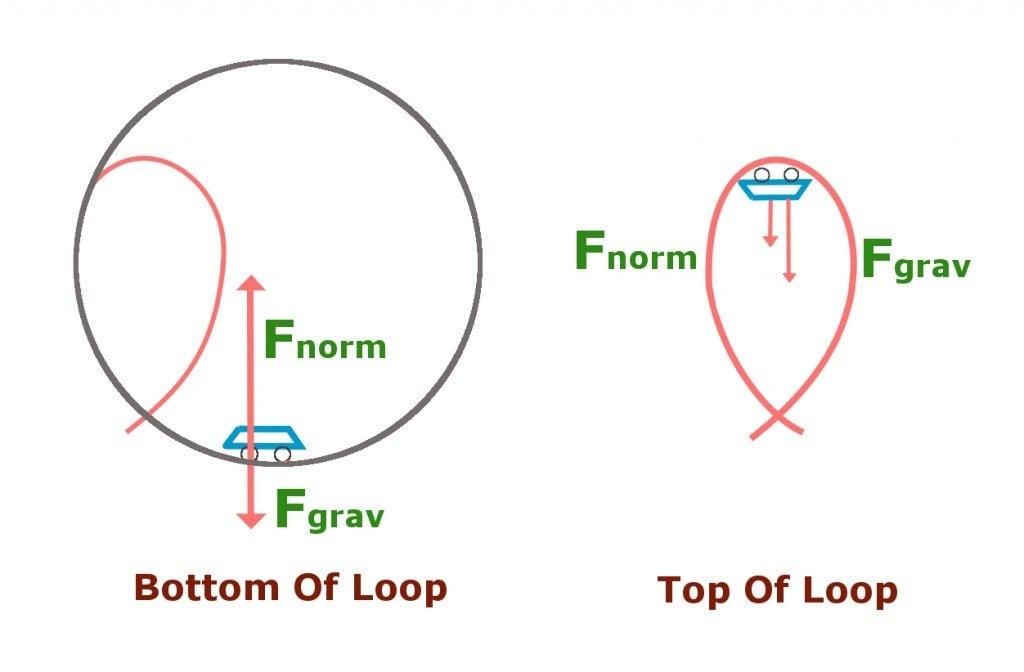









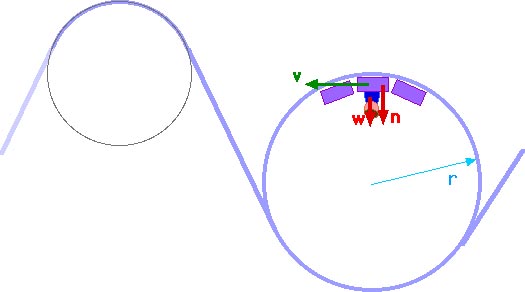





0 Response to "39 roller coaster free body diagram"
Post a Comment