35 fluorescence energy level diagram
Photon #1 hits molecule · Photon #1 absorbed, electron at ground level gains energy and jumps to higher level · Electron loses some of that energy · Electron jumps ... The energy level diagram and transfer process of Sm 3+ in the mica. The emission spectra of the series of Sm 3+ -doped FP and S−FP samples with different Sm 3+ doping concentration (from 0.25 to 1.5 mol%) were also measured, and the emission intensity (600 and 647 nm) dependence with the Sm 3+ doping concentration for the samples are plotted ...
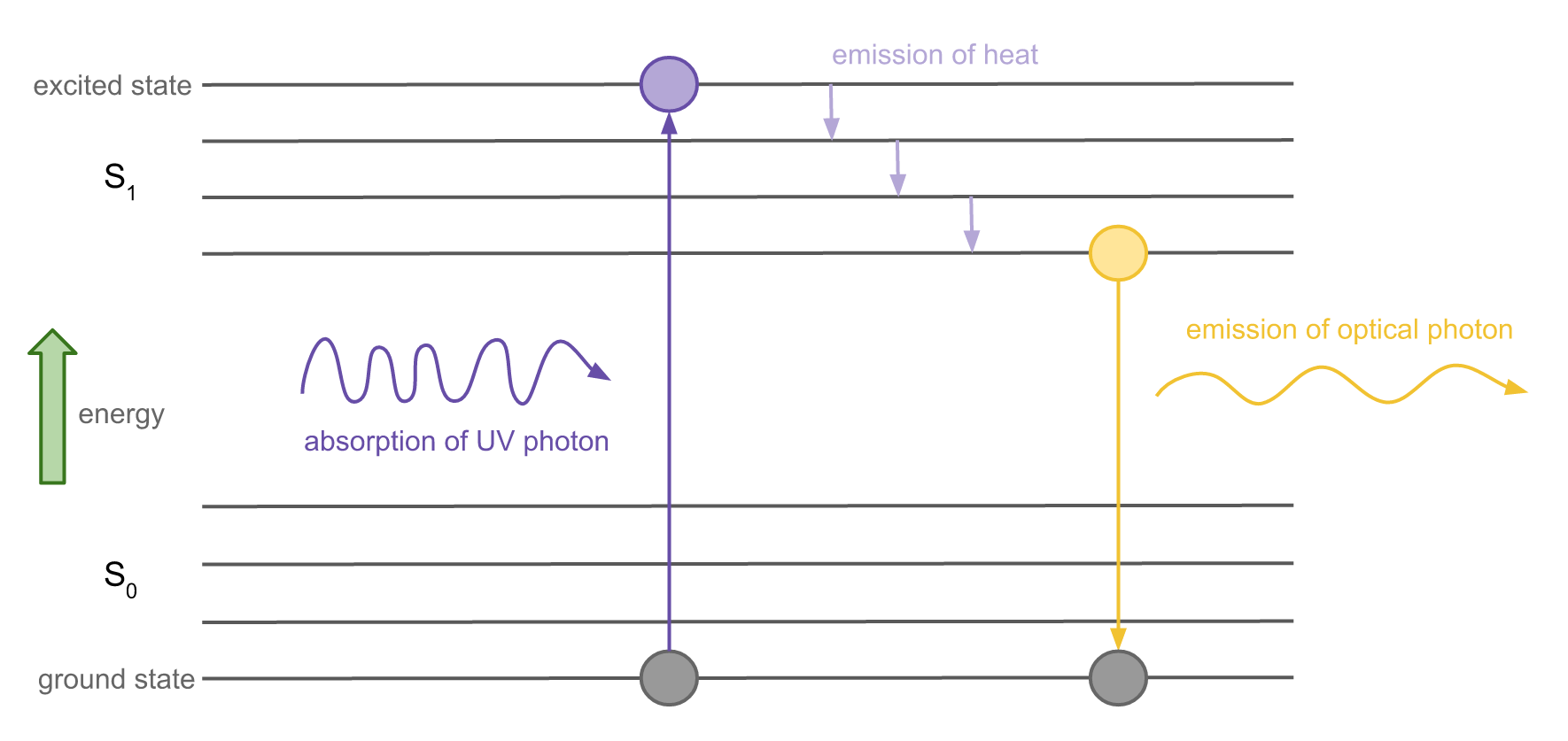
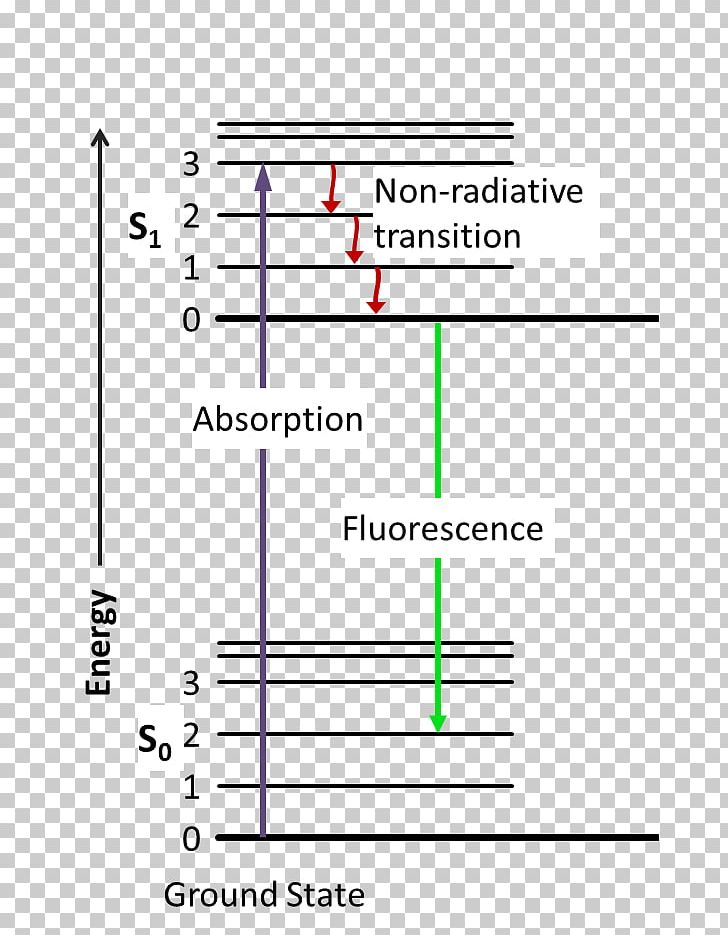
Feb 28, 2016 — At each energy level, fluorophores can exist in a number of vibrational energy levels, which are represented by the multiple lines in each ...
Fluorescence energy level diagram
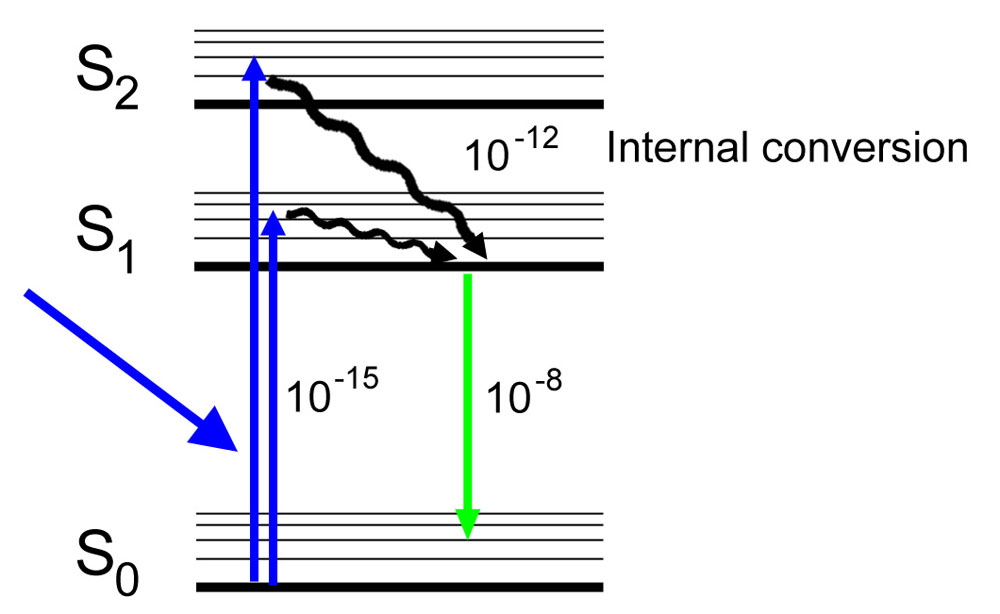
To evaluate saturation broadening, a two-level energy model is used, following previous studies. 42-45 42. T. B. Smith, " Deconvolution of ion velocity distributions from laser-induced fluorescence spectra of xenon electrostatic thruster plumes," Ph.D. thesis (University of Michigan, 2003). 43. Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light; typically, but not necessarily, visible light. rotational energy levels of the excited states in different molecular orbitals. The various energy levels involved in the absorption and emission of light by a fluorophore are classically presented by a Jablonski energy diagram (see Figure 1), named in honor of the Polish physicist Professor Alexander Jablonski.
Fluorescence energy level diagram. fluorescence. In the first case, the laser photon does not have enough energy to excite molecular fluorescence. In the second case, the fluorescence may be excited, but the emission is widely separated in energy from the Raman signal so that the Raman spectrum can be recorded without the fluorescence interference. The simplified energy level diagram in Fig. 3 depicts the possible energy transfer mechanism for the Yb 3+, Tm 3+:Y 2 SiO 5 sample as well as the process involved in the population of the relevant emitting state of the Tm 3+ ion. Download : Download high-res image (350KB) Download : Download full-size image; Fig. 3. Fluorescence is a type of radiative emission that occurs when a molecule absorbs energy at a wavelength where it has a transition dipole moment. The excitation energy provided to the molecule at the ground state promotes photons to an excited singlet state, where they then decay to the lowest vibrational energy level of this excited singlet state. a, Jabłoński diagram illustrating one- or two-photon excitation followed by relaxation through fluorescence, internal conversion, quenching or intersystem crossing.b, Chemical structure and ...
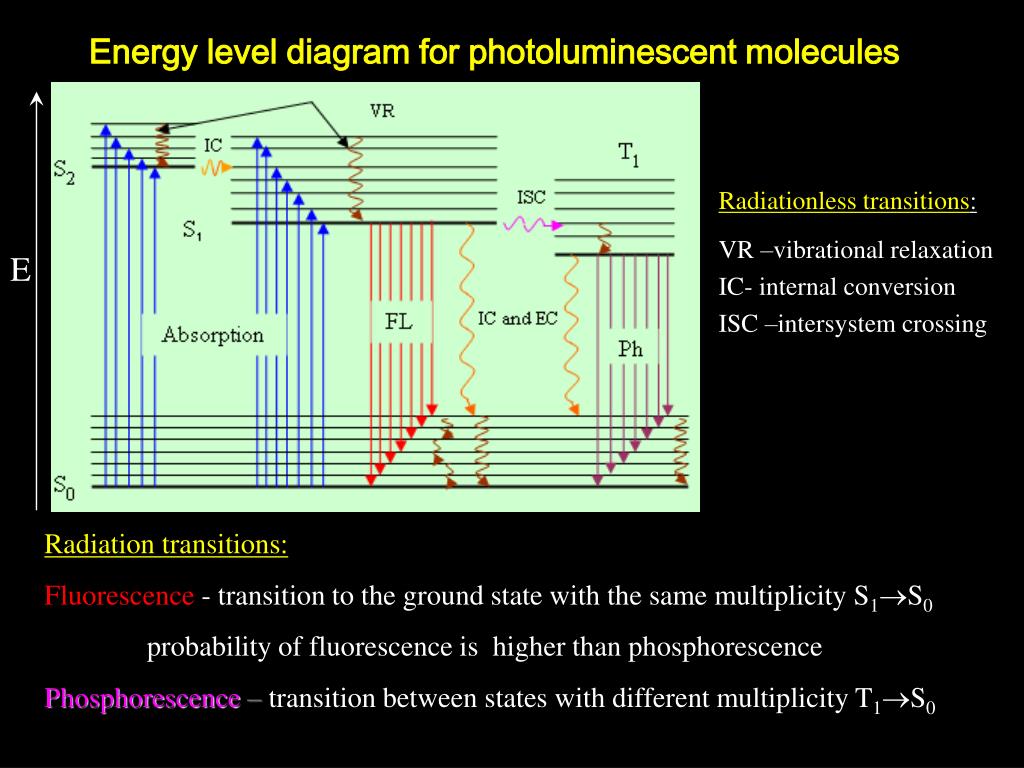
diagrams divide energy levels within the same spin multiplicity into different columns ... At the first excited state, fluorescence can compete in regard to ...8 pages TADF-sensitizing-fluorescence (TSF) strategy suffered a disturbing energy loss causing by the T1 states of fluorescence dopant (FD) due to its low T1-state energy and forbidden of radiative transition. We supposed if a FD with a fluorescent emission spectrum matching the emission of the TADF sensitizer and i If the spin state of the initial and final energy levels are different (e.g. T1 --> S0), the emission (loss of energy) is called phosphorescence. In the diagram ... Photoluminescence provides readers with the appropriate background to thoroughly understand chemical literature involving photoluminescence measurements and interpret photoluminescence data from their own research. It includes a primer on experimental methods as well, so that readers with the appropriate instrument-specific training at their institution can begin conducting reliable ...
The process of the fluorescence is illustrated by the Jablonski diagram shown in Figure 1. A light quantum of energy hvA supplied by an external source is ... Fluorescence is the temporary absorption of electromagnetic wavelengths from the visible light spectrum by fluorescent molecules, and the subsequent emission of light at a lower energy level. When it occurs in a living organism, it is sometimes called biofluorescence. The energy level diagram of Bi 3+, Tb 3+ and Eu 3+ ions are shown in Fig. 3. It is well-known that the luminescence behaviour of Bi 3+ ions is greatly influenced by the surrounding lattice , but it always emits blue light in the LaInO 3 host. Download : Download high-res image (216KB) Download : Download full-size image; Fig. 3. The Jablonski Diagram is widely used in fluorescence spectroscopy, ... a molecular energy level diagram to illustrate the absorption and emission of light, ...
Accordingly, the energy level diagram and the UC energy transfer (ET) processes of Yb 3+ /Er 3+ co-doped phosphors were illustrated in Fig. 2d. The ground state electrons were excited to 2 F 5/2 (Yb 3+) and 4 I 11/2 (Er 3+) excited states through the ground state absorption process (GSA) with the irradiation of 980 nm laser.
In vivo fluorescence of the whole body in (a) prone, (b) supine, and (c) lateral. B) Schematic diagram of a nude mouse by intragastric administration and intravenous injection with cssEr-PEG and cssNd-PEG aqueous dispersions, respectively. C) Design and fabrication of the developed assay. (i) Lateral flow test strip. (ii) Assay.
The LUMO energy level of H 2 bpydc (-2.72 eV) is lower than that of 4-MU (-1.96 eV), indicating that the excited electrons of H 2 bpydc cannot transfer from the LUMO of H 2 bpydc to 4-MU. Thus, the possibility of photo-induced electron transfer (PET) effect can be ruled out.
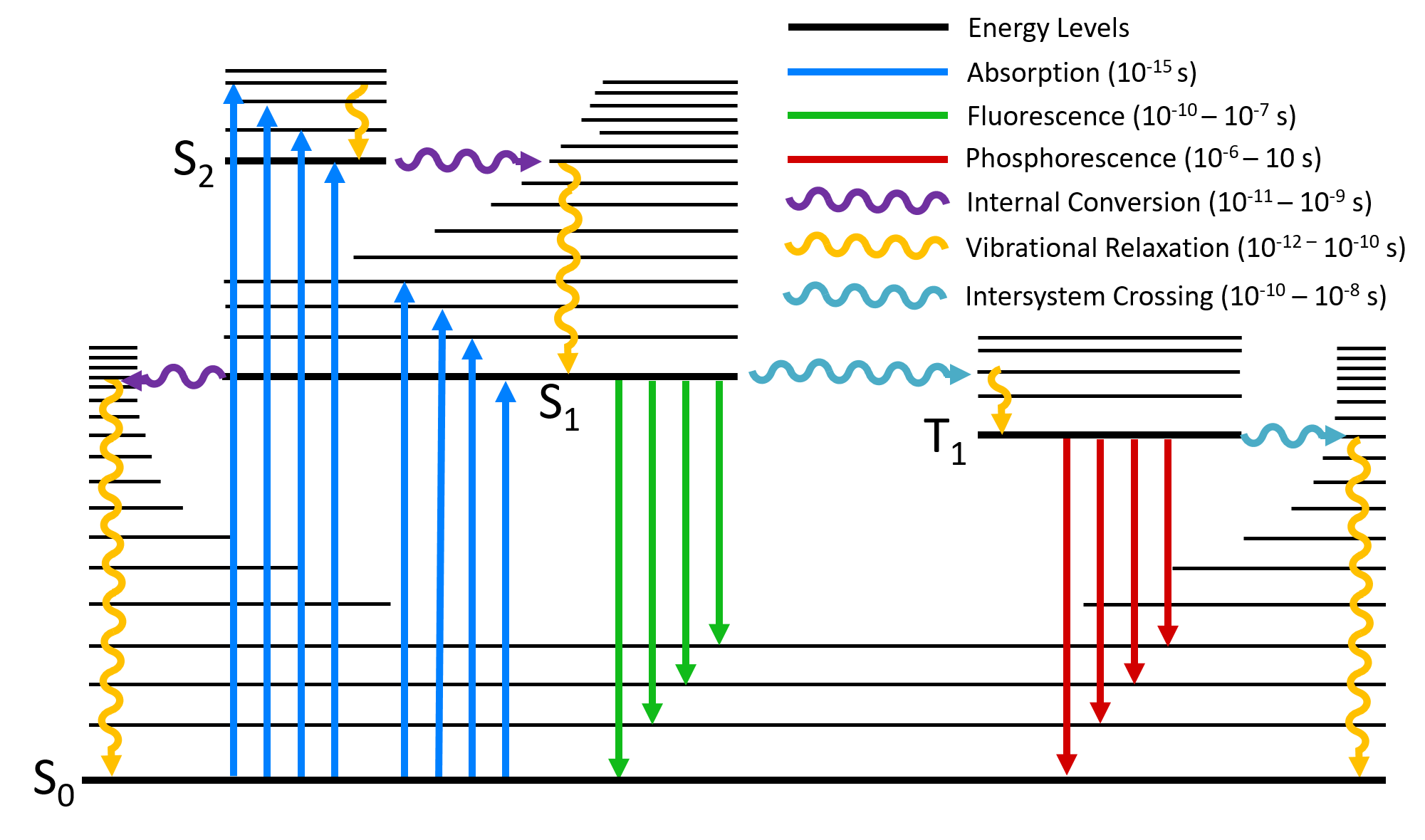
Fluorescence — Another pathway for molecules to deal with energy received from photons is to emit a photon. This is termed fluorescence. It is indicated on ...Introduction · Vibrational Relaxation and... · Fluorescence · Intersystem Crossing
The abscissa of the colocated scatter diagram indicated red fluorescence (lysosome), and the ordinate of the colocated scatter diagram indicated green fluorescence (DNA-AF488). Hochest33342 was used to stain cell nucleus. ... resulting in a loss of cellular energy. First, we checked the level of NAD + in B16-F10 cells and PIG1 cells with HZ ...
The energy-level diagram outlines the mechanism: After excitation from the ground state (purple arrow), the molecule makes a brief stop on the black manifold of e 3 Π g states, as predicted by Herzberg, before relaxing to the red manifold of d 3 Π g states.
How lasers work. Before you can understand how a laser works, you need to know how an atom can give off light. If you're not sure how this happens, take a look at the box how atoms make light in our introductory article about light. A laser is effectively a machine that makes billions of atoms pump out trillions of photons (light particles) all at once so they line up to form a really ...
Fluorophores can exist in a variety of vibrational energy levels. ... state transitions that occur with fluorescence, phosphorescence, and delayed fluorescence.
Meanwhile, a small part continues to be non-radiatively transferred to the lower energy level 6 H 13/2 and emit 2.8 μm fluorescence through the 6 H 13/2 → 6 H 15/2 process, which gives a reasonable explaining of why the fluorescence intensity at 1.95 μm is stronger than that at 2.8 μm.
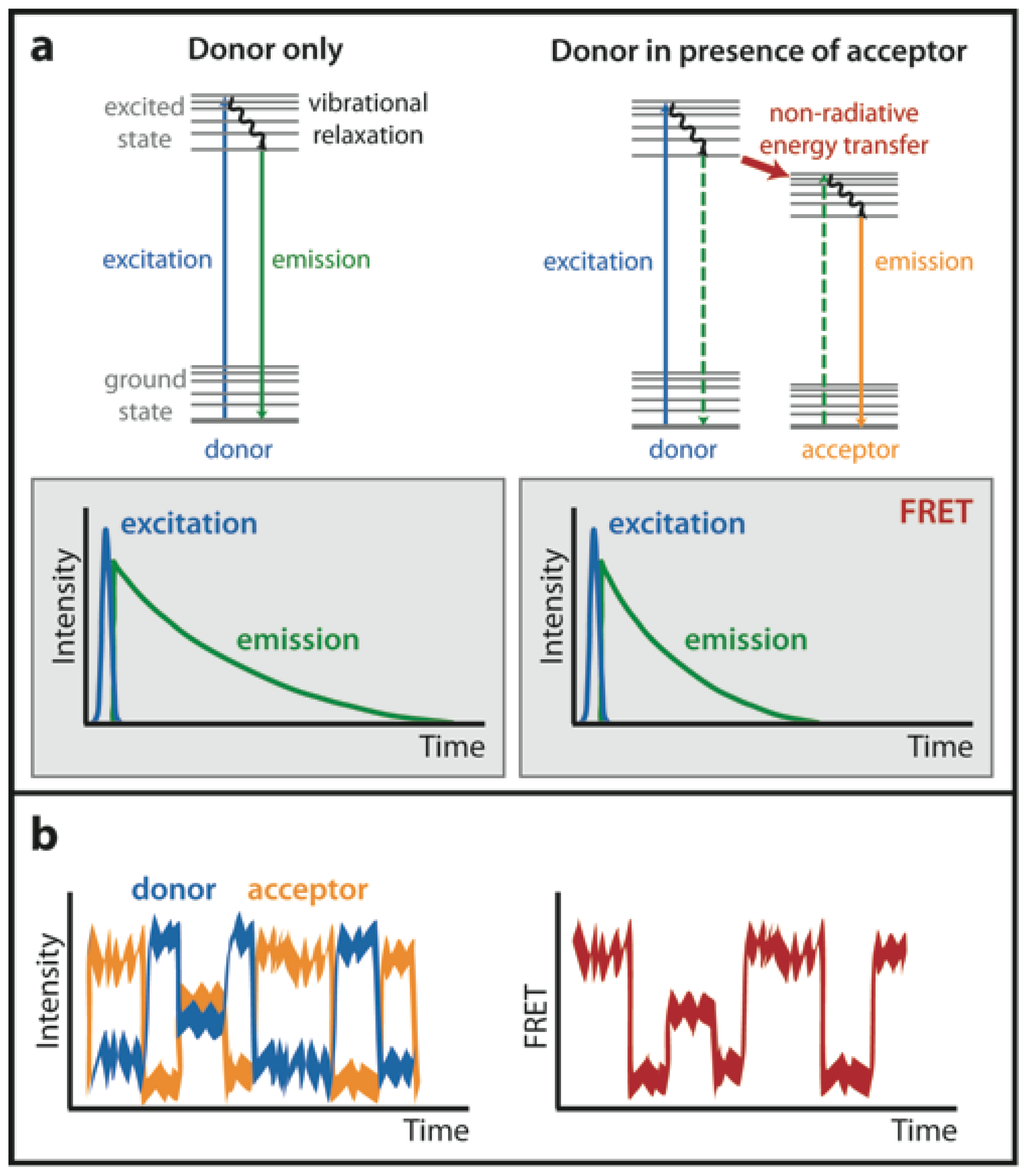
Presented in Figure 3 is a Jablonski diagram illustrating the coupled transitions involved between the donor emission and acceptor absorbance in fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Absorption and emission transitions are represented by straight vertical arrows (green and red, respectively), while vibrational relaxation is indicated by wavy ...
Jablonski diagram including vibrational levels for absorbance, non-radiative decay, and fluorescence. Radiative transitions involve the absorption of a photon, ...
Jablonski Diagram: When radiation of suitable energy is absorbed by the molecule, then an electronic excitation takes place. Let the electron get excited from ground state S 0 to singlet excited state S 2.S 2 state is highly unstable and has a lifetime of only 10-11 sec, so it decays into another excited state S 1 by Radiationless Decay (RD). This is called internal conversion (IC).
The buffer resonator is coupled to the external microwave line via a capacitance (energy damping rate κ b = 13.7 × 10 6 s −1 at the working point ω b /2π = 6.946 GHz), whereas the waste ...
As displayed in Fig. 3a, the energy band structure based on a rGO structure model (inset of in Fig. 3a) shows a band gap of 0.3 eV (energy bands are discontinuous near the Fermi level) leading to ...
5). Spectroscopy based on Emission contd., Figure 5-1: Energy level diagram for a molecule showing pathways for deactivation of an excited state; vr is vibrational relaxation; ic is internal conversion; ec external conversion, and isc is intersystem crossing. The lowest vibrational energy level for each electronic state is indicated by the thicker line.
Nov 13, 2015 · Fluorescence Microscopy Basic Concepts in Fluorescence. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical (for example, absorption of light), mechanical (friction), or chemical mechanism.
Nevertheless, the energy gap of Core3 increases to 3.68 eV, indicating that Core3 might be a deep blue emitter. With the more extended resonance system configuration from Core1 to Core3, the levels between LUMO and LUMO+1, HOMO, and HOMO-1 become closer, like the HOMO and HOMO-1 become degenerate with an energy level of −6.14 eV.
Introduction. Cancer is a major disease seriously threatening human life and health 1-3.Early diagnosis is an effective method to reduce cancer mortality, improve the survival rate, and prolong life of patient 3, 4.Compared with the traditional diagnosis methods (such as dripping-blood chip detection 5, genetic testing 6, biopsy 7, computed tomography 8, B-ultrasound 9, magnetic resonance ...
rotational energy levels of the excited states in different molecular orbitals. The various energy levels involved in the absorption and emission of light by a fluorophore are classically presented by a Jablonski energy diagram (see Figure 1), named in honor of the Polish physicist Professor Alexander Jablonski.
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light; typically, but not necessarily, visible light.
To evaluate saturation broadening, a two-level energy model is used, following previous studies. 42-45 42. T. B. Smith, " Deconvolution of ion velocity distributions from laser-induced fluorescence spectra of xenon electrostatic thruster plumes," Ph.D. thesis (University of Michigan, 2003). 43.





















0 Response to "35 fluorescence energy level diagram"
Post a Comment