40 cf molecular orbital diagram
1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram for CF+ assuming a large 25-2p orbital interaction. 2. What is the highest occupied molecular orbital (also known as the HOMO)? 3. Is this species paramagnetic? 4. What is the bond order? Question: 1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram for CF+ assuming a large 25-2p orbital interaction. 2. Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker. These quizzes enable you to build your own molecular orbital diagram from components. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons.
Accurate Hartree-Fock self‐consistent‐field wavefunctions have been computed for CF, CF +, and CF − at several internuclear separations by the Roothaan expansion method. Similar wavefunctions were also computed for SiF, SiF +, and SiF − at the parent molecule internuclear separation. A Dunham analysis of the energy curves for the three CF species yielded values for the spectroscopic ...

Cf molecular orbital diagram
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Molecular orbitals were first introduced by Friedrich Hund and Robert S. Mulliken in 1927 and 1928. The linear combination of atomic orbitals or "LCAO" approximation for molecular orbitals was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones. His ground-breaking paper showed how to derive the electronic structure of the fluorine and oxygen molecules from quantum principles. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
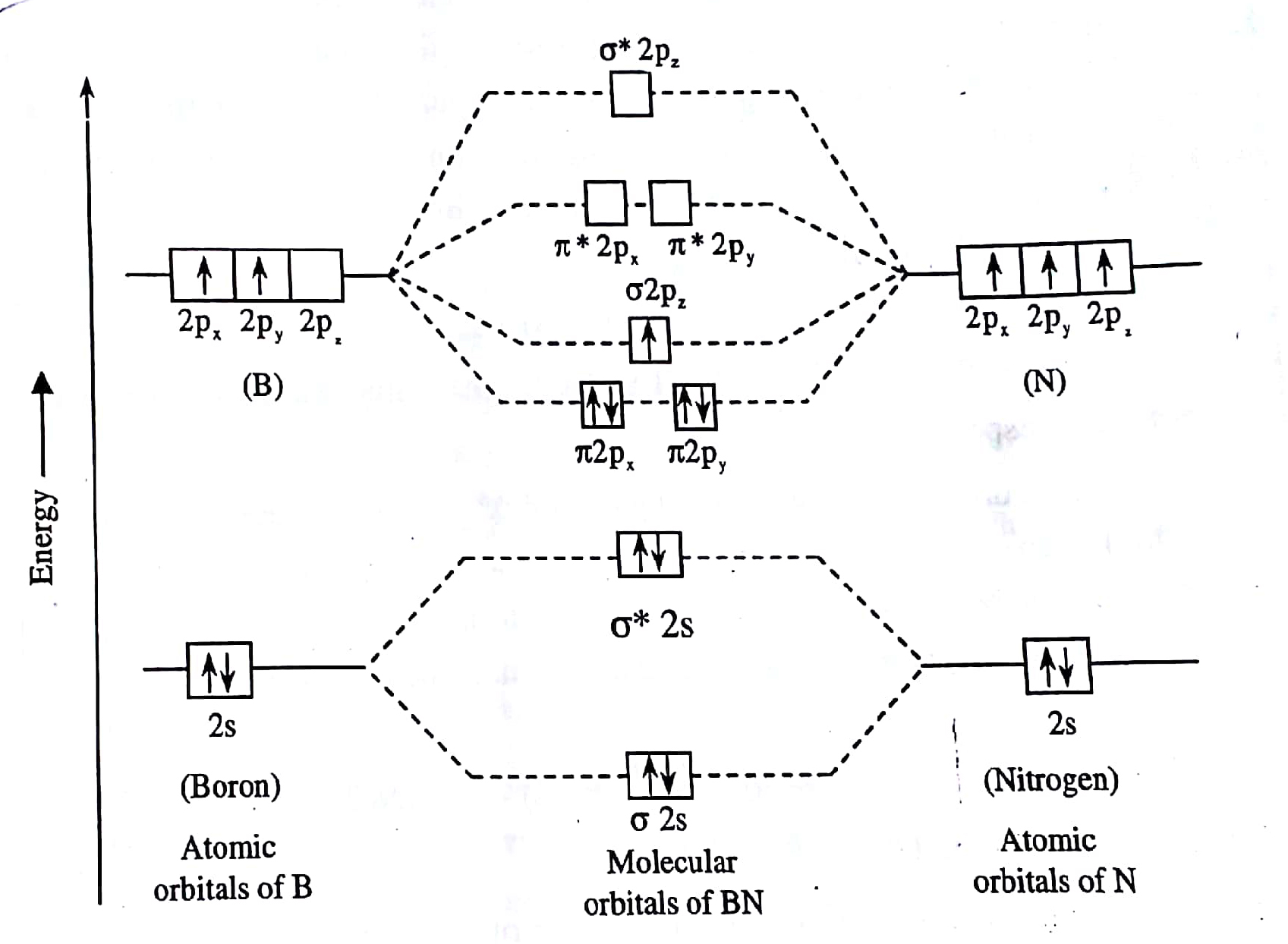
Cf molecular orbital diagram. P16.18) Images of molecular orbitals for LiH calculated using the minimal basis set are shown here. In these images, the smaller atom is H. The H1s AO has a lower energy than the Li2s AO. The energies of the MOs are (left to right) -63.9, -7.92, and +2.14 eV. Make a molecular orbital diagram for this molecule, associate the MOs with the images, Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) When two different atoms are bonded together, their molecule is called heteronuclear molecule. where C1 and C2 are two constants having different values for different atoms. Also the molecular orbitals formed are unsymmetrical due to difference in electronegativities. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Molecular orbital diagram for Cf(DPA) 3 3-. S13 Supplemental Figure 15. Molecular orbital diagram for the An(H 2 O) 8 3+ 3+and An(H 2 O) 9 species. S14 Supplemental Figure 16. Contribution of An f orbitals to An:H 2 O molecular orbitals in the An(H 2 O) 9 3+ complexes. S14 Supplemental Figure 17. Molecular orbital diagram for the aqueous An(H 2 ...
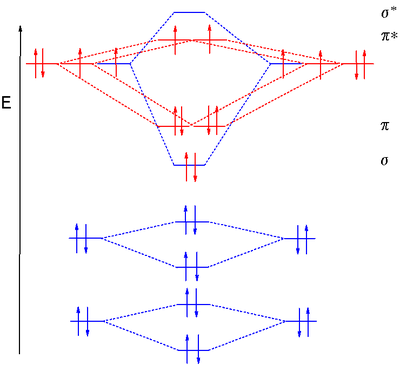
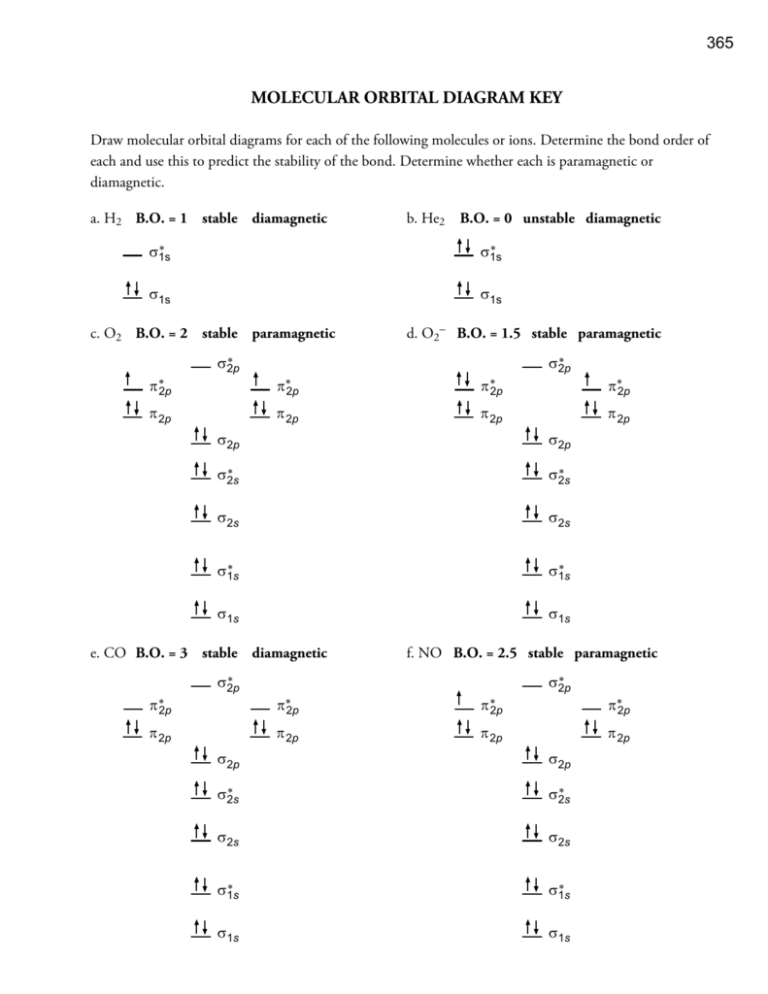
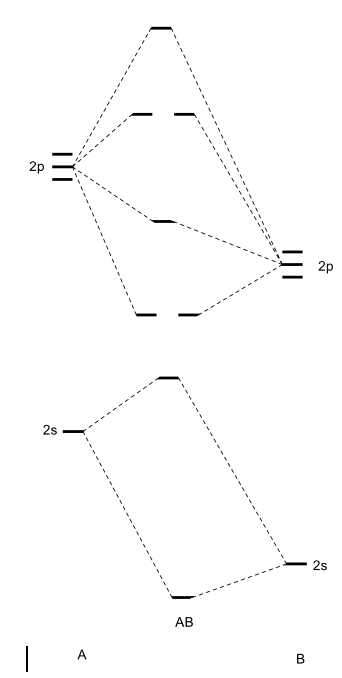
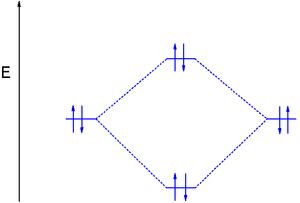
In general, this mixing of n atomic orbitals always generates n molecular orbitals. The hydrogen molecule provides a simple example of MO formation. In the following diagram, two 1s atomic orbitals combine to give a sigma (σ) bonding (low energy) molecular orbital and a second higher energy MO referred to as an antibonding orbital. Generate a molecular orbital diagram for Be 2 and remove an electron from the highest occupied molecular orbital to give the diatomic a positive charge. Now calculate the bond order of the cationic species. If the bond order is greater than zero, the molecule can exist. Solution . Re: Finding bond length for CF-, CF and CF+. If two atoms have different electronegativities, the energy of pi p orbitals is usually lowered. Based on the MO diagram, CF has a bond order of 2.5. In CF+, an electron is taken off from pi 2p orbital (which is the highest occupied orbital), bond order becomes 3. In CF-, an electron is added to pi ... The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
Such formulae enable us to calculate the contributions of the particular donor-acceptor resonance structures (e.g., DA, D + A −, etc., cf. p. 520) in the Slater determinants built of the molecular orbitals (14.37) of the total system. If one of these structures prevailed at a given stage of the reaction, this would represent important information about what has happened in the course of the ... The occupied molecular orbitals and conduction molecular orbitals contain DOS. In bulk particles, DOS is a continuous function of energy, while in CNTs (and other 1D nanoparticles), DOS is made of discontinuous spikes, ascending and then descending sharply—the Van hove singularities ( Figure 39 ; v1, v2 and v3 are DOS for HOMO and c1, c2 and ... There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start... Sigma pi bond formation Orbital overlap concept ncert
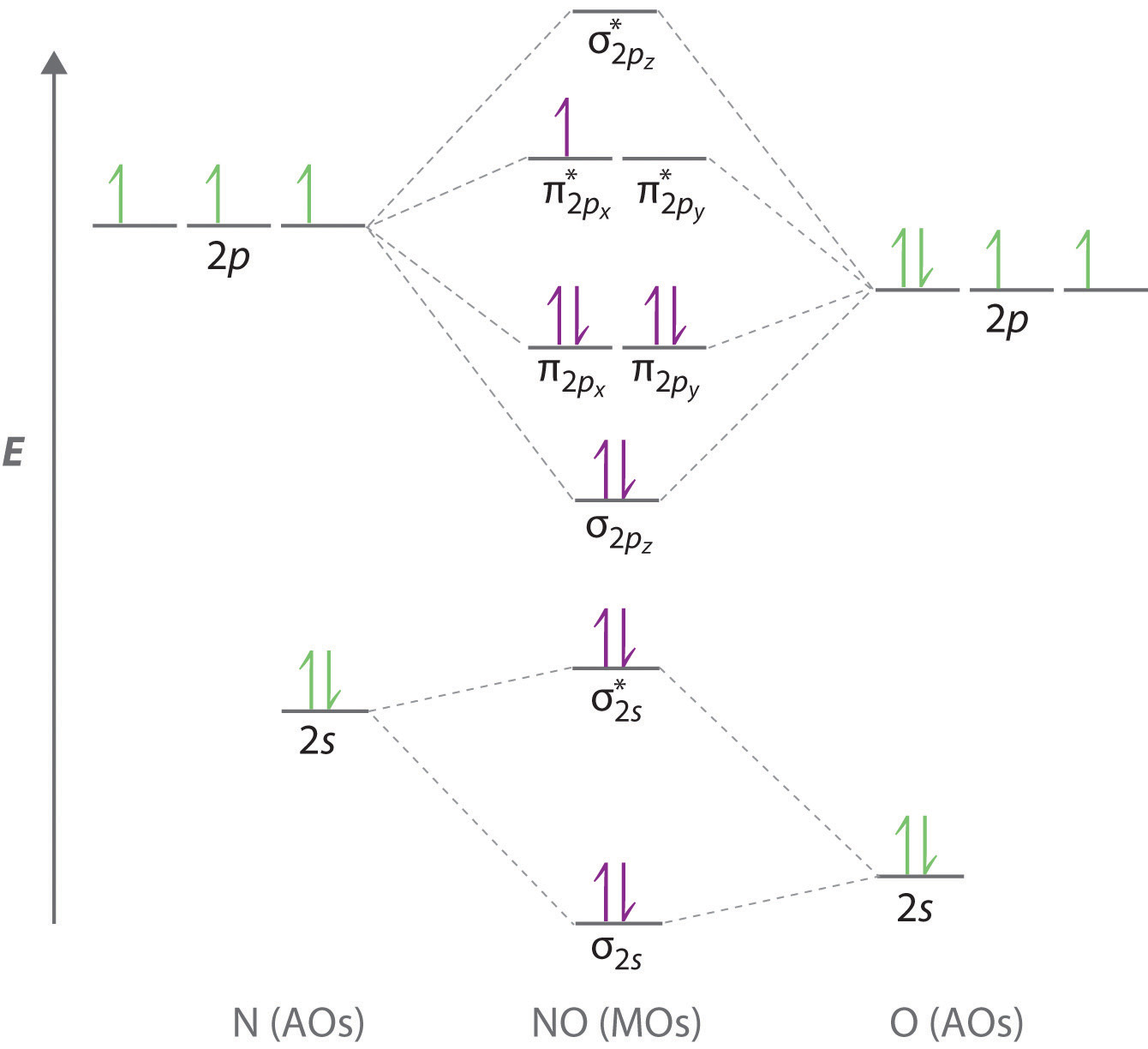
Sep 15, 2011 · The MO for CF has the pi orbitals below the sigma orbital. For the heteronuclear diatomic molecules where one atom has Z < 8, the pi orbitals are usually below the sigma orbital like NO and CO. Top. 2 posts • Page 1 of 1. Return to “*Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond Order, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism)”.
Molecular Orbital diagram fro N2 Bond Order The number of bonds between a pair of atoms is called the bond order. Bond orders can be calculated from Lewis structures, which are the heart of the valence-bond model. ... In CF 4 the C-F bondlength is 1.32 Å (predicted 1.44 Å) In SiF 4 the Si-F bond length is 1.54 Å (predicted 1.81 Å)
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#...
Show activity on this post. I'm trying to build a molecular orbital diagram for BF 3 and I'm running into problems with irreducible representations on the F side. 2s for B has an irreducible representation of A1. 2p for B has an irreducible representation of E' and A''2. 2s for F considered non bonding. 2p (along the bond axis) for F has an ...
For CF; Hydrogen; Atomic Orbital Diagram; Carbon Orbital Diagram; MO Theory; HE2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; S2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; MO Diagram of No; O2 MO Diagram; H2O MO Diagram; Cl2 Molecular Orbital Diagram; For Ph5; NH3 MO Diagram; BN Molecular Orbital Diagram; HF MO Diagram; For BH3; MO Diagram for Carbon; For Li2; SP3 Orbital ...
Predicting Reactions Using Frontier Orbitals • Here are two species you have never seen before. Using Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory (FMO Theory), predict the first step of the reaction between these two species. Draw the curved-arrow mechanism that shows how they react, and predict the immediate product of that reaction.
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero
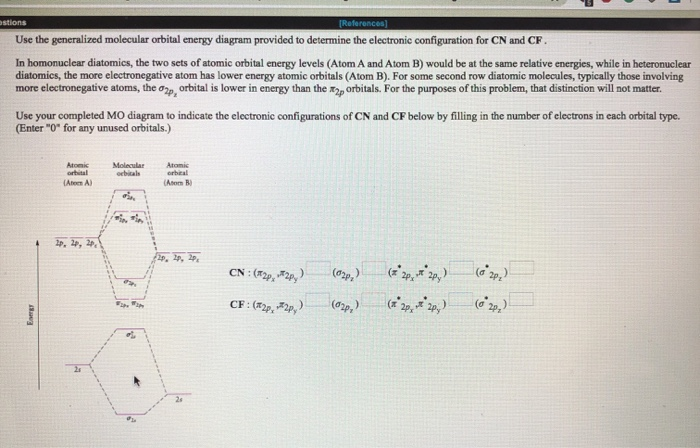
Molecular orbitals are linear combination of atomic orbitals. Prepare molecular orbital energy level diagram for cyanide ion as shown below. CF is a hetero nuclear diatomic molecule. Atomic number of carbon is 6 and atomic number of fluorine is 9. Write the electronic configurations of carbon and fluorine as shown below.

Homework3 Problem 1 A Prepare The Mo Diagram For The Cyanide Ion Cn Use Sketches To Show Clearly How The Atomic Orbitals Interact To Form Mos B What Course Hero
Oct 26, 2016 · Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
6 Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Table 2.1 Some real atomic orbitals: Z is the atomic number and a is the Bohr radius (a h 2/4 π2me 0.53 × 10 8 cm) ψ 1 π 3 1 2 s e Z a ⎛ Zr a − / ψ 2 π 3 2 1 2 42 s Zr a2 e Z a ⎛ Zr ⎝⎜ ⎞ ⎠⎟ ⎛ ⎝⎜ ⎞ ⎠⎟ / ψ π 2 θ 5 1 2 2 p 42 z e Z a ⎛ r Zr a / cos ψ π 2 θϕ 5 1 2 2 p 42 x e Z a ⎛ r Zr a / sin cos ψ
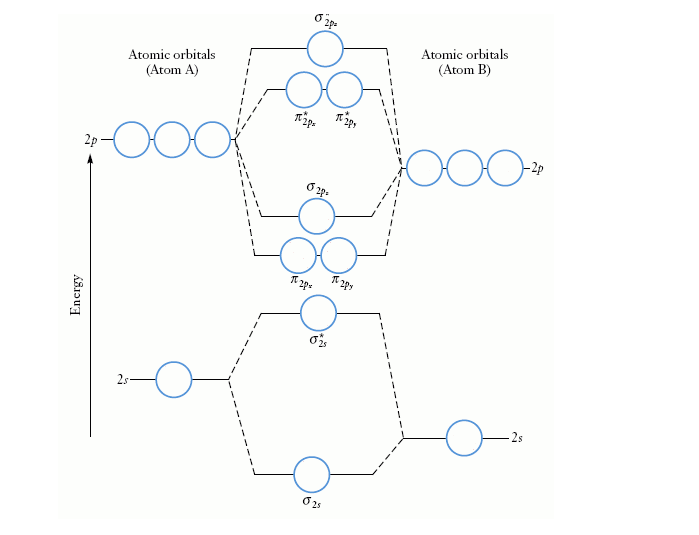
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
Question 7 3 points Save A Draw the molecular orbital diagram (MO diagram) for the heteronuclear diatomic species CF to answer the following questions. Only show the valence Atomic orbitals and valence Molecular orbitals. The order of MO energy levels for CF will be the same as for the O2 homonuclear diatomic molecule.
Answer: The manifold I remember for n=2 diatomics is single-single-double-single-double-single. Repeat that over and over again. It's the sequence of the energy levels in the molecular orbital scheme for n-2 diatomics. after that, just count the number of electrons and put them into the energy le...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Molecular orbitals were first introduced by Friedrich Hund and Robert S. Mulliken in 1927 and 1928. The linear combination of atomic orbitals or "LCAO" approximation for molecular orbitals was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones. His ground-breaking paper showed how to derive the electronic structure of the fluorine and oxygen molecules from quantum principles.
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.

Write The Molecular Orbital Structure For The Ne2 At Nr 10 Molecule Does This Molecule Exist Homeworklib
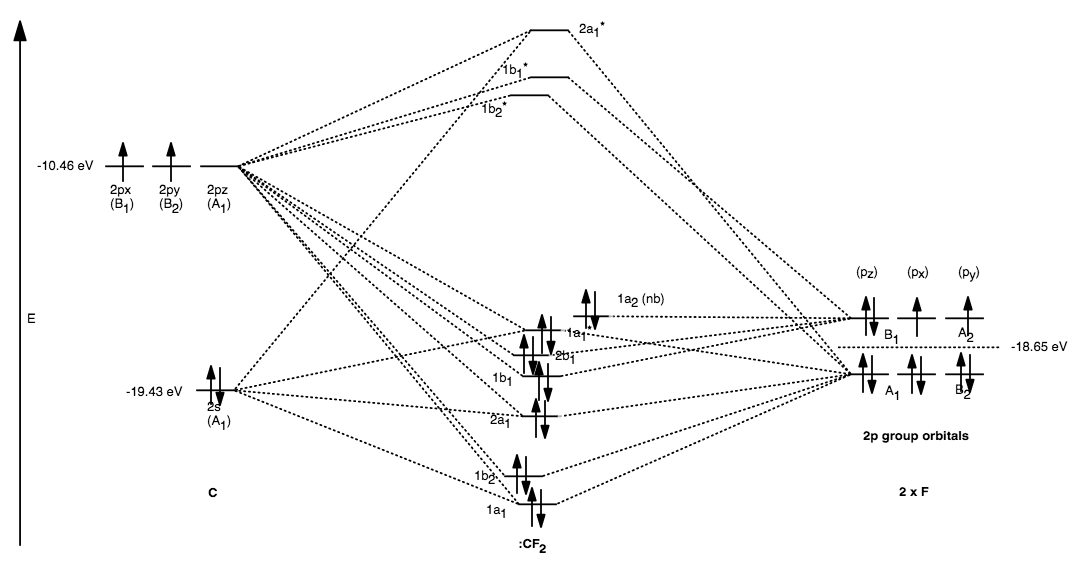
In Ddotcx 2 Both The Electron Get Paired Up In Sp 2 Hybrid Orbital Thus Ddotcx 2 Exists In The Form Of Singlet State Why Here X Refers To Halogen Socratic
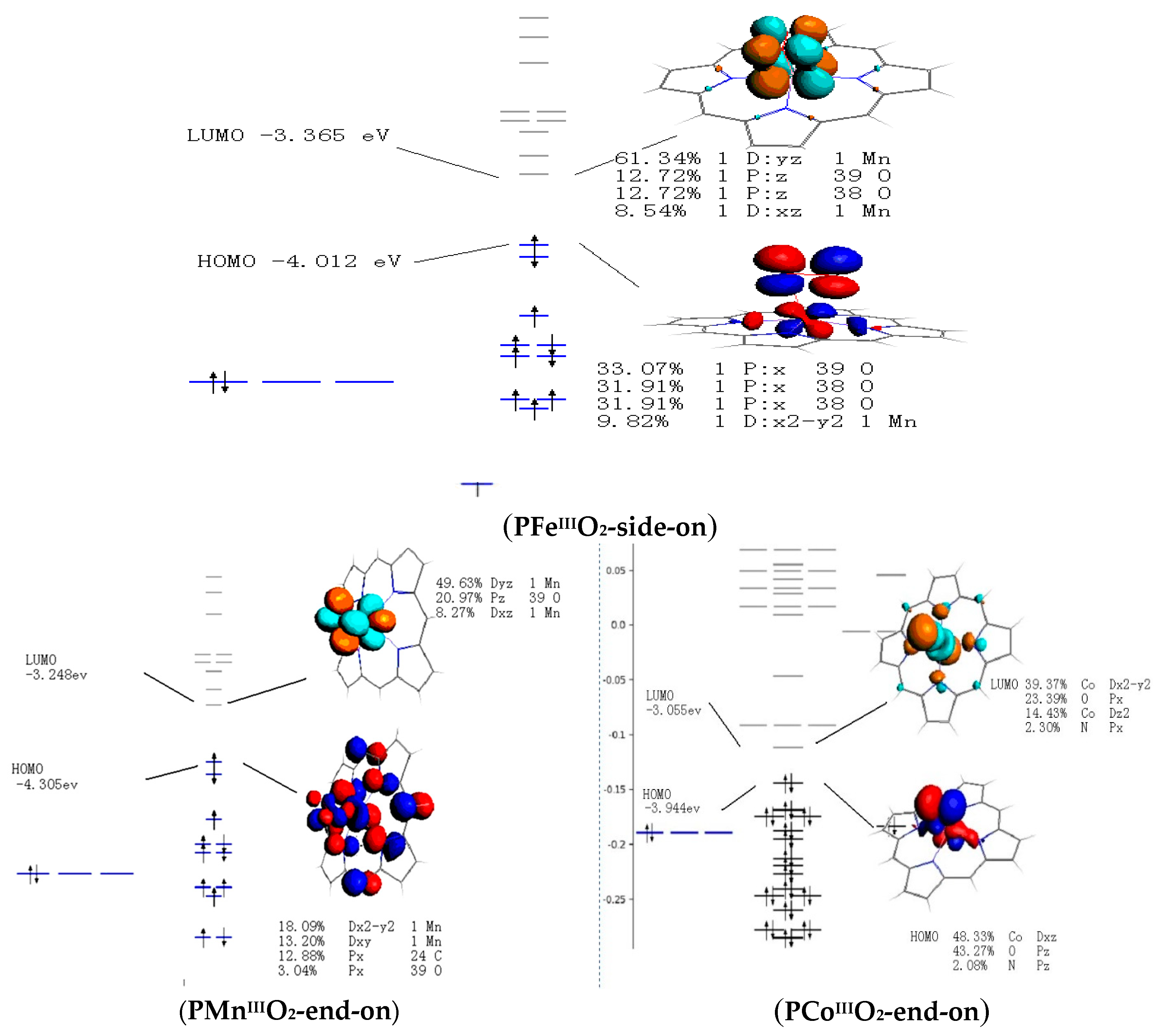
Catalysts Free Full Text Theoretical Study On Electronic Structural Properties Of Catalytically Reactive Metalloporphyrin Intermediates Html

Solved Chapter 11 Problem 39e Solution Selected Solutions Manual General Chemistry 10th Edition Chegg Com
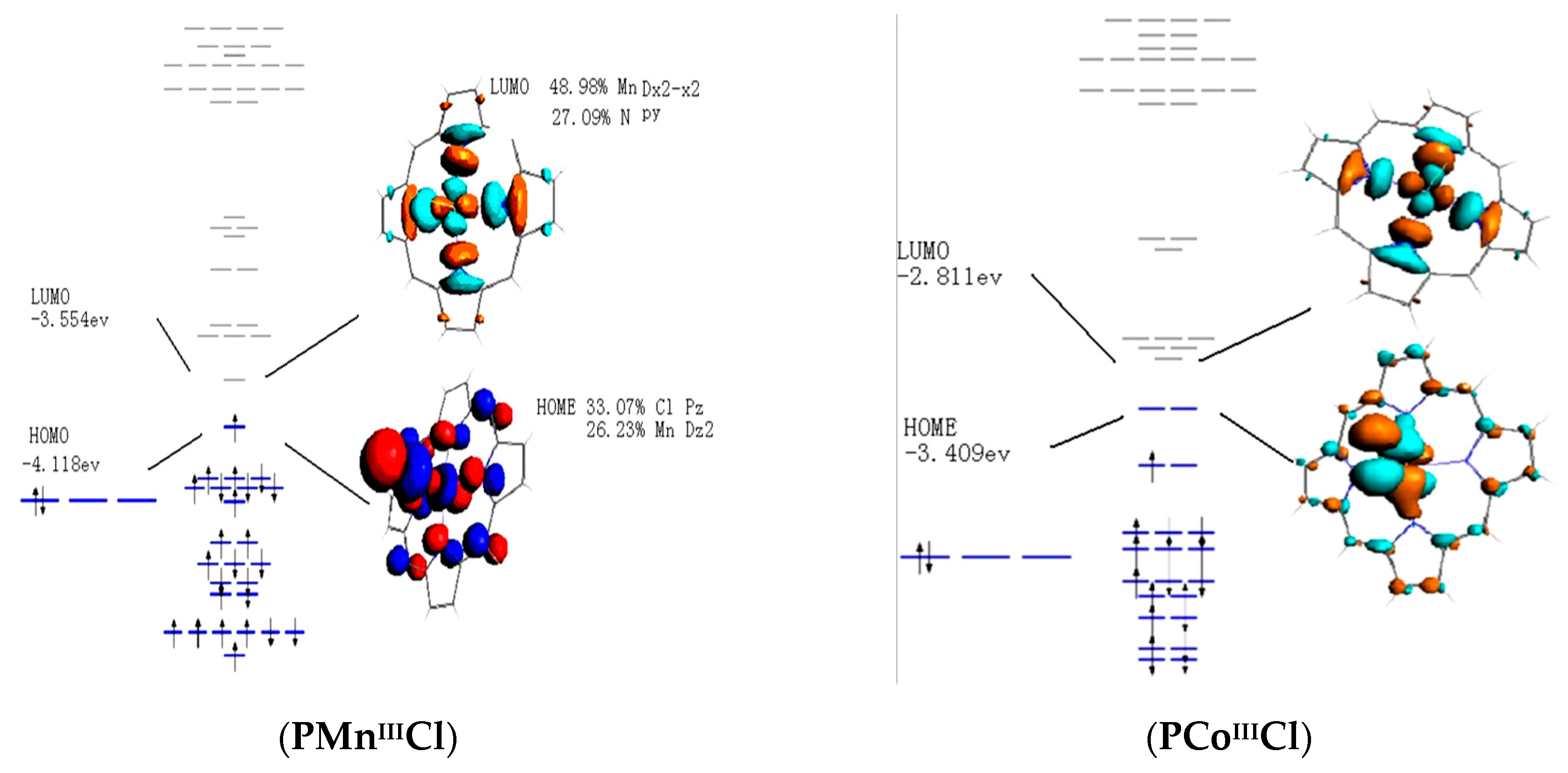
Catalysts Free Full Text Theoretical Study On Electronic Structural Properties Of Catalytically Reactive Metalloporphyrin Intermediates Html
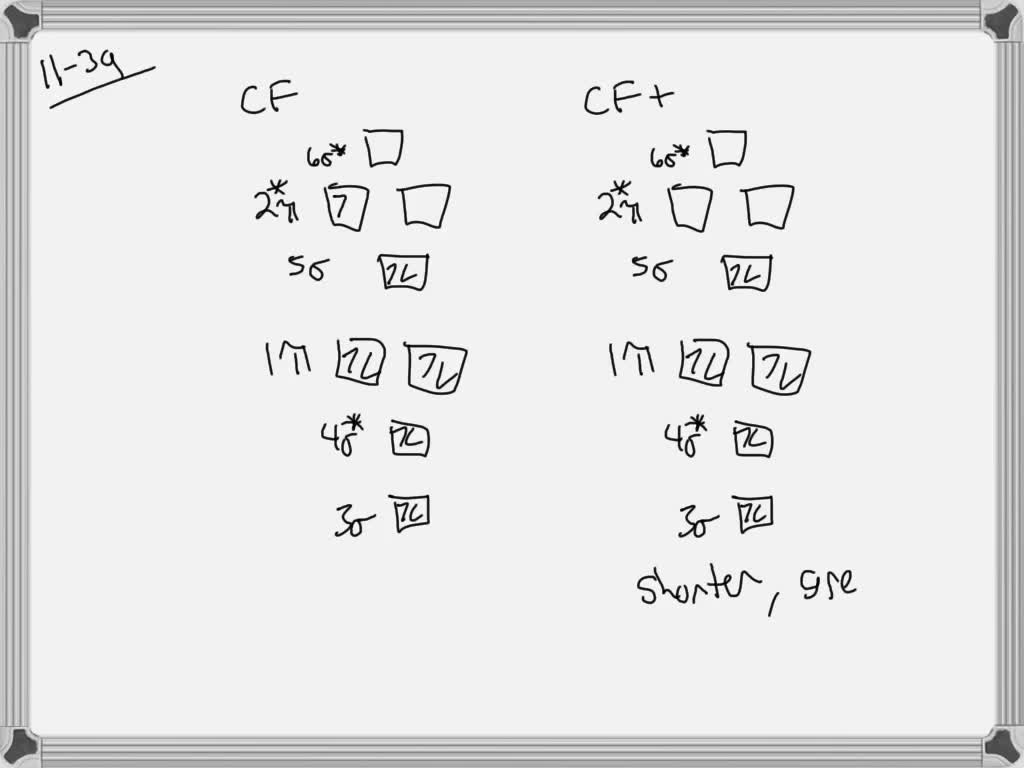
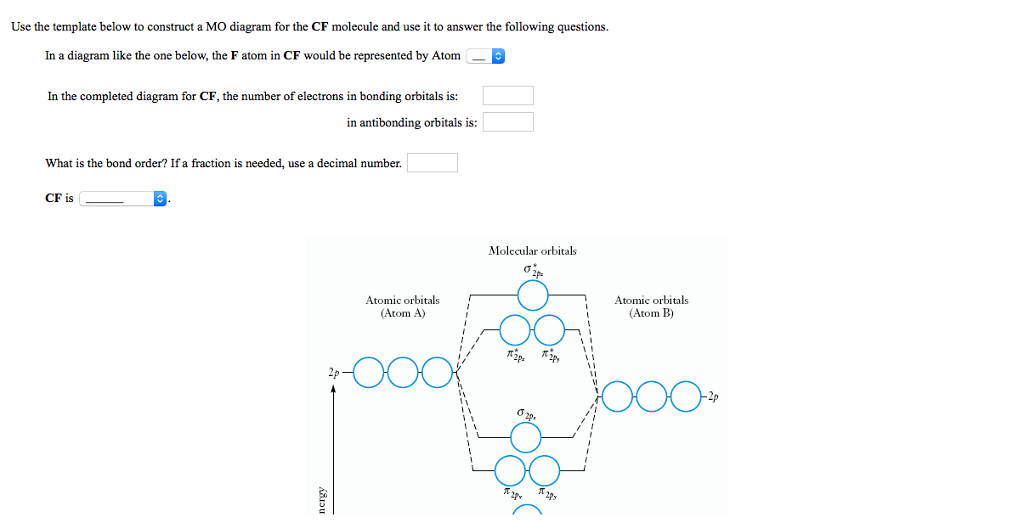
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cf Would You Expect The Bond Length Of Mathrm Cf To Be Longer Or Shorter Than That Of Cf

Draw Orbital Diagram Of Fluonine Molecule And Hf Molecule Calculate O N Of Sulphur In So Molecule Brainly In









0 Response to "40 cf molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment