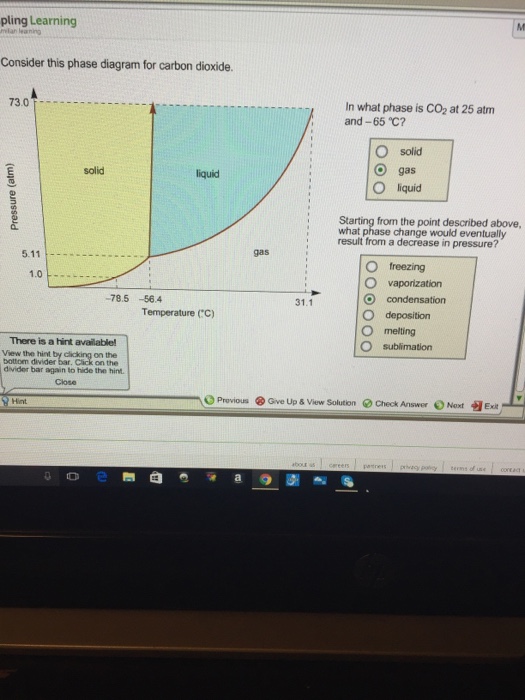
38 consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.
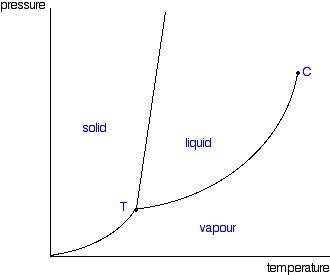
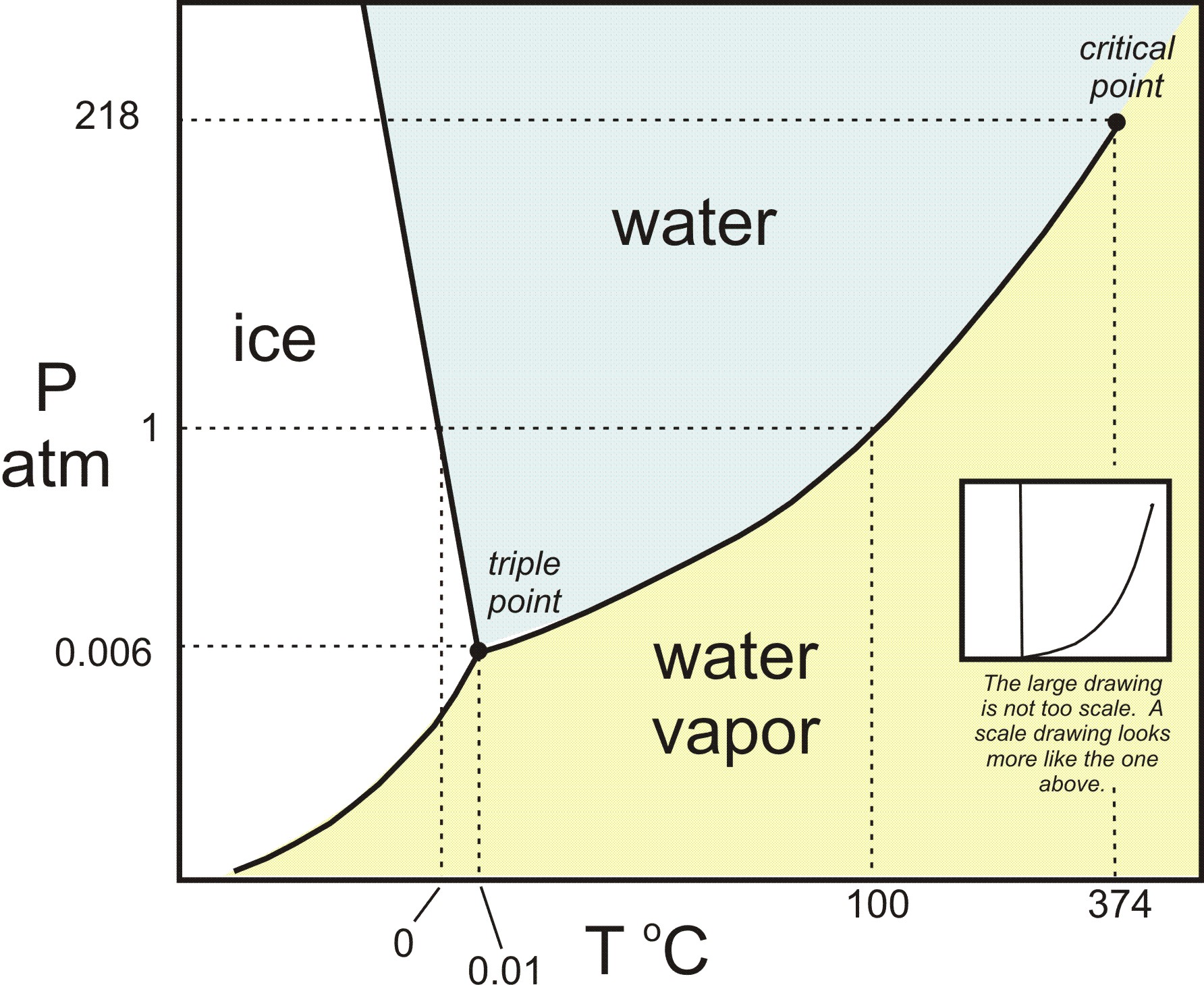
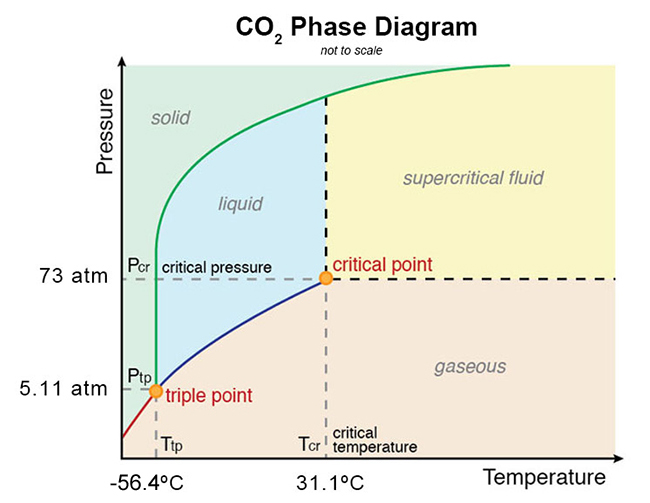
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 25 atm and −65 °C? gas solid liquid Starting from the same point, 25 atm and −65 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? deposition vaporization melting sublimation freezing condensation. For carbon dioxide and water are shown in figure 1. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in figure 5 as another example. Solid co2 sublimes when heated. When co 2 is solved in water the mild carbonic acid is formedcooled co 2 in solid form is called dry ice. In contrast to the phase diagram of water the phase diagram of co 2 ...
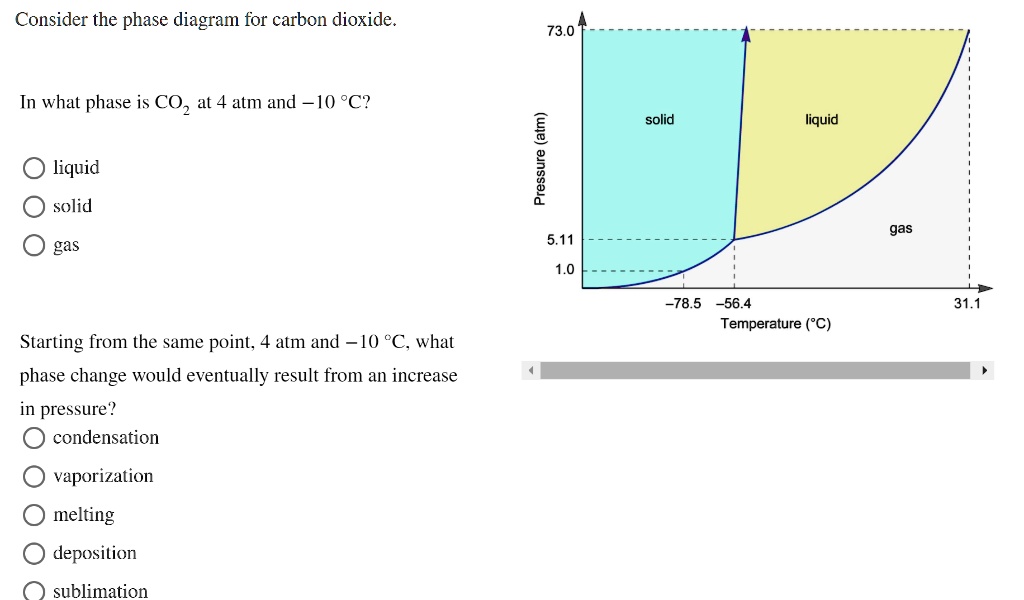
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide in what phase is CO 2 at 4 atm and -10 °C? a. Solid. b. Gas. Q. Under standard conditions (298 K and 1 atm), which statement is true?a] diamond converts to graphite spontaneouslyb] graphite converts to diamond spon... Q. Consider this phase diagram for carbon. Which phases are present at the lower ...
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.
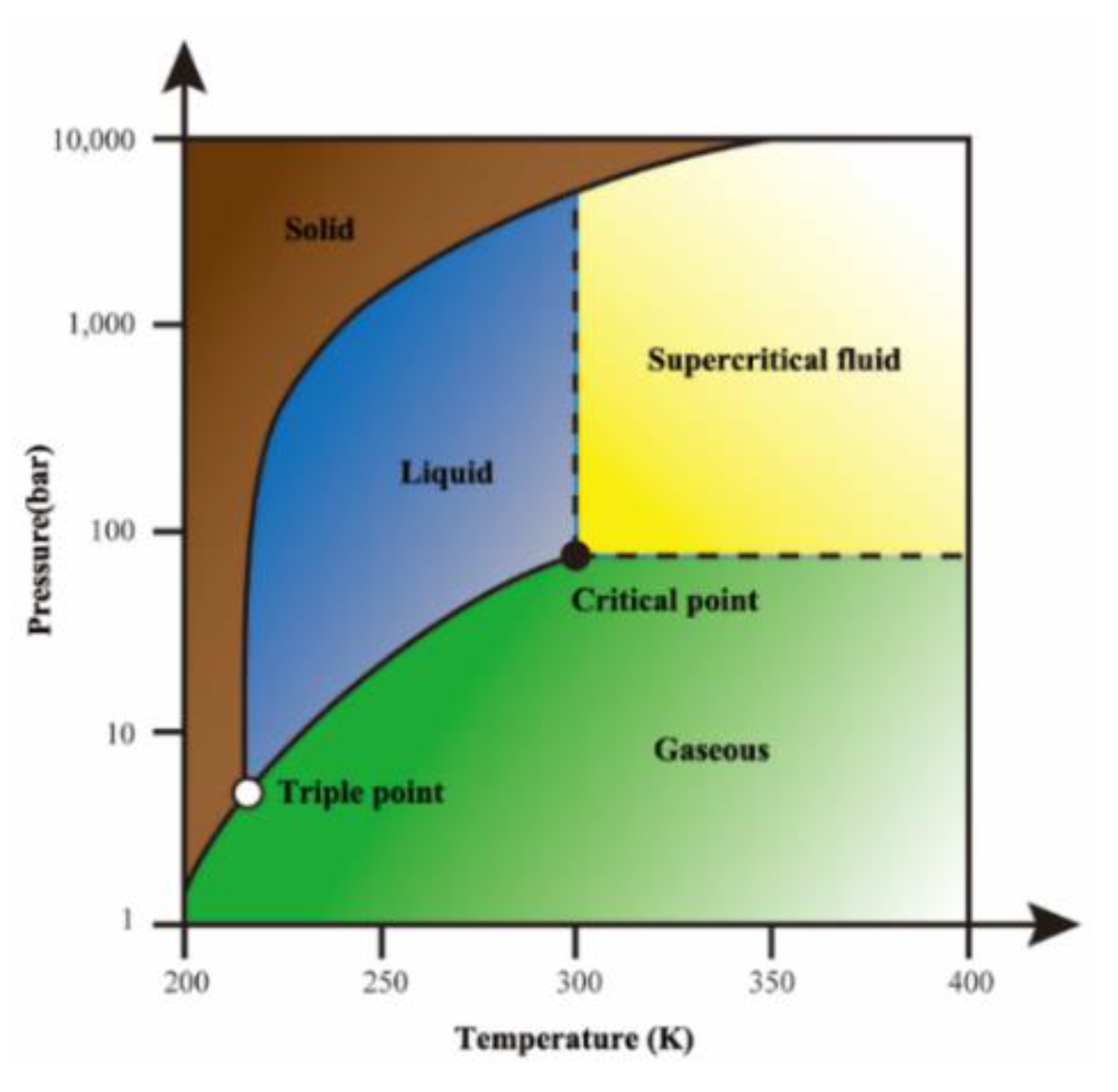
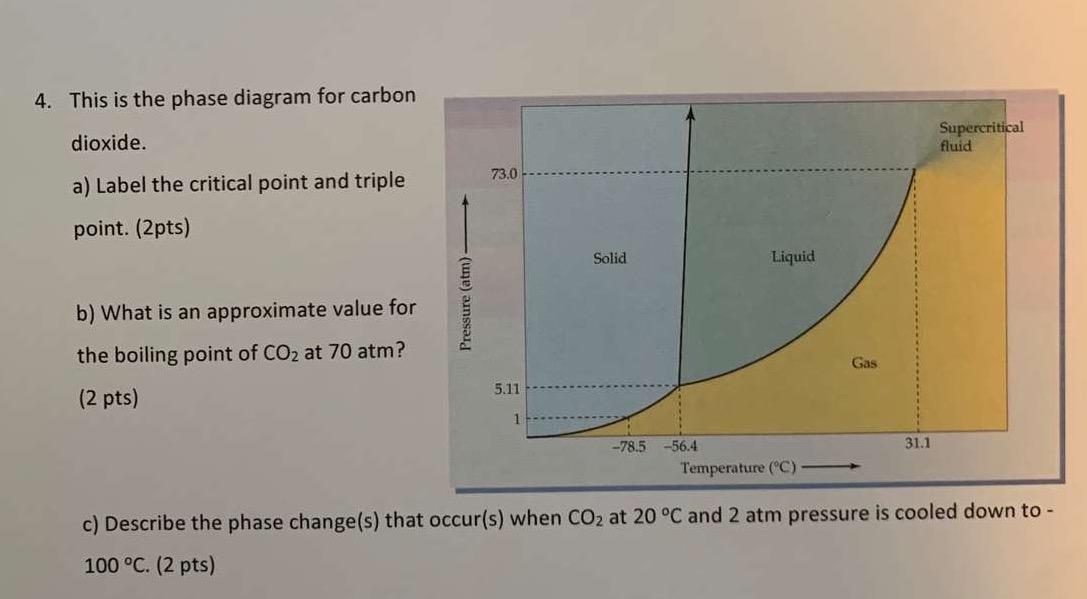
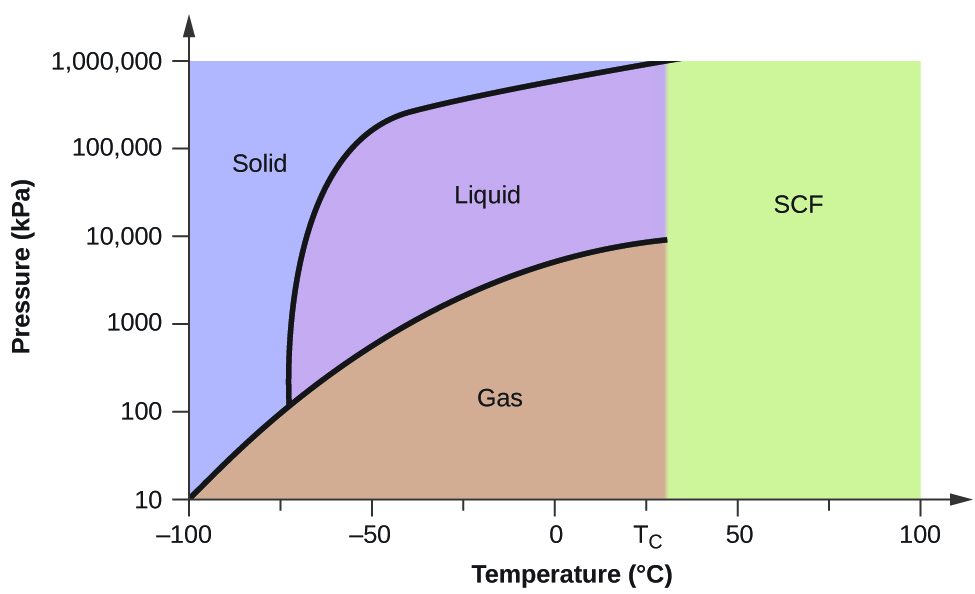
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ... Phase Diagram Carbon Dioxide. carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram s a t u r at i o n li ne title phase diagram xls created date 11 10 1999 5 44 57 pm phase diagrams university of waterloo the critical temperature for carbon dioxide is 31 1°c and the critical pressure is 73 atm the critical temeprature the fluid is called super critical fluid ... Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 Degree C ? Solid Gas Liquid Starting from the point described above what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? Melting freezing deposition sublimation vaporization condensation.
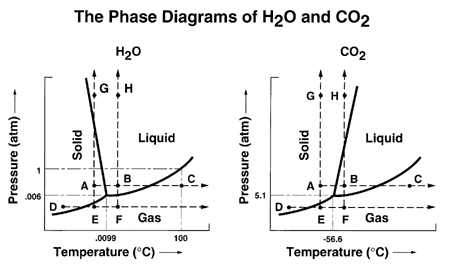
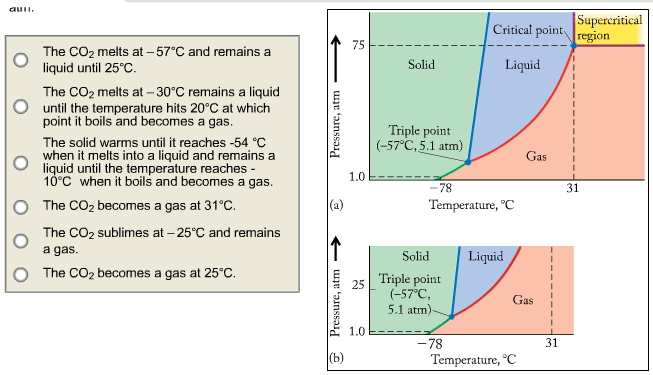
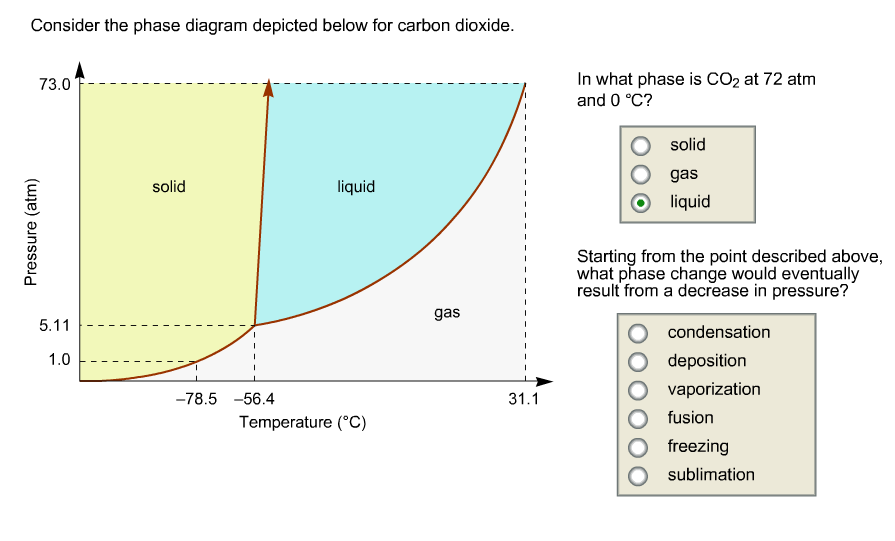
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.. Carbon dioxide - 290 - Noshly - Wise eating, made easy. (Katharine Riley) Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound that is found as a gas in the Earth's atmosphere. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen. The powerpoint discusses the phase diagram of carbon dioxide. 4) Consider the phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide given in the text on page 315. Explain the following observations: A thin wire with weights attached is draped over a block of "dry ice," a second wire with weights is draped over a block of ice. The wire cuts through the ice but not through the "dry ice." Answer Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? Question: Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? Phase diagram for carbon dioxide 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90-80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 Temperature/oC Pressure / atm liquid gas solid bp line mp line subl line "Vapour pressures … above one atmosphere". In fact, the vapour pressure data start at page 215 for a large number of organic and inorganic substances, and preceding that, for various ...
The phase diagram for carbon dioxide. The only thing special about this phase diagram is the position of the triple point which is well above atmospheric pressure. It is impossible to get any liquid carbon dioxide at pressures less than 5.11 atmospheres. That means that at 1 atmosphere pressure, carbon dioxide will sublime at a temperature of ... Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 °C?a) solidb) liquidc) gas Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure?a) condensationb) depositionc) sublimationd) vaporizatione) meltingf) freezing. Question. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 °C? a) liquid b) gas c) solid Starting from the same point, 4 atm and -10 °C, what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? a) sublimation b) melting c) freezing d) condensation e) vaporization f) deposition. Asked over 1 ... carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram s a t u r at i o n li ne title phase diagram xls created date 11 10 1999 5 44 57 pm Phase Diagram For Co2 Consider This Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide - Mechanical Engineering Archive October 27 2016
Well, consult the phase diagram. And then you literally just read it like any other graph: find your x coordinate and find your y coordinate. (x,y) -= (P,T) = ("15 atm", -60^@ "C") And one should easily see that "CO"_2 is a solid at this T and P, as it should be, left of its triple point temperature but higher up than the triple point pressure. Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO_2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? solid gas liquid Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? condensation deposition sublimation freezing vaporization melting Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating ... Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxidea. Solid co2 is more dense than liquid co2. 10 4 Phase Diagrams Chemistry The solid liquid curve exhibits a positive slope indicating that the melting point for co 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances water being a notable exception as described previously.
This photo about: Phase Diagram Of Carbon, entitled as Consider This Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide - Mechanical Phase Diagram Of Carbon - also describes Consider This Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide - Mechanical and labeled as: ], with resolution 2061px x 3653px
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...

Phase Behavior For Carbon Dioxide Ethanol System Experimental Measurements And Modeling With A Cubic Equation Of State Sciencedirect
This photo about: Phase Diagram Carbon Dioxide, entitled as Consider This Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide - Carbon Dioxide Phase Diagram Carbon Dioxide - also describes Consider This Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide - Carbon Dioxide and labeled as: ], with resolution 1415px x 3041px
(b) With the decrease in pressure, both the fusion and boiling point of carbon dioxide will decrease. (c) For carbon dioxide, the critical temperature is 3 1. 1 o C and critical pressure is 73.0 atm. If the temperature of carbon dioxide is more than 3 1. 1 o C, it can not be liquefied, however large pressure we may apply.
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 Degree C ? Solid Gas Liquid Starting from the point described above what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? Melting freezing deposition sublimation vaporization condensation.
Phase Diagram Carbon Dioxide. carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram carbon dioxide temperature pressure diagram s a t u r at i o n li ne title phase diagram xls created date 11 10 1999 5 44 57 pm phase diagrams university of waterloo the critical temperature for carbon dioxide is 31 1°c and the critical pressure is 73 atm the critical temeprature the fluid is called super critical fluid ...
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...

Discuss The Phase Diagram Of The Co2 System Here You Have To Describe All The Lines Areas And Triple Brainly In

Defining A Materials Database For The Design Of Copper Binary Alloy Catalysts For Electrochemical Co2 Conversion Lee 2018 Advanced Materials Wiley Online Library

5 Consider The Phase Diagram For Carbon Dioxide 10 Supercritical Fluid Solid Liquid Pressure Atm 78 5 56 4 Homeworklib
Molecules Free Full Text The Effect Of Functional Groups On The Phase Behavior Of Carbon Dioxide Binaries And Their Role In Ccs Html
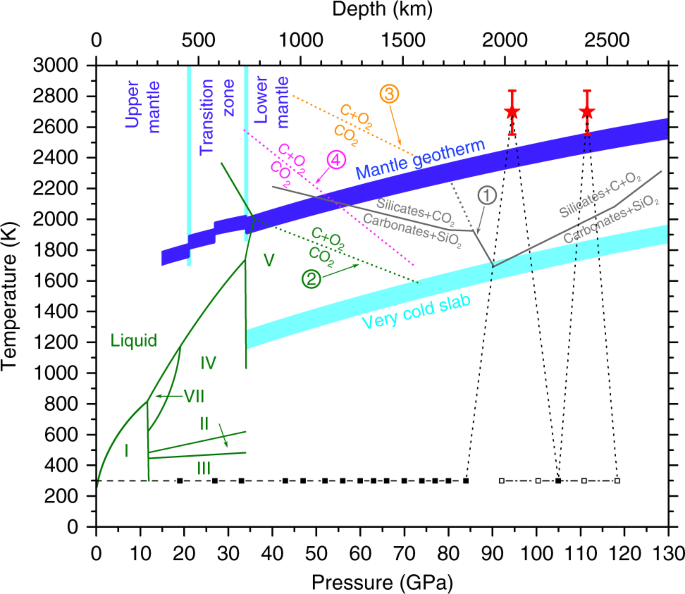
Energies Free Full Text Rock Breaking And Dynamic Response Characteristics Of Carbon Dioxide Phase Transition Fracturing Considering The Gathering Energy Effect Html

Answer The Following Questions Based On The P T Phase Diagram Of Carbon Dioxide A At What Temperature And Pressure Can The Solid Liquid And Vapour Phases Of Co2 Co Exits













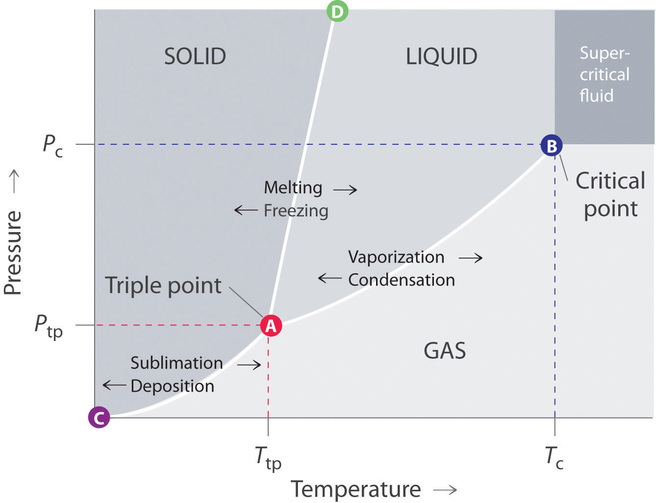
0 Response to "38 consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide."
Post a Comment