40 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for polo shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the. labeled graph; makes sure you indicate where the optimal consumption now 3 ($5) or $15 and the price of good Y is now 3($10) or $30), the budget line Giffen goods are a type of goods whose demand curve is an upward sloping line.
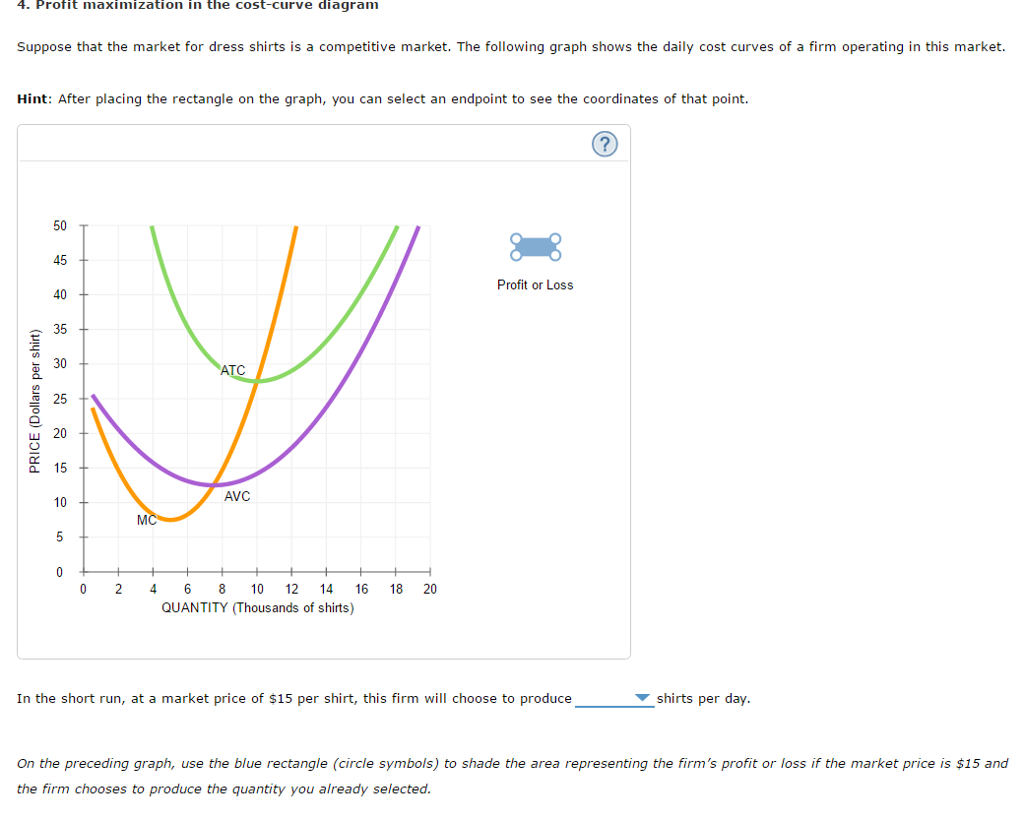
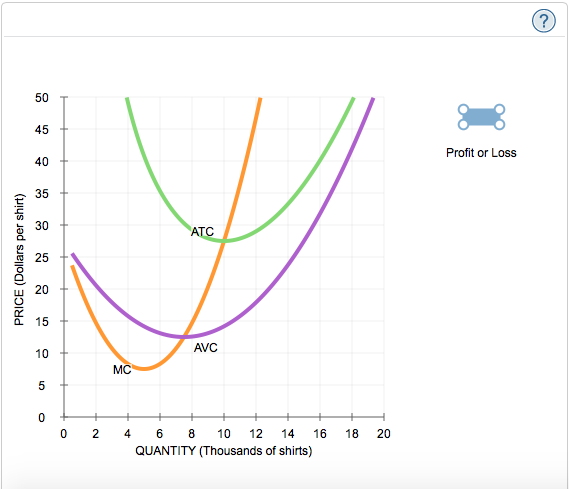
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market.
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
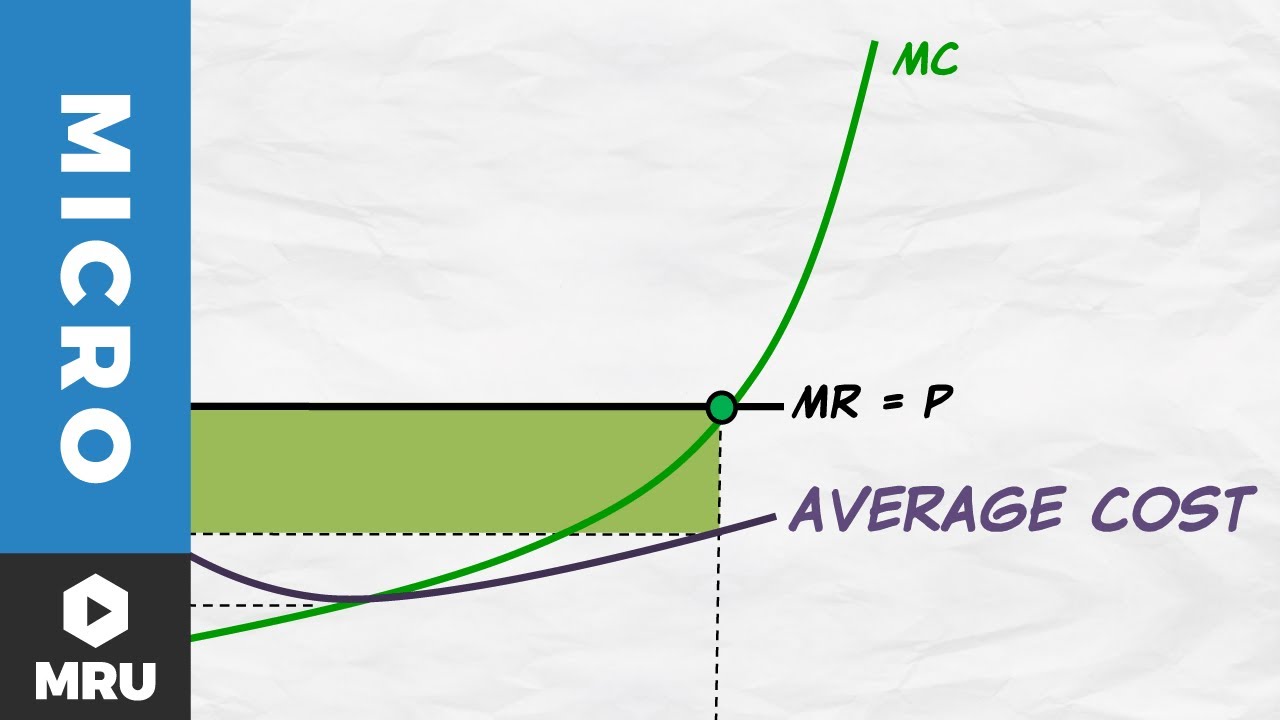
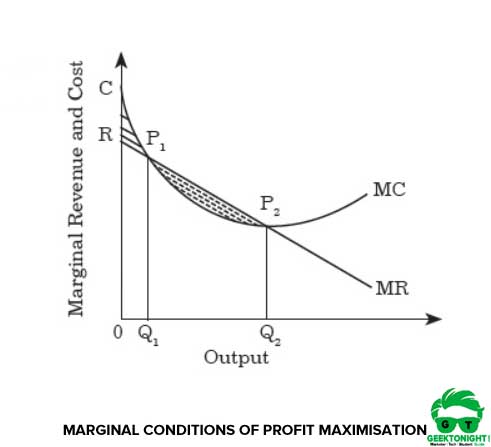
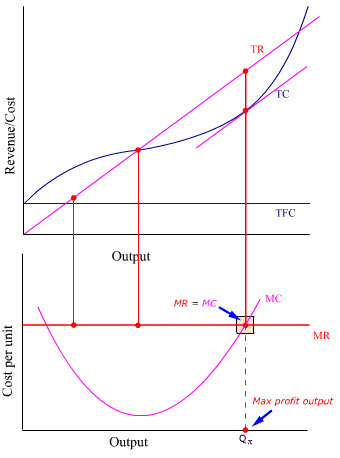
Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Diagram of Profit Maximisation. To understand this principle look at the above diagram. Points: 0.5 / 1 Back to Assignment Attempts: 2.5 Keep the Highest: 2.5 / 3 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn't make a profit at every level of output.
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for microwave ovens is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 80 70 60 50 Proft or ... The profit maximisation theory is based on the following assumptions: 1. The objective of the firm is to maximise its profits where profits are the difference between the firm's revenue and costs. 2. The entrepreneur is the sole owner of the firm. 3. Tastes and habits of consumers are given and constant. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Aa Aa Consider a perfectly competitive market for black hoodies. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. PRICE (Dollars per hoodiel 20 Profit or Loss MC 16 ATC 12 AVC 4 2 4 6 8 10 12 OUTPUT (Thousands of hoodies Help Clear All In the...
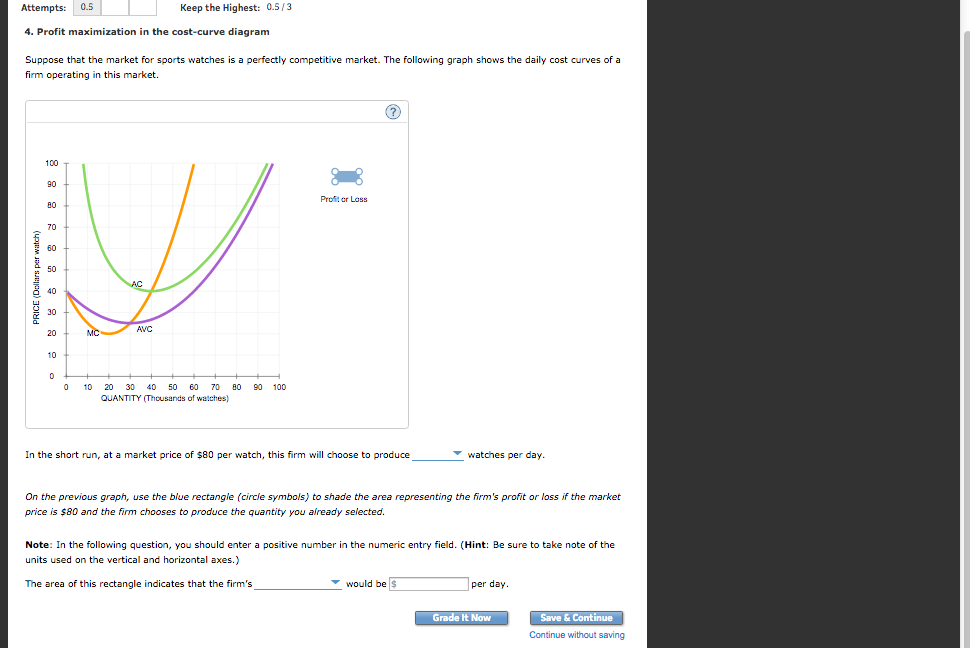
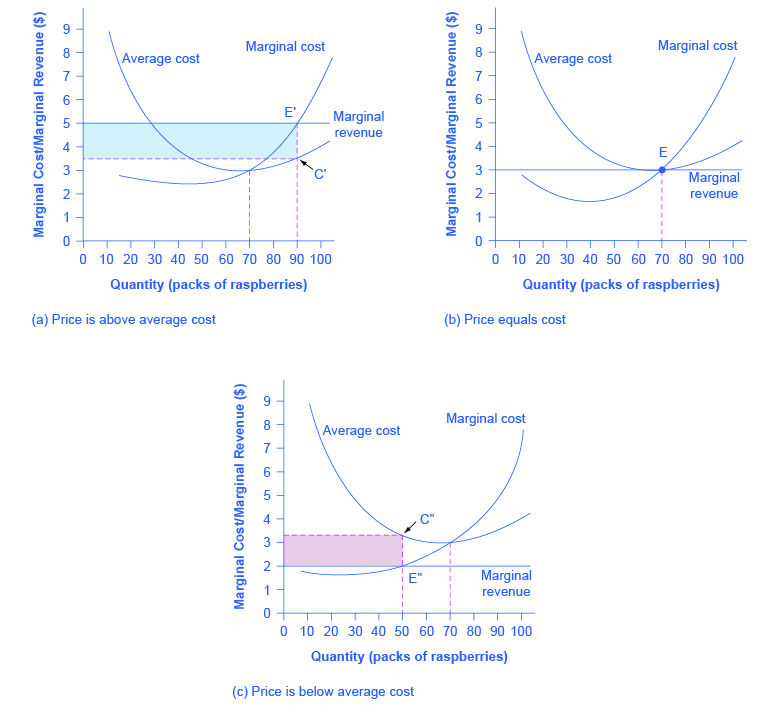
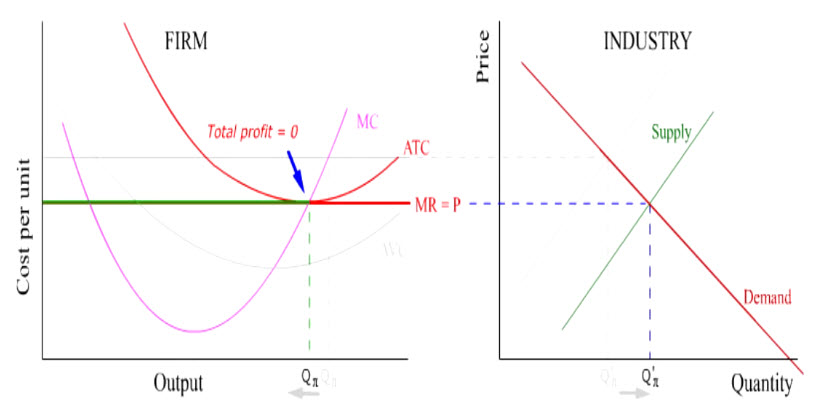
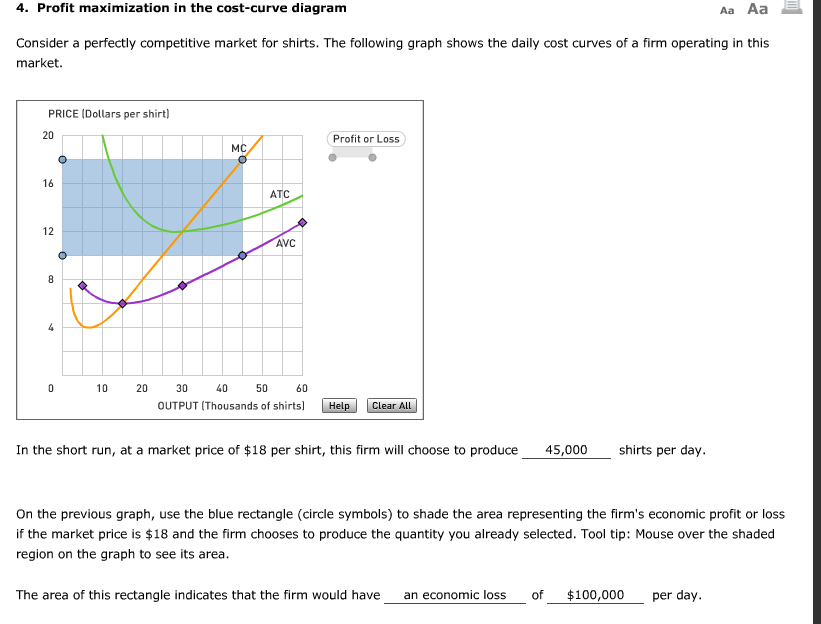
What two rules does a perfectly competitive firm apply to determine its profit-maximizing quantity of output? 1. Determined at the point where price = marginal cost ... What two lines on a cost curve diagram intersect at the zero-profit point? average curve (MC) and marginal revenue (MR) curve. ... where all firms are earning zero profit. Understanding the Profit Maximizing Rule. We can also understand the profit maximizing rule intuitively. In the graph below, Qpm is the profit maximizing quantity. If the firm produces at a point to the left of Qpm (for example, the point at which marginal cost is at its minimum), then we notice that marginal cost is less than marginal revenue. Profit Maximization In the Cost Curve Diagram. solved 6 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram c in this case the fixed cost of the firm producing shirts is $81 000 per day in other words if it shuts down the firm would suffer losses of $81 000 per day until its fixed costs end such as the expiration of a building lease solved 4 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram s answer to ... 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
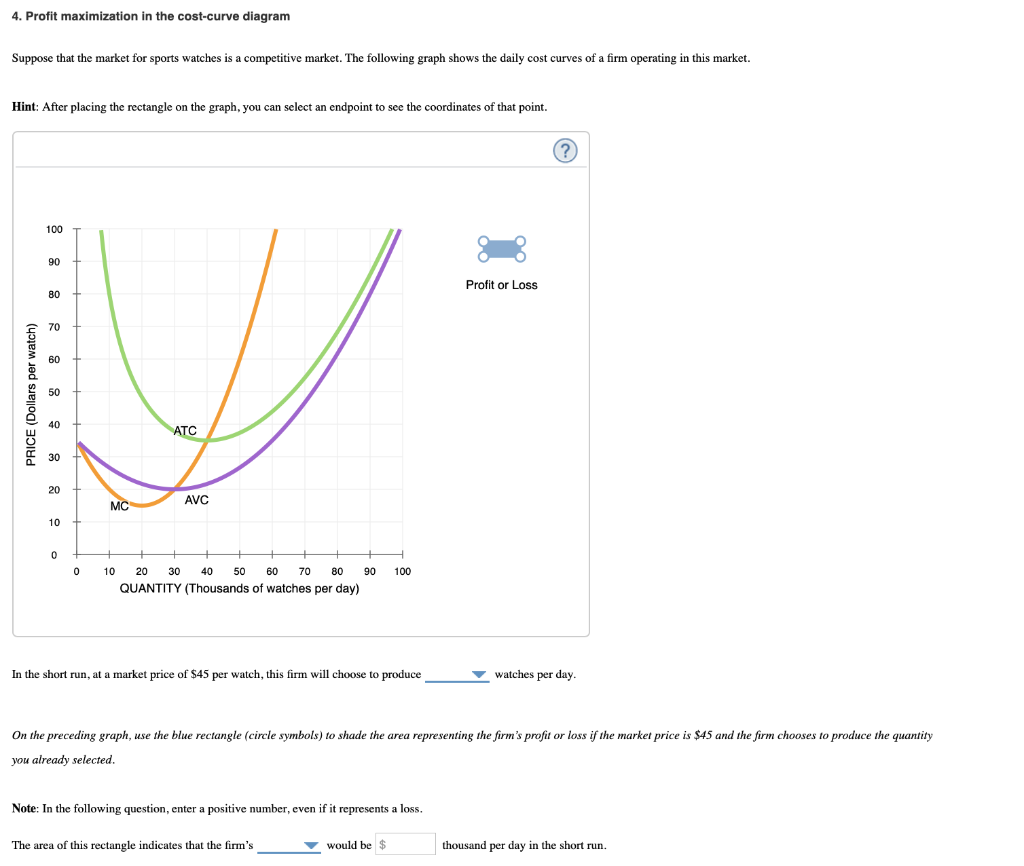
Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing. Profit is defined as: Profit = Revenue - Costs Π(q) = R(q) - C(q) To maximize profits, take the derivative of the profit function with respect to q and set this equal to zero. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 40 36 Profit or Loss 32 28 24 20 ATC 16 12 ... Question: 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.In the short run, at a market price of $20 per candle, this firm will choose to produce candles per day. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
4 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Profits and losses with the average cost curve. The objective of the firm is to maximise its profits where profits are the difference between the firms revenue and costs. The entrepreneur is the sole owner of the firm. Sign up to access the rest of the document.
Profit Maximization Model of a Firm (With Diagram) ... TC curve depicts total economic costs at different levels of output. It will be seen from the upper part of Fig.2.1 at OM level of output, total revenue equals total economic costs and therefore at this level of output the firm is just breaking even. ... In the lower part of Figure 2.1 we ...
Profit maximization. AP.MICRO: CBA‑2 (EU) , CBA‑2.D (LO) , CBA‑2.D.1 (EK) Transcript. Learn about the profit maximization rule, and how to implement this rule in a graph of a perfectly competitive firm, in this video.

Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Png 4 Prot Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Air Fresheners Is A Course Hero
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 45 40 Profit or loss ATC PRICE ...
Profit Maximizing uAnd at q 4, MR<MC. This means that it costs more to make one more than it will bring in when it is sold uThis means the firm will lose money uSo the firm would want to decrease production to bring MC down q/t $ MC MR q 1 q 2 q 3 q 4
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market, The following graph shows the daly cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point 35 Proi or Loss ATC AVC MC 0 10 12 20 14 12 ...
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 Profit or Loss o 70 ATC 60 2 50 40 ...
The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 100 t 90. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. Changes in total costs and profit maximization. An increase in fixed cost would cause the total cost curve to shift up rigidly by the amount of ...
Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from Table 1. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at Q = 60, TR = 240 and TC = 165. The difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. The firm doesn't make a profit at every level of output.
Points: 0.5 / 1 Back to Assignment Attempts: 2.5 Keep the Highest: 2.5 / 3 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
Solved I Average 3 4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Frying Pans Is A Competitive Market The Followi Course Hero
Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Diagram of Profit Maximisation. To understand this principle look at the above diagram.
Solved C Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks People Window Help A R O 943 El 30 Sat 13 29 Q Q Nit Homework Ch14 X Gt O O Mindta Course Hero

4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aa Aa Consider A Perfectly Competitive Market For Teddy Homeworklib

4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagramsuppose That The Market For Black Sweaters Is A Competitive Homeworklib
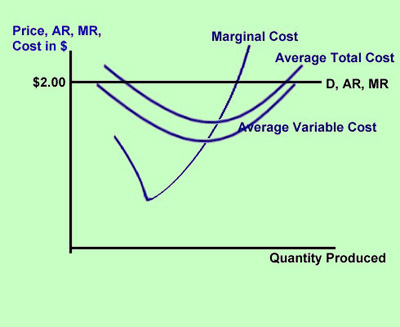
Section 4 Profit Maximization Using A Purely Competitive Firm S Cost And Revenue Curves Inflate Your Mind

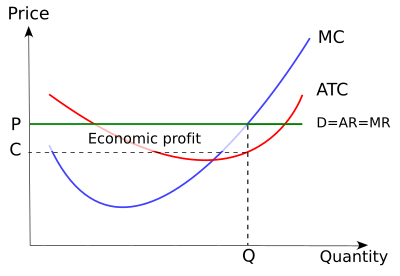
The Graph Shows A Firm In A Perfectly Competitive Market Making A Profit The Graph Includes The Firm S Marginal Cost Curve Average Total Cost Curve And Average Variable Cost Curve Assume The
















0 Response to "40 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram"
Post a Comment