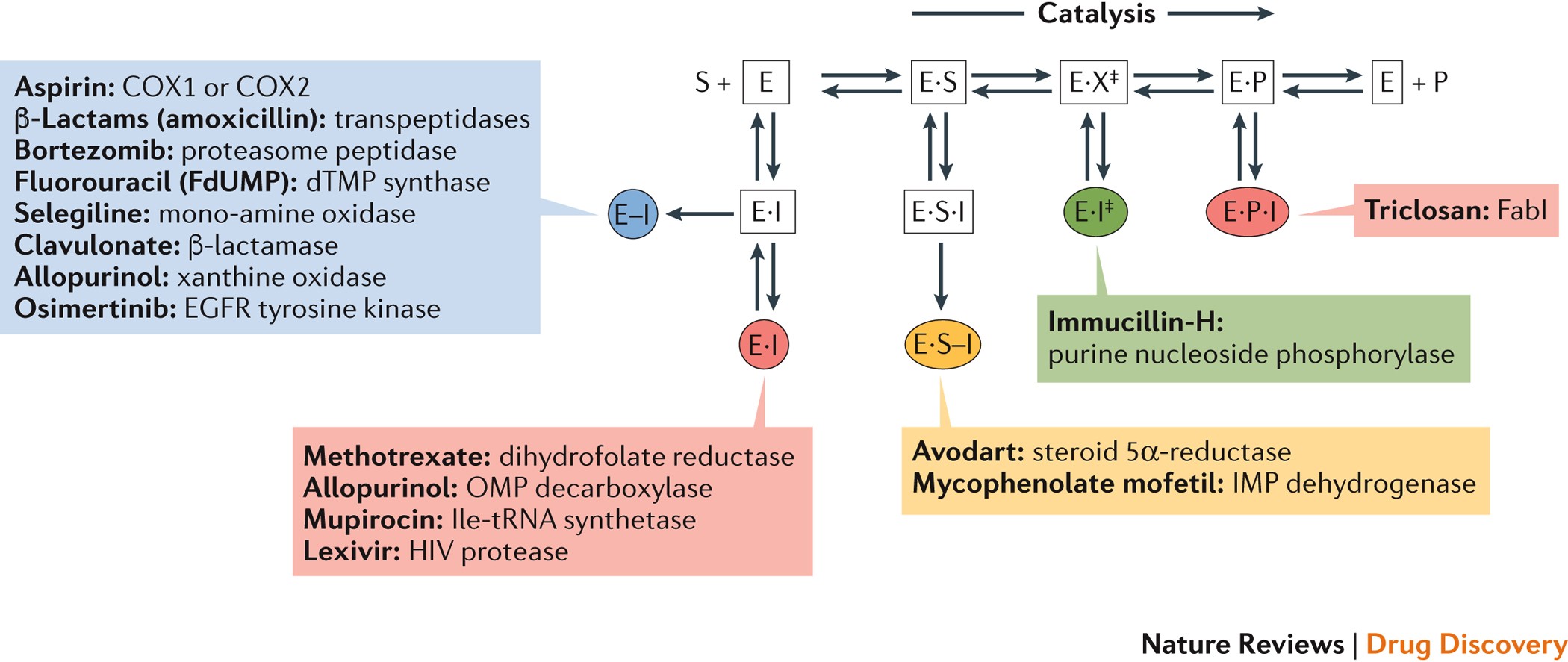
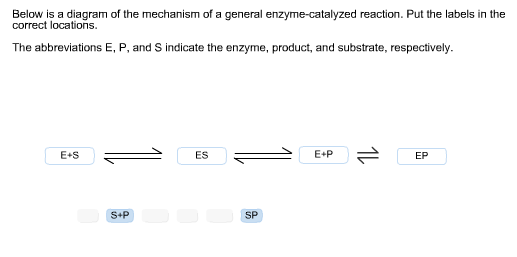
37 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
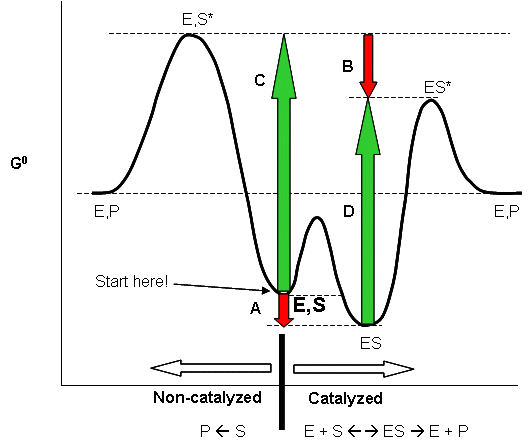
Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ... 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as depicted in the reaction diagrams shown in Figure 2. This lower activation energy results in an increase in rate as ...
biochemistry chapter #6 Flashcards - Quizlet 17) An enzyme stabilizes the transition state that is bound in the active site. What effect will this have on the energy diagram below? The diagram shown below is for the uncatalyzed reaction. A) Energy of point 1 is raised. B) Energy of point 2 is raised. C) Energy of point 2 is lowered. D) Energy of point 3 is lowered. E) Energy of point 4 is ...

Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
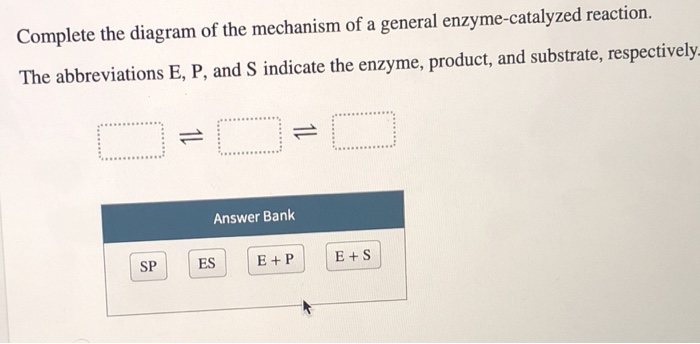
› topics › engineeringCalvin Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The general effects of these changes are shown in Table I. Plants that live in an environment normally deficient in a nutrient may optimize use of the nutrient partly by maximizing its ANUE. However, this can have a deleterious effect on the efficiency of water use (see below). Answered: Complete the diagram of the mechanism… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Answer Bank E + P SP E + S ES. Enzyme Catalysis: Definition, Mechanism, & Types - Embibe Enzyme Catalysis. Enzyme catalysis is an important topic covered under the chapter of "Surface Chemistry" in NCERT Chemistry books for Class 12. Enzymes are complex nitrogenous substances (proteins) that have high relative molar mass with order of 10,000 or even more and are derived from living organisms. Specific reactions may be catalysed ...
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. Compute activation energies for the first step of each mechanism, and identify which corresponds to the catalyzed reaction. 6.5: Enzymatic Reaction Mechanisms - Biology LibreTexts 6.5: Enzymatic Reaction Mechanisms. We can apply what we learned about catalysis by small molecules to enzyme-catalyzed reactions. To understand the mechanism of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, we try to alter as many variables, one at a time, and ascertain the effects of the changes on the activity of the enzyme. Enzyme Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics In general, three defined scenarios have been considered where whole-cell-catalyzed processes may present advantages over the free-enzyme-catalyzed ones: (1) the required enzyme is intracellular; (2) the enzyme needs a cofactor to carry out the catalytic act, and (3) the goal depends on a multienzymatic process. Answered: The diagram shows the mechanism of a… | bartleby The abbreviations E, P and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Transcribed Image Text: The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Answer Bank E+P SP ES S+P EP E+S.
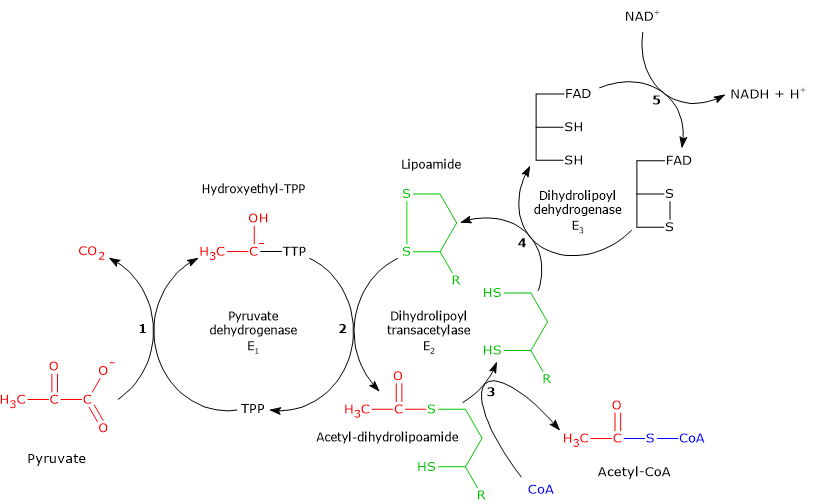
Enzyme - Catalytic Mechanisms Flashcards - Quizlet The tighter an enzyme binds to the transition state, the (greater, lower) the rate of the catalyzed reaction relative to that of the uncatalyzed reaction. Greater Transition state analogs Enzyme Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are time-dependent. ... or enzyme displacement, mechanism where one product is released prior to the binding of the second substrate. This third major type of bimolecular reaction is depicted in the following diagram where E' indicates that the enzyme exists in a chemically modified form. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › GluconeogenesisGluconeogenesis - Wikipedia Gluconeogenesis is a pathway consisting of a series of eleven enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The pathway will begin in either the liver or kidney, in the mitochondria or cytoplasm of those cells, this being dependent on the substrate being used. Many of the reactions are the reverse of steps found in glycolysis. [citation needed] Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes - Chemistry An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two atoms or compounds. The substance that loses the electrons is said to be oxidized, while the substance that gains the electrons is said to be reduced. Redox reactions always have to occur together.
Solved Below is a | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively. 1.2: Background - Chemistry LibreTexts A reaction for a typical substrate and enzyme is illustrated below showing the intermediate enzyme-substrate complex, the products and the released enzyme. Figure 1. A Schematic Representation of an Enzyme-Catalyzed Mechanism 6. Enzyme Kinetics involves the study of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, which may involve the study of the reaction rate ... Solved Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general ... Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and Sindicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. ES E+P = EUS Answer Bank SP. Question: Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Chapter 7 Enzyme RQ + HW Flashcards | Quizlet Evaluate which of the following statements is/are true about enzymes and the transition from reactants to products. 1. An enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction, which means the transition state is not as energetically unfavorable as it would be without the presence of an enzyme. 2.
› chapters › 74319Bioethanol Production: An Overview | IntechOpen Jul 29, 2020 · The mechanism of the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass to glucose occurs in three steps and are presented in Figures 2–6. The first step is the linking of the β-1,4 bond of the cellulose with water molecule catalyzed by endoglucanase (1,4-β-D-glucanohydrolase) resulting to the formation of cellodextrin with a shorter chain, and free ...
12.7 Catalysis | General College Chemistry II A heterogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is present in a different phase (usually a solid) than the reactants. Such catalysts generally function by furnishing an active surface upon which a reaction can occur. Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gas ...
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e - OpenStax The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step.
Biochemistry I Chapter 11 Problems Flashcards - Quizlet A transition state analog is a stable molecule that resembles the transition state of an enzyme catalyzed reaction, and is a potent _____ of that enzyme. *inhibitor Little can be learned about enzyme reaction mechanisms by examining the corresponding nonenzymatic reactions of model compounds.
12.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts 1. Figure 12.7. 1: This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation. Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as ...
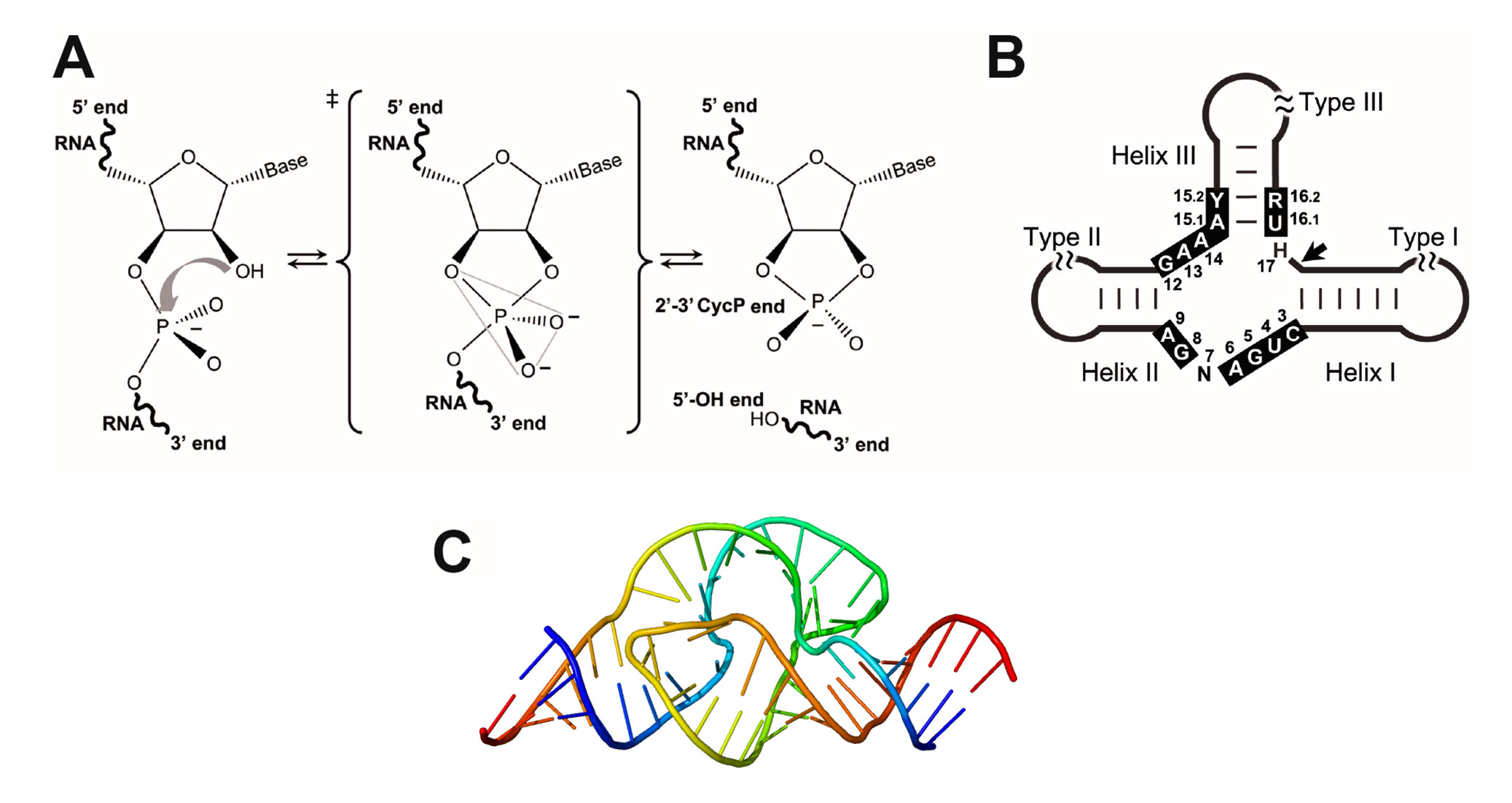
Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts ... For an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, it should be stressed that, under conditions where the overall reaction is spontaneous, each elementary step must exhibit a negative free energy change, and this must be properly reflected in the progression profile of the reaction. ... In this sense, the energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is an ...
of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in ... of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in t… Show more Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively ______
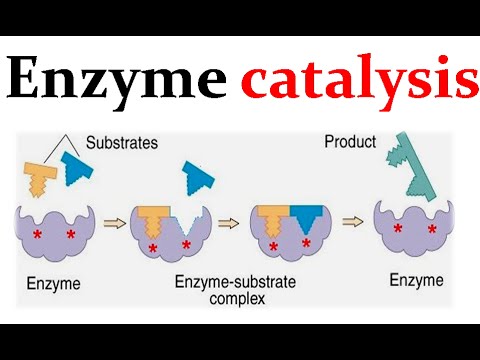
4.3: Mechanisms of Catalysis - Biology LibreTexts Found in our digestive system, chymotrypsin's catalytic activity is cleaving peptide bonds in proteins and it uses the side chain of a serine in its mechanism of catalysis. Many other protein-cutting enzymes employ a very similar mechanism and they are known collectively as serine proteases (Figure 4.52).
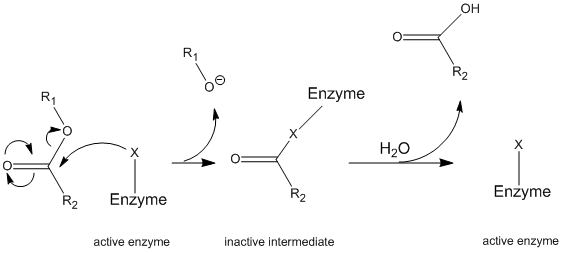
Mechanism of Enzyme Reaction (With Equations) The enzyme functions to lower the amount of energy required to bring the substrate to the transition state as shown in Fig. 8.25. An example may be cited to explain the significance of activation energy. A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen will remain unchanged indefinitely, although they have the ability to combine producing water.
Reactions and Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis - VEDANTU The biochemical reactions susceptible to acid-base catalysis include peptide and ester hydrolysis, tautomerization, the reaction of phosphate groups and addition to carbonyl groups. These reactions typically involve Asp, Glu, His, Cys, Tyr and Lys residues. Many enzymes utilize a concerted acid-base mechanism (i.e., both acid and base catalysis).
QUIZ 2 mega quizlet Flashcards | Quizlet - An enzyme that temporarily undergoes covalent catalysis as part of its mechanism. - A type of enzyme inhibitor where KM is unaltered. - The type of reaction catalyzed by proteases. - An enzyme that is part of a pigment formation pathway and has a low-temperature optimum. - A protease enzyme with a low pH optimum.
Enzyme Catalysis: Definition, Mechanism, & Types - Embibe Enzyme Catalysis. Enzyme catalysis is an important topic covered under the chapter of "Surface Chemistry" in NCERT Chemistry books for Class 12. Enzymes are complex nitrogenous substances (proteins) that have high relative molar mass with order of 10,000 or even more and are derived from living organisms. Specific reactions may be catalysed ...
Answered: Complete the diagram of the mechanism… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Answer Bank E + P SP E + S ES.
› topics › engineeringCalvin Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The general effects of these changes are shown in Table I. Plants that live in an environment normally deficient in a nutrient may optimize use of the nutrient partly by maximizing its ANUE. However, this can have a deleterious effect on the efficiency of water use (see below).


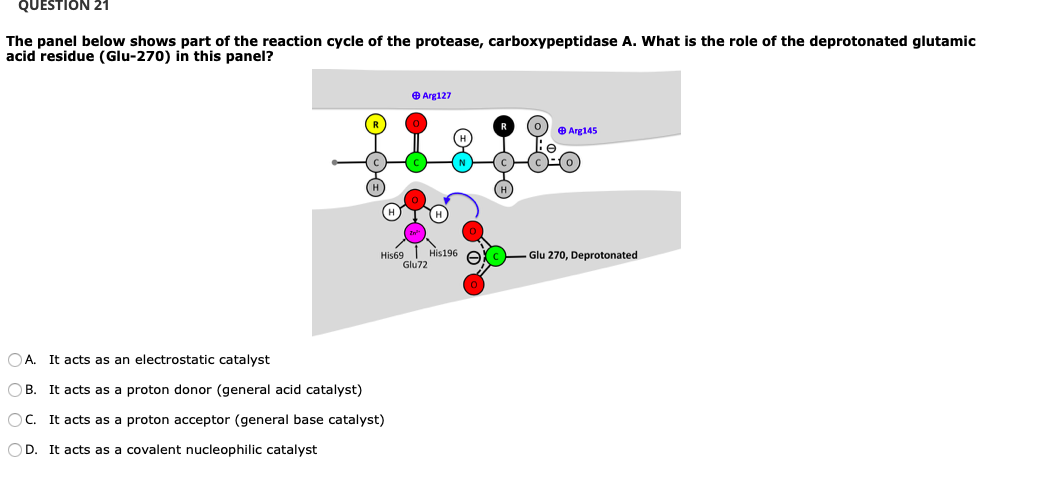



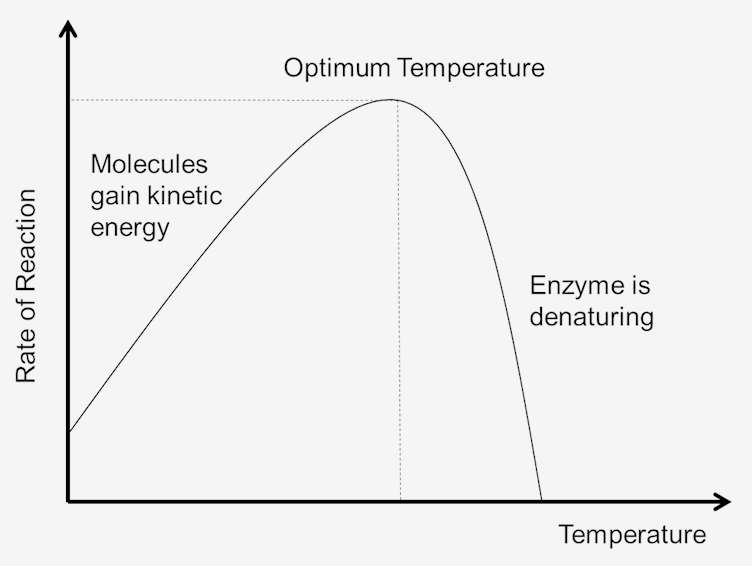

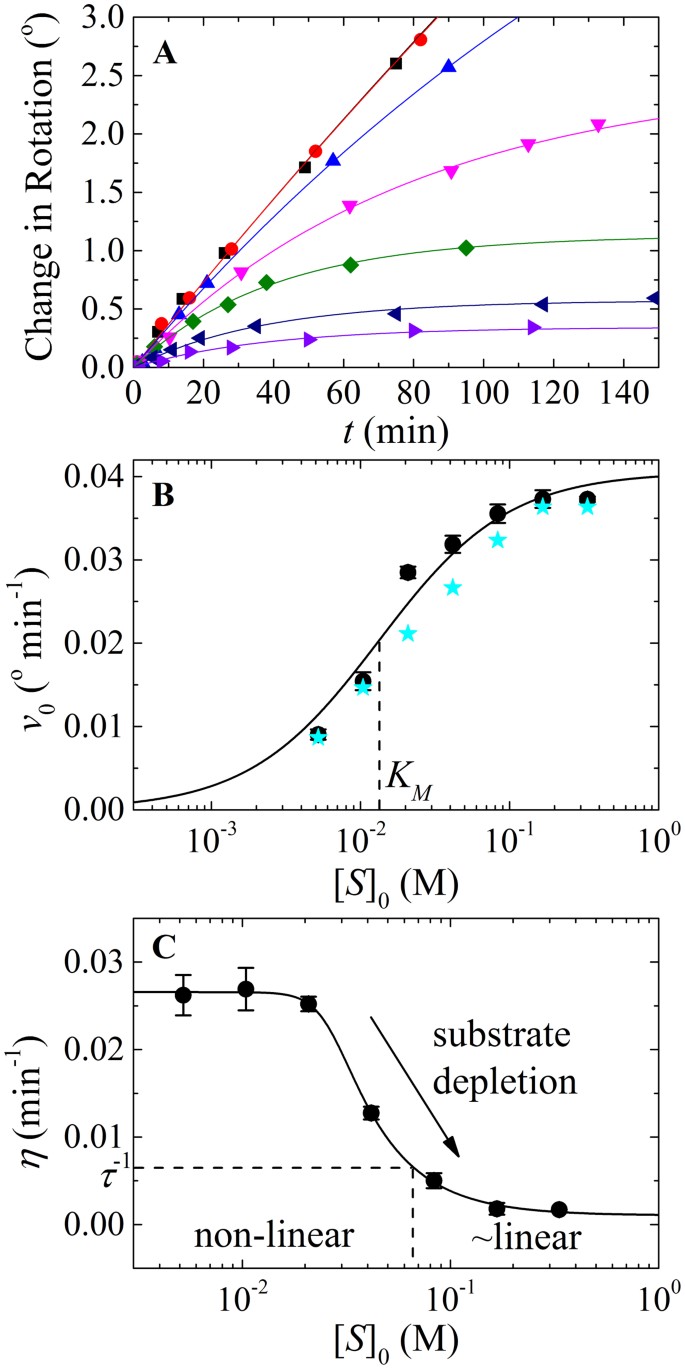











0 Response to "37 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment