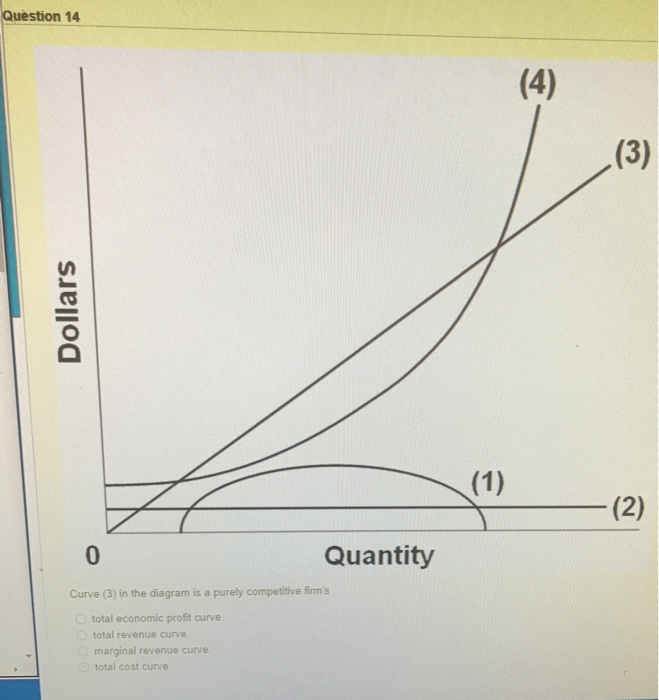
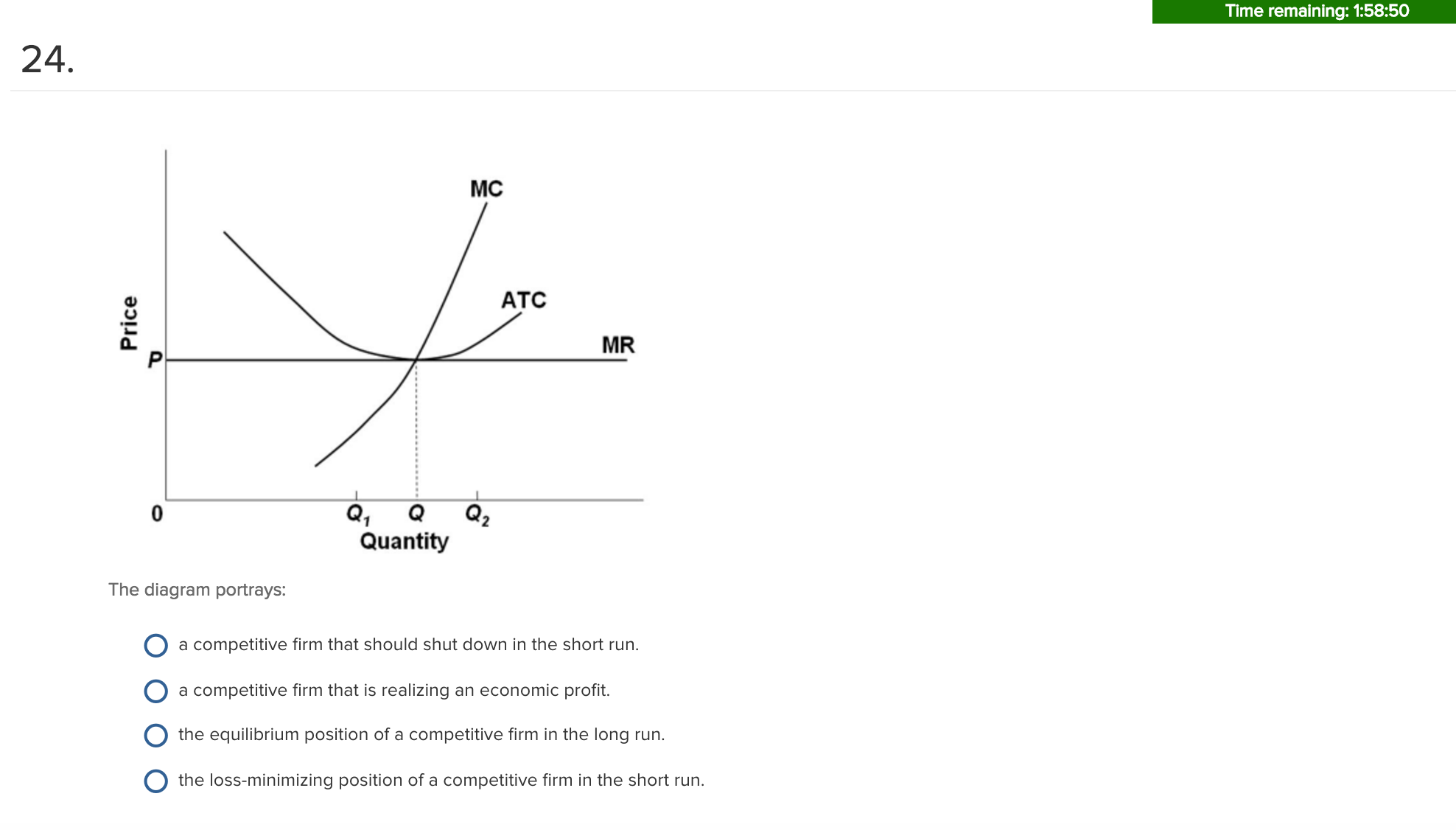
40 curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
For the firm, the demand curve will shift with changes in the firm's worker productivity, demand for the firm's products, and the price of the product (all three change the MRP). A firm's supply curve shifts up or down with the market wage. See below for how to draw a perfectly competitive factor market with side by side graphs.
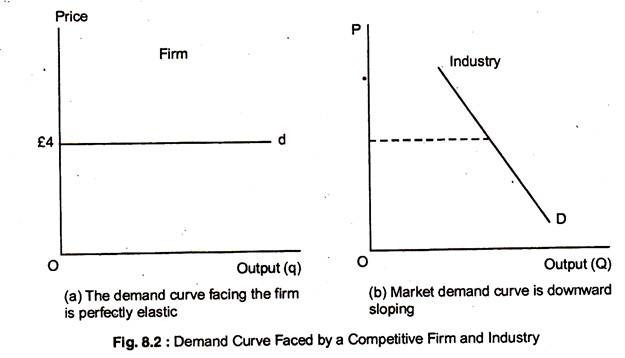
One of the major differences between a monopolist and a purely competitive firm is that the monopolist has a _____ demand curve, while the competitive firm has a _____ demand curve Group of answer choices Downward sloping; perfectly inelastic Perfectly inelastic; perfectly elastic Downward sloping; perfectly elastic Perfectly elastic; downward-sloping
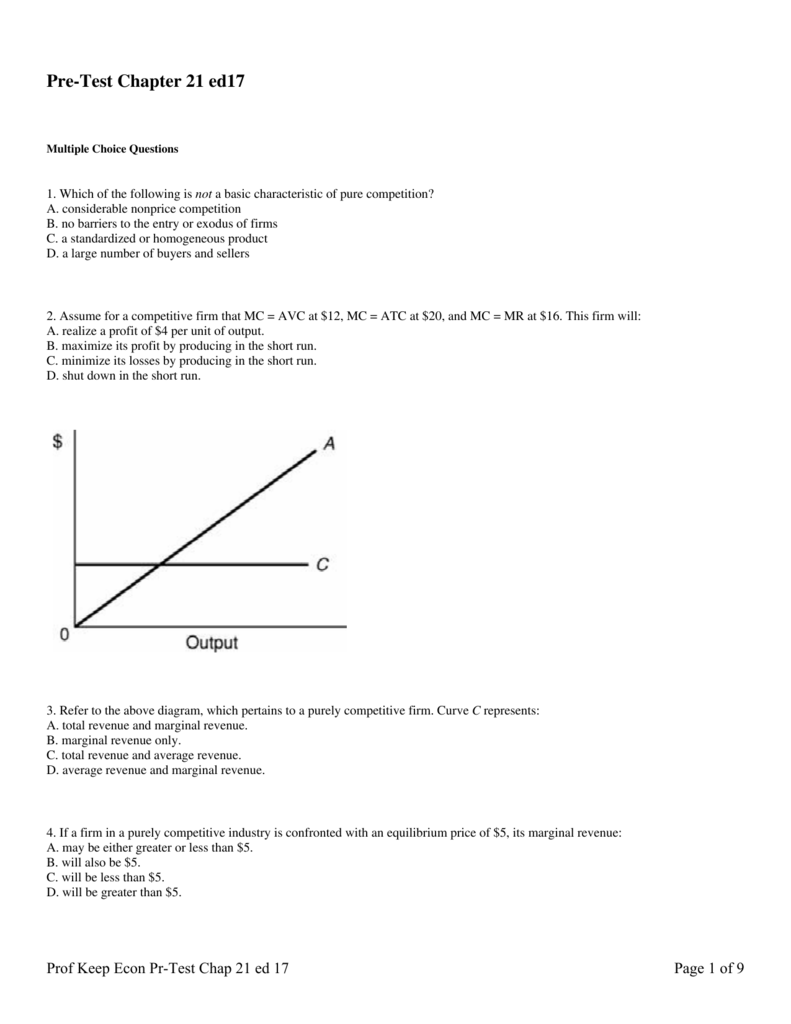
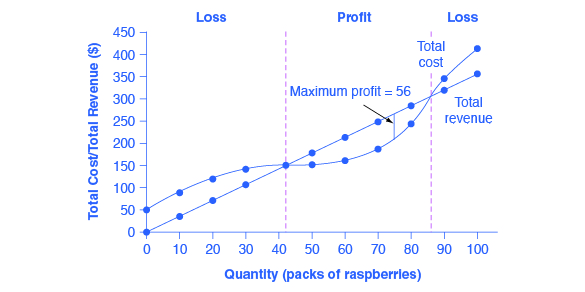
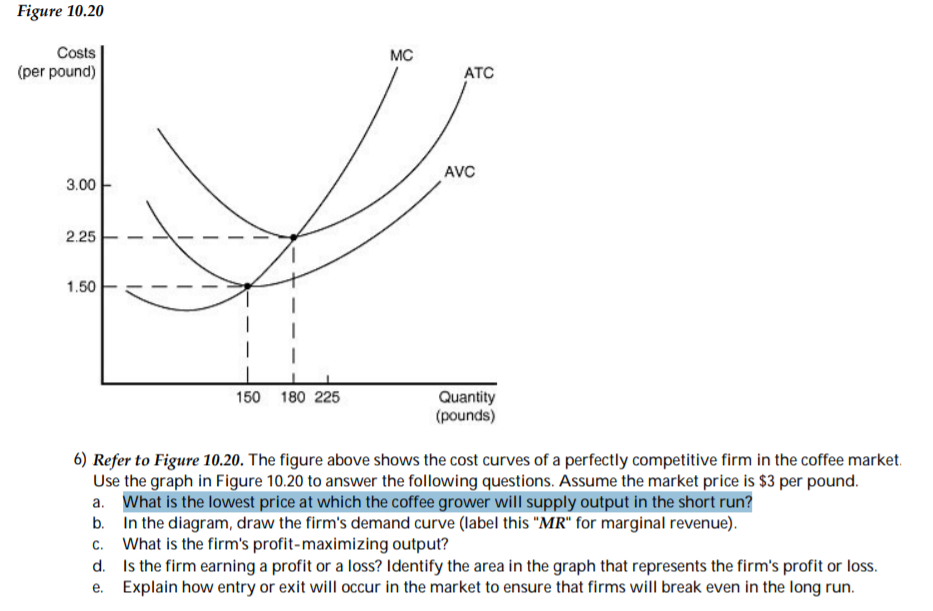
A firm in a purely competitive industry is currently producing 1000 units per day at a total cost of $450. If the firm produced 800 units per day; its total cost would be $300, and if it produced 500
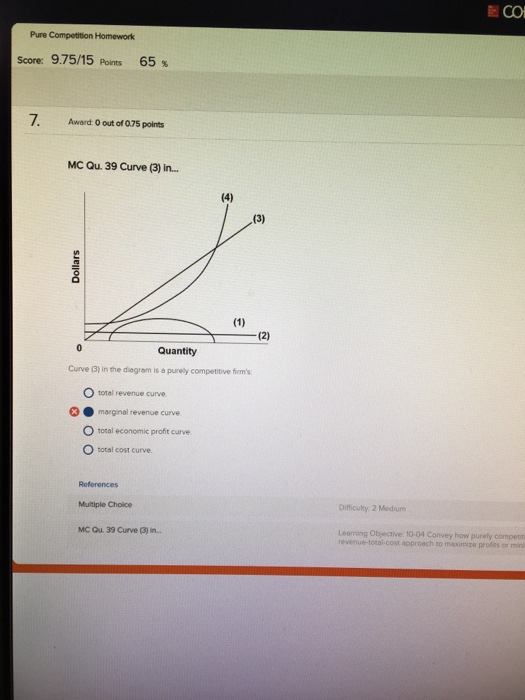
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
The supply curve of a one-of-a-kind original painting is: perfectly inelastic. ... Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:.
The demand curve faced by a purely competitive firm; A purely competitive firm can be identified by the fact that; If a firm is a price taker, then the demand curve for the firm's product is; In pure competition, the demand for the product of a single firm is perfectly; When administering an intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle ...
The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely competitive firm is: The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely competitive firm is: Categories Uncategorized. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's.
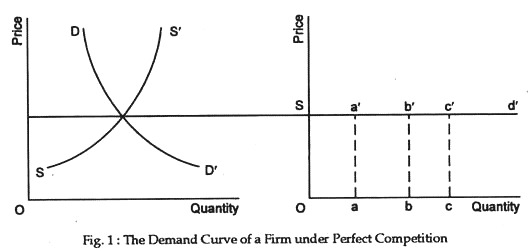
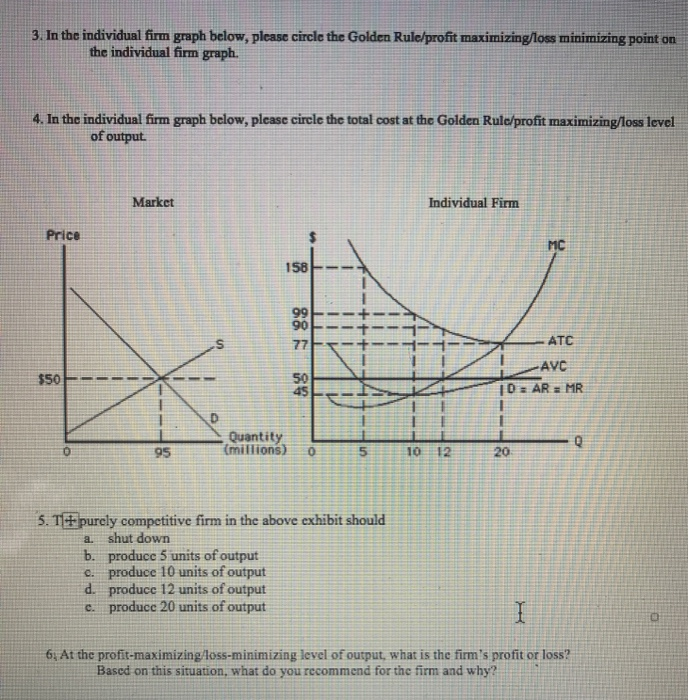
The profit maximizing firm produces at the point where MC intersects MR. The point where MC intersects MR is also the point which denotes the average cost. As new firms have entered the market, the demand curve of each firm in the perfectly competitive market shifts downwards, until it is a horizontal line.
Firms in Competitive Markets 氕氘氚 The Meaning of Competition competitive market: a market with many buyers and sellers trading identical products so that each buyer and seller is a price taker A competitive market, sometimes called a perfectly competitive market, has these characteristics: 1.
If the firms in an oligopolistic industry can establish an effective cartel, the resulting output and price will approximate those of A. a purely competitive producer. B. a pure monopoly. C. a monopolistically competitive producer. D. an industry with a low four-firm concentration ratio.
If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: supply curve to the right, and the individual firm's demand curve will shift down.. A purely competitive industry is an industry where they are numerous buyers and sellers of identical goods and services. There are no barriers to entry and exit of firms into the industry.
A perfectly competitive market is composed of many firms, where no one firm has market control. In the real world, no market is purely monopolistic or perfectly competitive.
If the demand curve faced by an individual firm is downward-sloping, the firm cannot be A)a monopoly firm. B)a purely competitive firm. C)an oligopolistic firm. D)a monopolistically competitive firm. Categories Questions. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published.
less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. Related questions 0 votes. 1 answer. a shift of the demand curve for thin-crust pizza would not be caused by a change in: asked 3 days ago in Other by megha00 Expert (39.9k points) 0 votes. 1 answer. which of the following sequences best explains the negative slope of the aggregate ...
A purely competitive firm can be identified by the fact that; If a firm is a price taker, then the demand curve for the firm's product is; In pure competition, the demand for the product of a single firm is perfectly; When administering an intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle, the nurse recalls that the volume in the syringe should ...
The law of diminishing marginal utility explains why: demand curves slope downward.
The graph titled Soy Bean Market is a graph of the market for soy beans, a perfectly (purely) competitive market. The graph titled Roy's Soys depicts an individual firm in the market for soy beans. The market and the firm are currently in long-run equilibrium at Point A. Show what happens in the short run … Continue reading "The graph titled Soy Bean Market is a graph of the market for soy ...
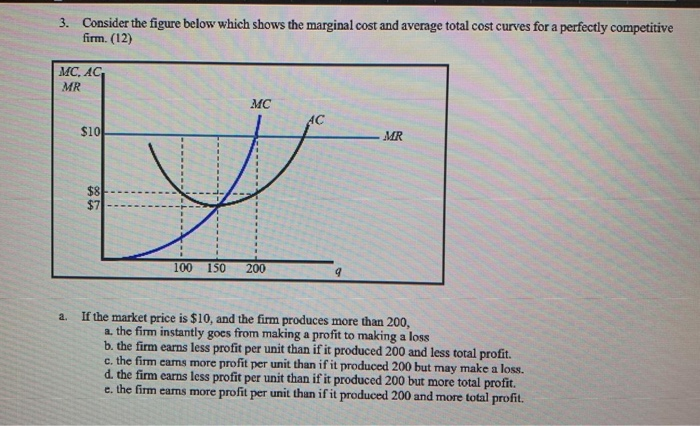
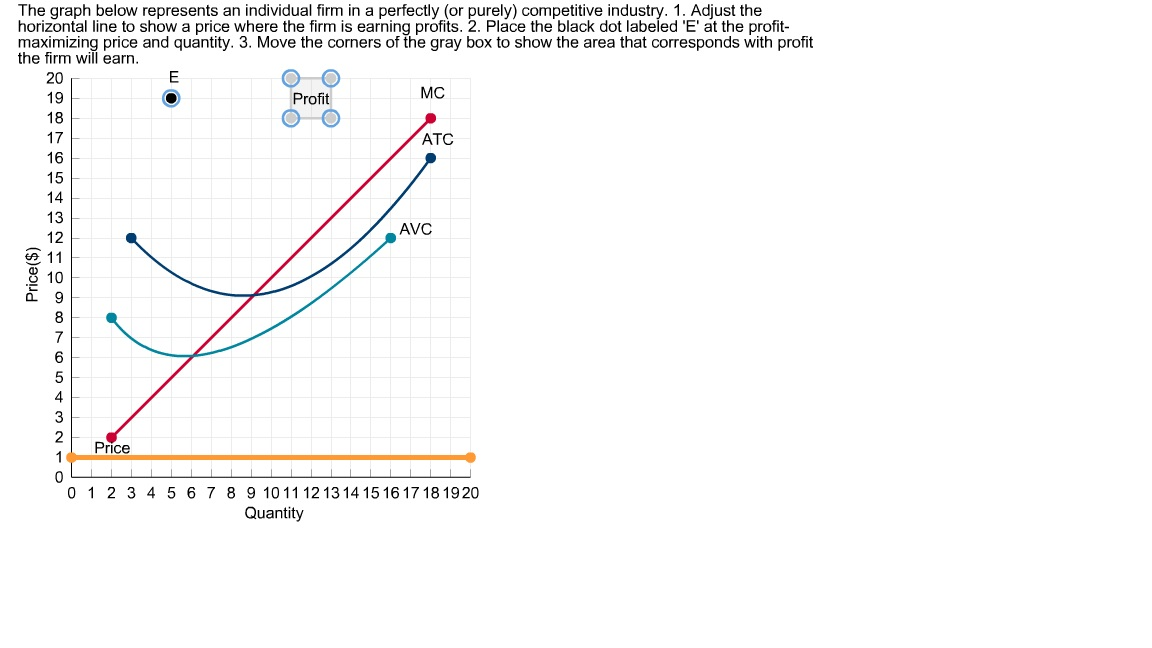
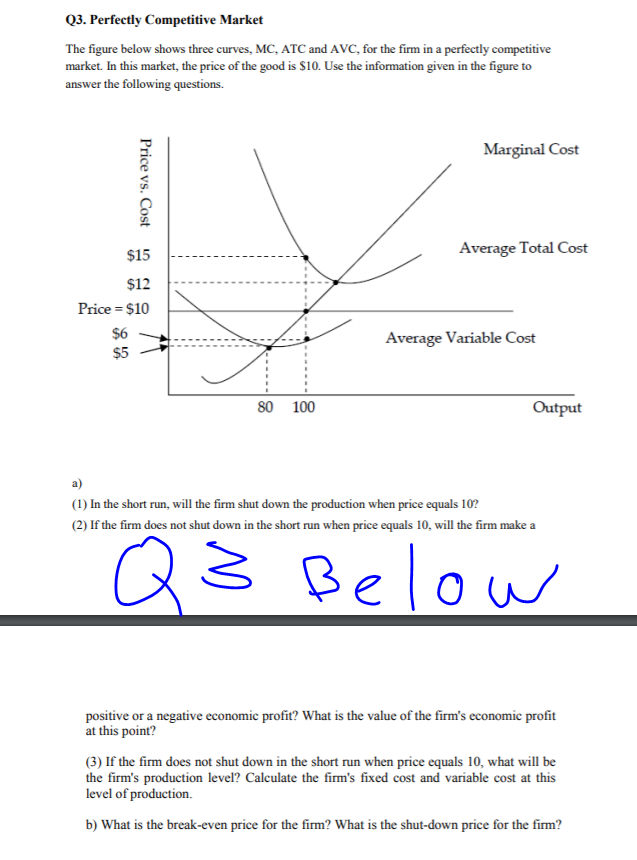
3. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. operating in this market. 50 45 Profit or LosS 40 35 30 25 15 AVC 10 QUANTITY (Thousands of Shirts per day
Perfect competition or pure competition (sometimes abbreviated to PC) is a type of market structure. It is important to note that this form of market structure does not actually exist in the real world and is thus considered to be theoretical. As an economic theory, then, it does not seek to literally describe reality but to stand as an ...
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's ... an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and an upward shift in ...
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve B from ECON 301 at DeVry University, Fremont.
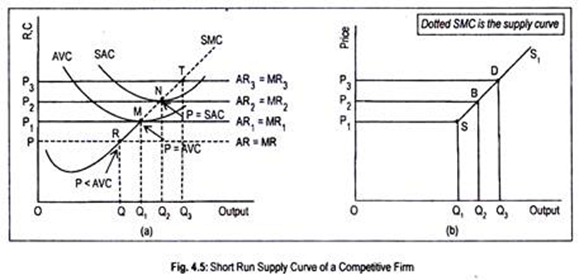
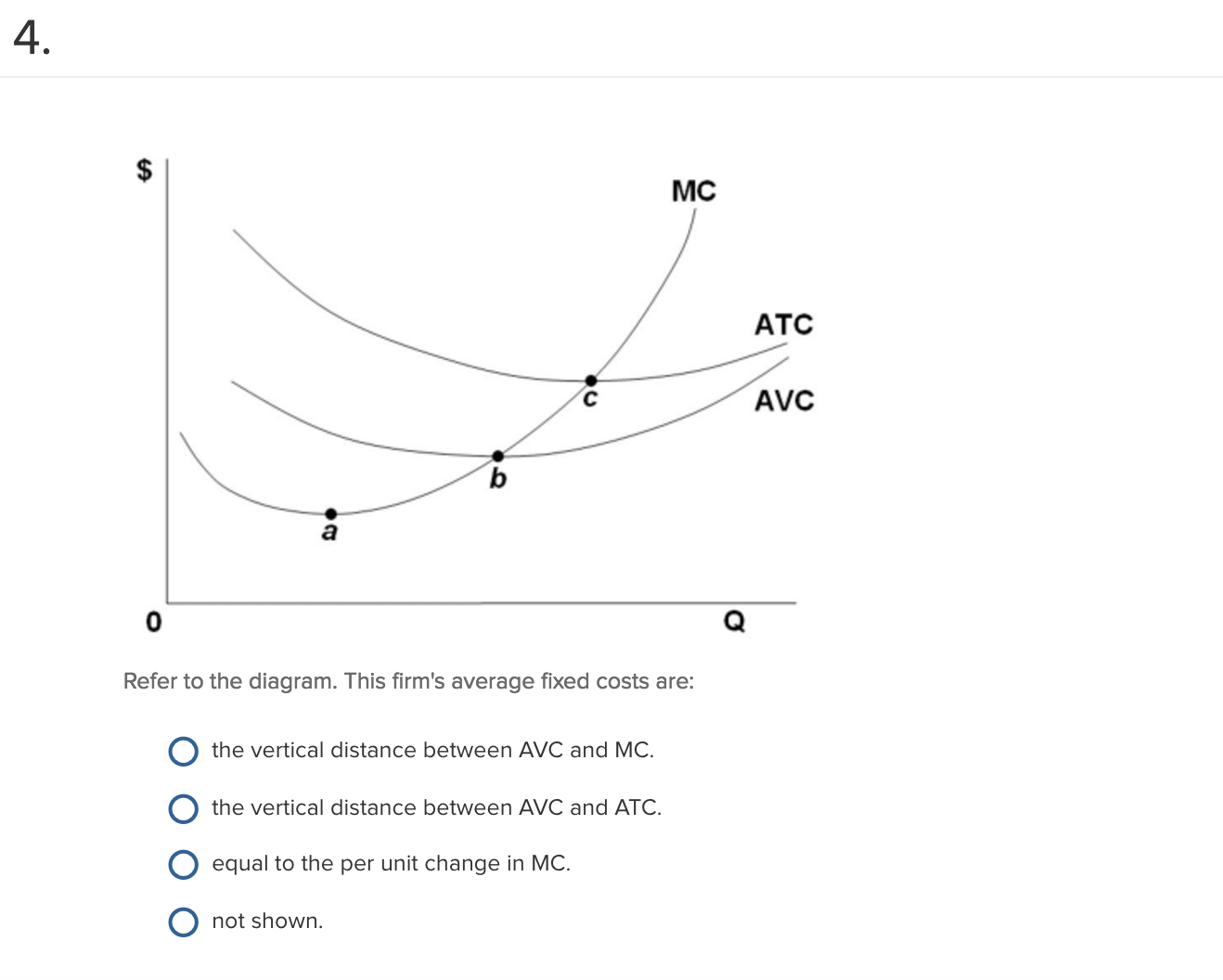
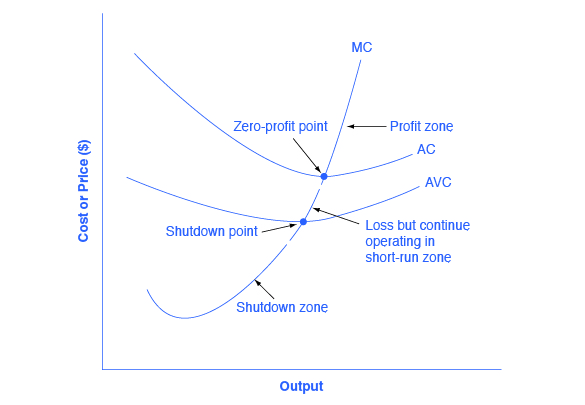
95. A competitive firms MC curve and AVC curve are given to, show which region of the curves show the firm's supply curve in the short run. (a) region HE (b) region EG (c) region EF (d) region IE. 96. A firm making zero economic profit - (a) earns super normal profits (b) incur losses (c) earns a normal profits (d) profit or loss is ...
Which of the following is a firm effect that has an impact on the competitive advantage of a firm? A. The exit barriers within the industry in which the firm operates B. The number of companies operating in the industry in which the firm operates C. The intensity of rivalry among existing companies in the firm's chosen industry D.
Newsprint is produced in a perfectly competitive market. Each identical firm has a total variable cost VC= 40q + .5q^2 with an associated marginal cost curve MC = 40 + Q. A firms fixed cost is equal t
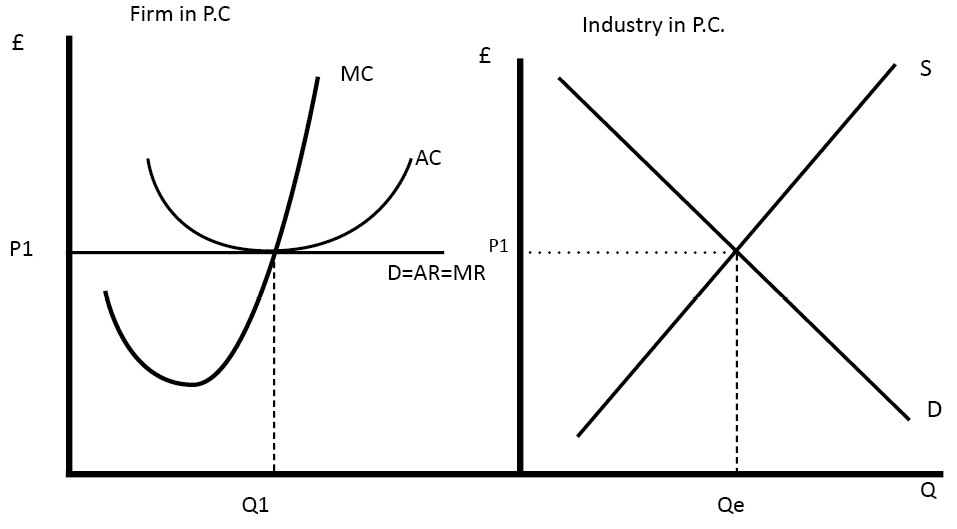
Key Points. Allocative efficiency occurs from the producers side as well as the consumers side. This is when demand is fully met, and production is optimised until marginal costs = marginal revenue - therefore no more profits are made.; In economics, allocative efficiency occurs at the point where supply and demand interesect.
In the short run, a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit ... A. an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), ... Rating: 4,7 · 12 reviews
Assume initially that the market for pizzas in the city is competitive. All firms have the same total cost function for making pizzas: \(TC = 6Q\) (and the corresponding marginal cost, or first derivative, is \(MC = 6\)). Draw the demand curve (label it D) and the competitive supply curve (label it S).
An industry comprising 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market for a ... Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's.
Perfect competition is a market structure in which the following five criteria are met: 1) All firms sell an identical product; 2) All firms are price takers - they cannot control the market price ...
A perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is a horizontal line at the market price. The marginal revenue received by the firm is the change in total revenue from selling one more unit, which is the constant market price. So a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is the same as its marginal revenue curve.
The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm: ... Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents:.
If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: _____ a. demand curve to the right, and the individual firm's demand curve will shift up. b. demand curve to the left, and the individual firm's demand curve will shift down.
A purely competitive firm can be identified by the fact that; If a firm is a price taker, then the demand curve for the firm's product is; In pure competition, the demand for the product of a single firm is perfectly; When administering an intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle, the nurse recalls that the volume in the syringe should ...
The above diagram suggests that: curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising Suppose that a business incurred explicit costs of $1 million and implicit cost of $200,000 in a specific year.
5. (Ch. 17 # 5) Sparkle is one firm of many in the market for toothpaste, which is in long-run equilibrium. a. Draw a diagram showing Sparkle's demand curve, marginal revenue curve, average cost curve, and marginal cost curve. microeconomics. Market demand is given as QD = 200 - 3P. Market supply is given as QS = 2P + 100.
Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which the following criteria are met: 1. All firms sell an identical product (the product is a "commodity" or "homogeneous"). 2. All firms are price takers (they cannot influence the market price of their product). 3. Market share has no influence on prices. 4.
An industry comprised of 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:.
12.Demand curve is perfectly elastic in the market form of: A) Perfect competition B) Monopoly C) Monopolistic competition D) Oligopoly ... Answer is A) Show Answer . ... 19.A purely competitive firm's supply schedule in the short run is determined by: A) Its average revenue B) Its marginal revenue






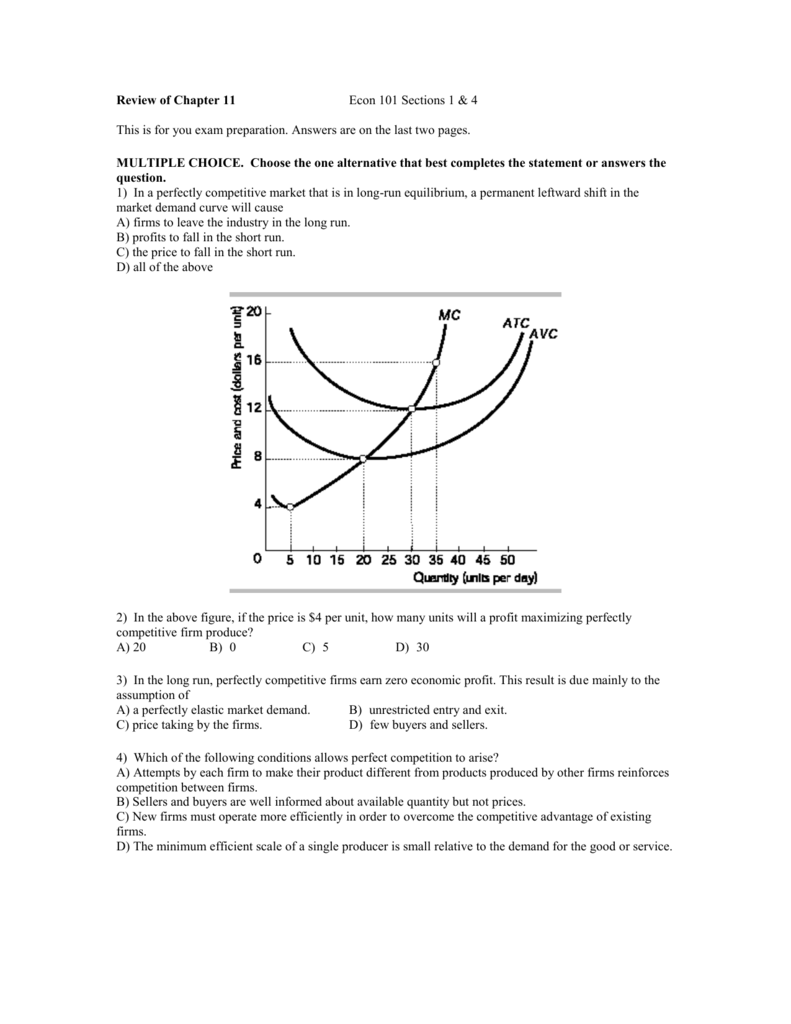

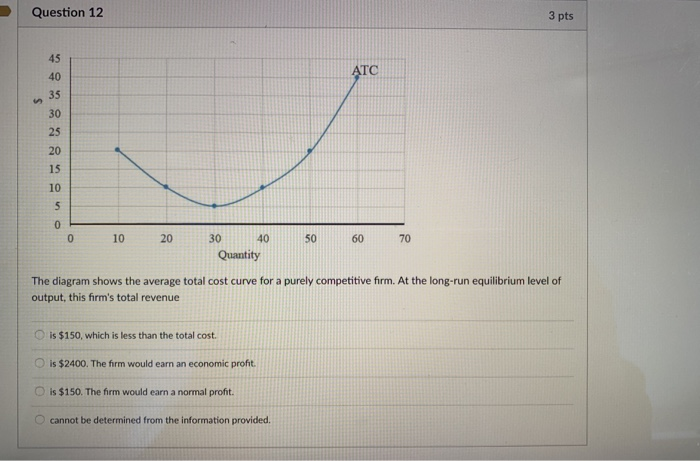
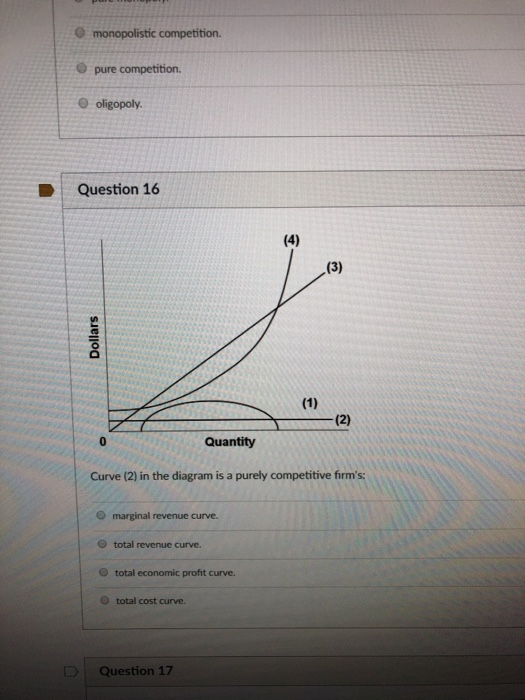

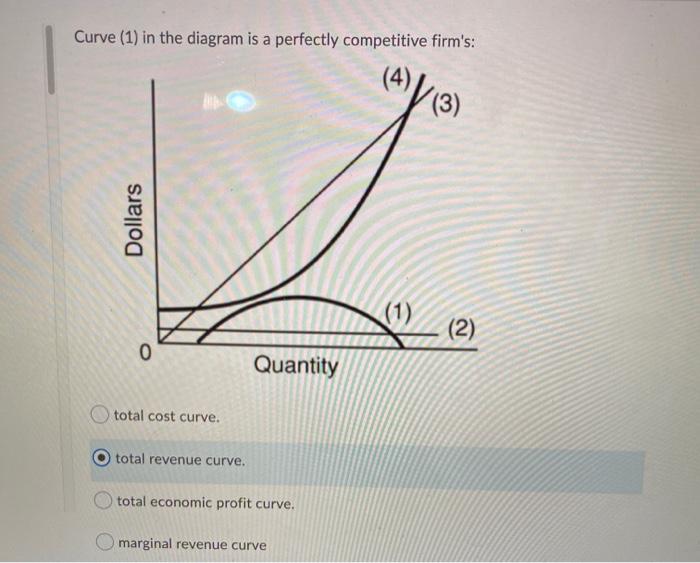







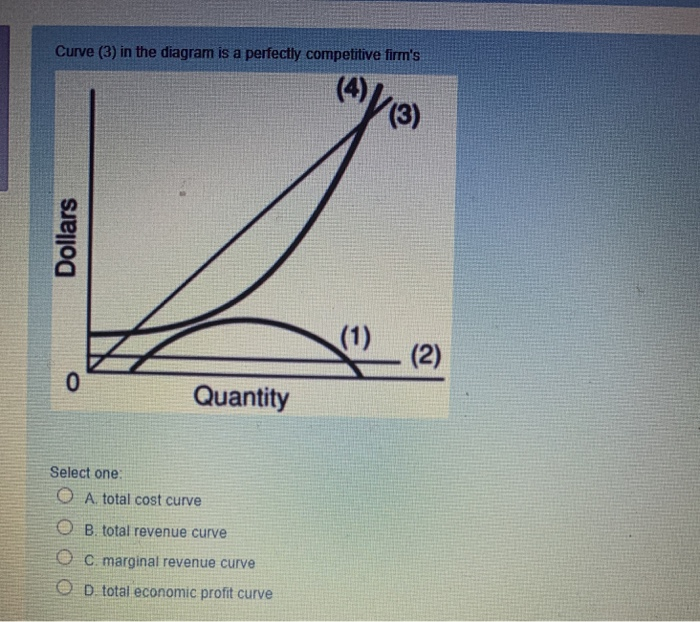
0 Response to "40 curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment