39 diverging lens ray diagram
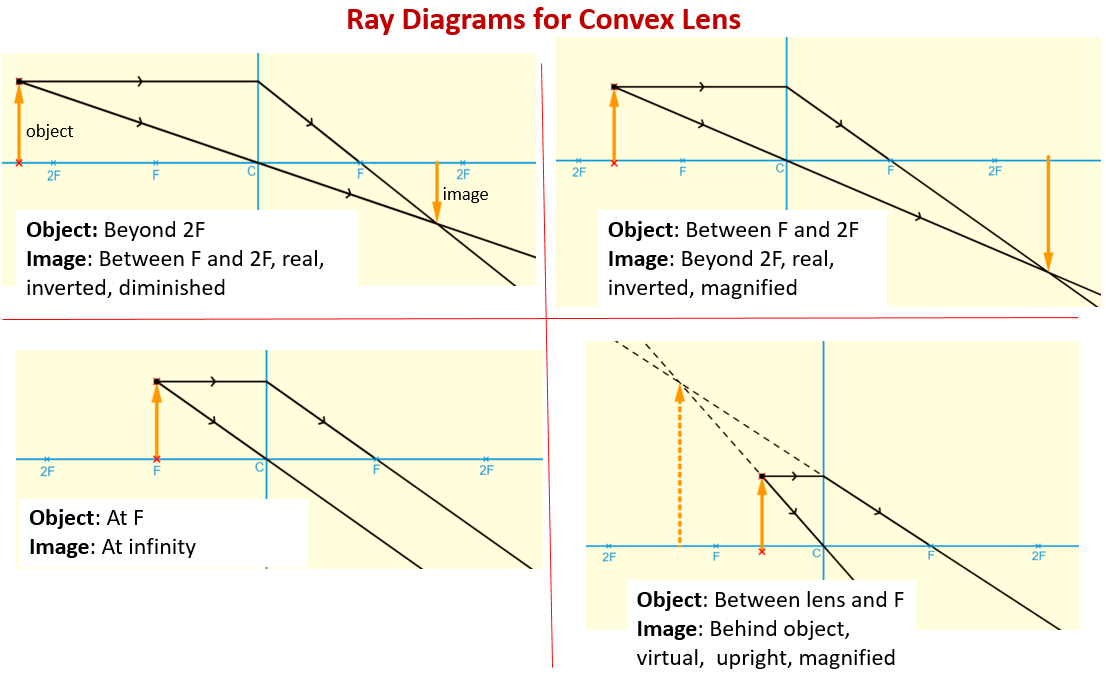
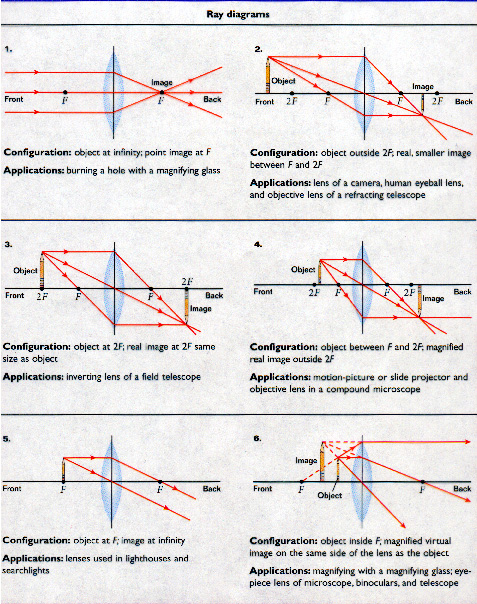
Apr 26, 2020 · For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t Jul 07, 2020 · Converging Lens vs. Diverging Lens: Converging Lens: Diverging Lens: It is thicker at the middle but thinner at the edges: It is thinner at the middle but bulging near the boundaries : It has a focusing action: It diverges a beam of light: It can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object
A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak diverging lens is placed between the converging lens and the image, where is the new image ...15 pages
Diverging lens ray diagram
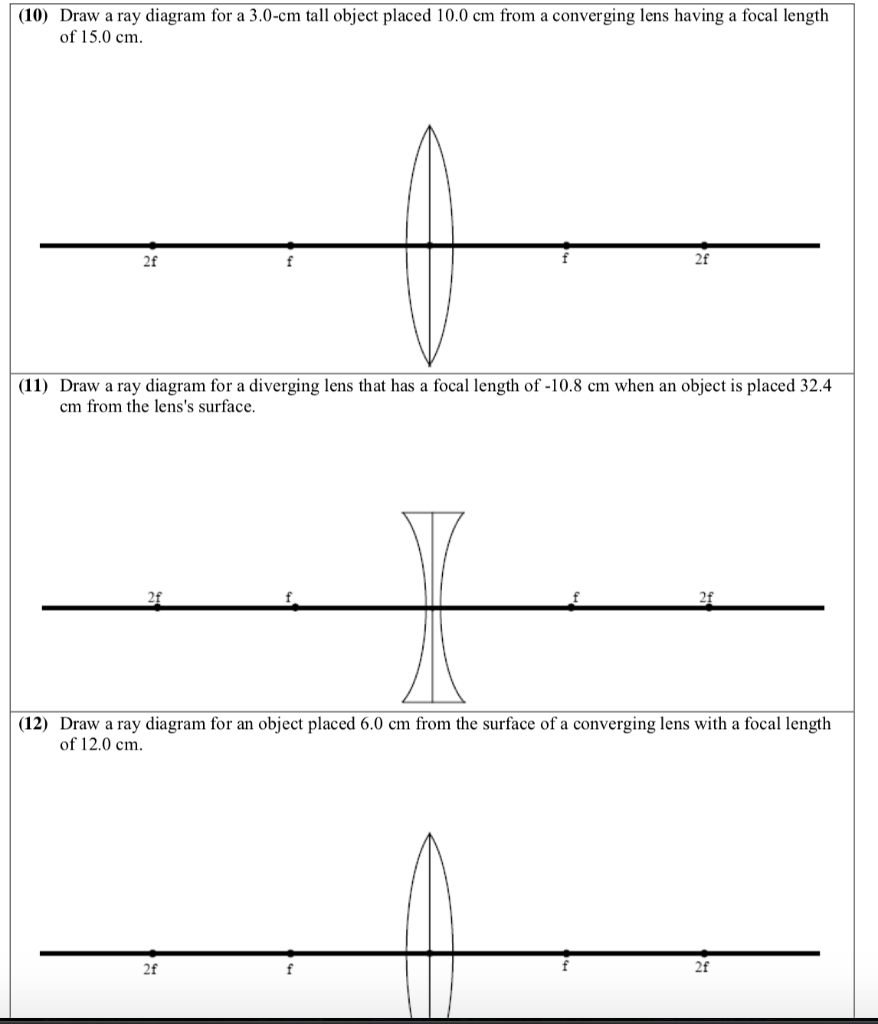
7. Make a ray diagram for an object placed closer to a diverging (concave) lens than the focal point. Is the magnification greater or less than 1? Can the magnification for a diverging lens ever be greater than 1? Explain. 8. Show by making ray diagrams that for any image, the magnification, M, is the ratio of image to object distances: M ... Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams ... Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in ...11 Apr 2020 · Uploaded by Bozeman Science The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens.
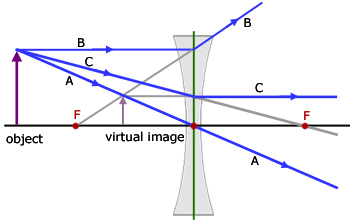
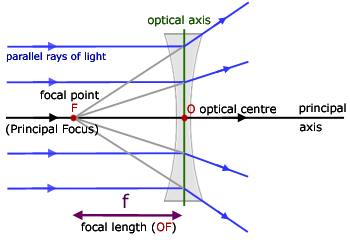
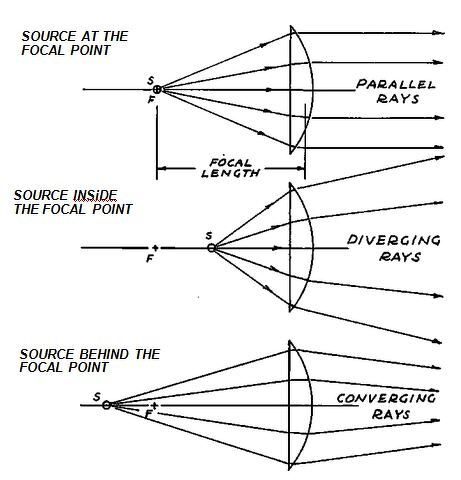
Diverging lens ray diagram. If the lens is biconcave or plano-concave, a collimated beam of light passing through the lens is diverged (spread); the lens is thus called a negative or diverging lens. The beam, after passing through the lens, appears to emanate from a particular point on the axis in front of the lens. Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Diverging Lens ... Diverging lens diagrams use the following three rules: ... Extend all lines until they connect. The spot where ...
Dec 10, 2019 · A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams ... Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in ...11 Apr 2020 · Uploaded by Bozeman Science
7. Make a ray diagram for an object placed closer to a diverging (concave) lens than the focal point. Is the magnification greater or less than 1? Can the magnification for a diverging lens ever be greater than 1? Explain. 8. Show by making ray diagrams that for any image, the magnification, M, is the ratio of image to object distances: M ...

Open Source Physics Singapore Ejss Thin Converging Diverging Lens Ray Diagram Lens Inquiry Learning Model
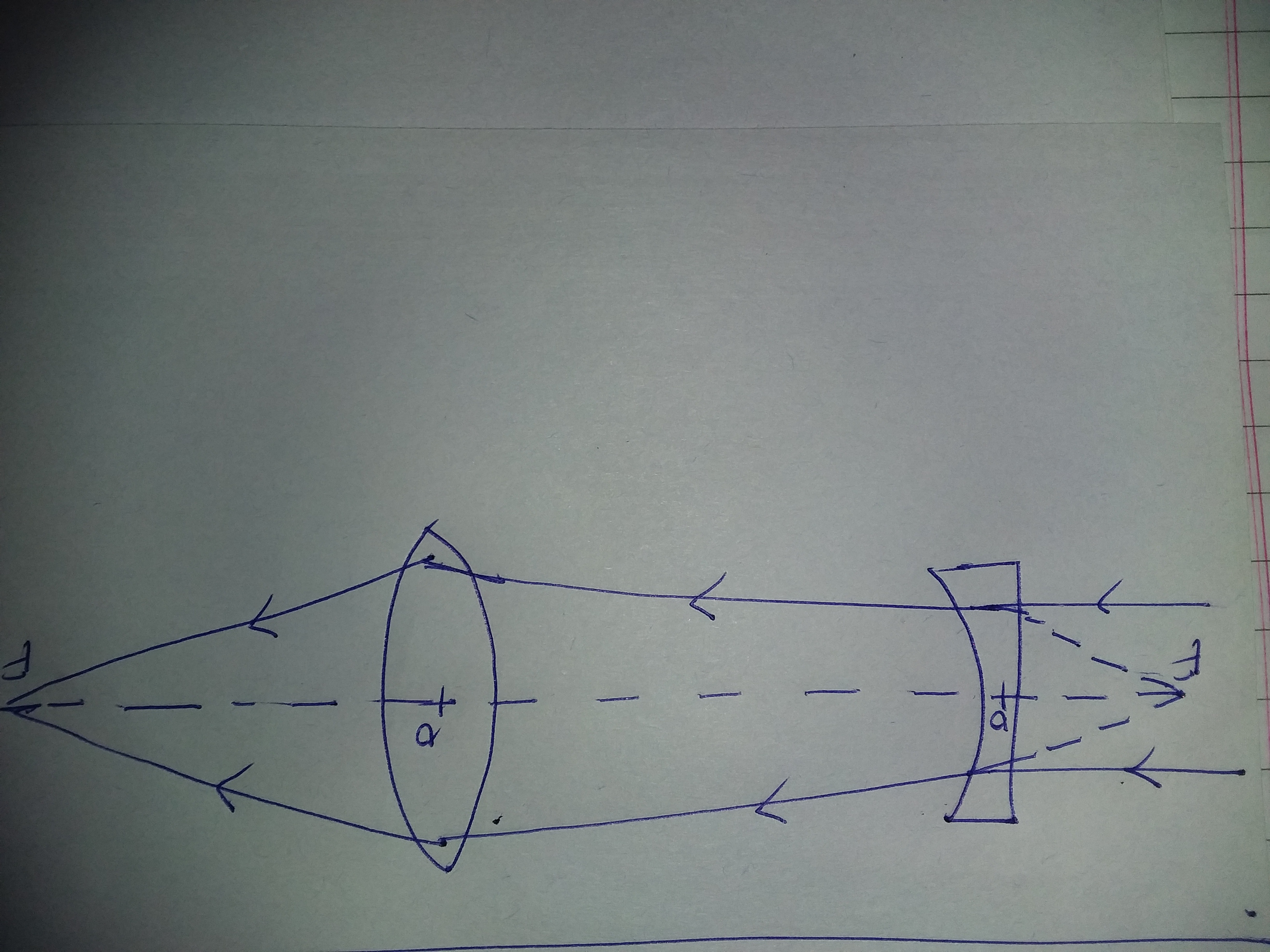
Complete The Ray Diagram When A Ray Passes Parallel Through A Plano Concave Lens And Then After Refraction The Ray Passes Through A Convex Lens Physics Topperlearning Com Tm9sl11
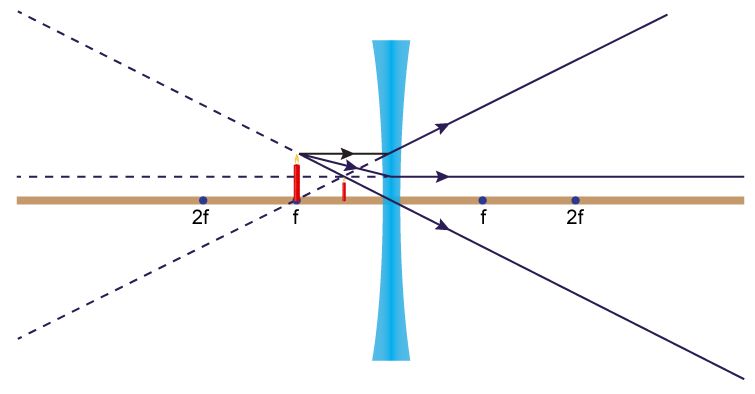
What Is The Ray Diagram Of Concave Lens When Object Is Placed At Focus Please Explain In Detail Physics Topperlearning Com Yqq7t00
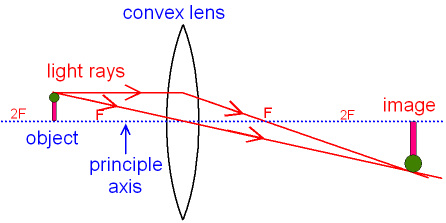
Gcse Physics Ray Diagram For An Image Made By A Convex Lens What Is A Real Image What Is An Inverted Image Gcse Science
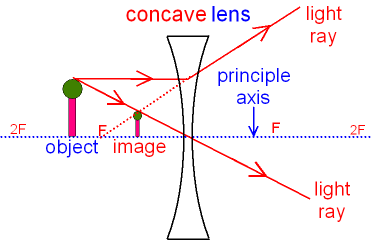
Gcse Physics What Is The Ray Diagram For A Concave Lens What Is A Virtual Image What Is An Upright Image Gcse Science

Draw Neat And Well Labelled Ray Diagrams For Image Formation By A Convex Lens When An Object Is At 2f 1

Draw The Ray Diagram In Each Case To Show The Position And Nature Of The Image Formed When The Object

Draw A Ray Diagram For The Diverging Lens With The Object Height Of 4 Cm At The Distance Of 8 Cm Away The Focal Point Is At 3 Cm Find The Image Study Com
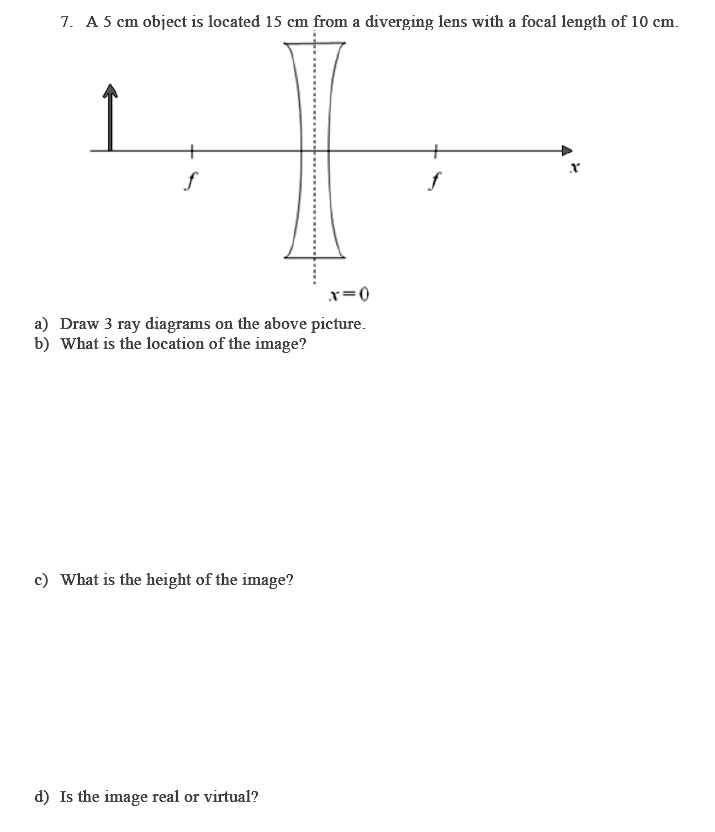
Solved A 5 Cm Object 1s Located 15 Cm Fron Diverging Lens With Focal Length Of 10 Cm T Draw 3 Ray Diagrams On The Above Picture What Is The Location Of The












0 Response to "39 diverging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment